Android的消息机制在Android开发中占有重要地位,所以也是面试的常见客。如果没有时间看源码,可以搜索网络上的一些资源,知道了解即可。网上现在关于Android消息机制的文章有很多,大多介绍的都差不多,但是为了自身水平的提高,还是亲自看下源码学习下。
系列地址:
Android消息机制浅析——基本使用
Android消息机制浅析——原理探究
Android消息机制浅析——面试总结
一、项目情景
在项目实际开发中我们使用Hanlder消息机制最频繁的莫过于放松数据到主线程进行View的数据更新。在Android开发中,我们无法再子线程中进行View视图的更新,所以这就需要我们放到主线程去操作,这里就使用Android的消息机制进行。以此,来避免错误:
android.view.ViewRootImpl$CalledFromWrongThreadException: Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.常见的案例情景:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private TextView tv_text;
private Button btn_ok;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
tv_text = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text);
btn_ok = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_text);
btn_ok.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
handler.sendEmptyMessage(0);
}
}).start();
}
});
}
private Handler handler = new Handler(){
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
tv_text.setText("点击更换文字");
}
};
}子线程中进行发送消息,然后交由主线程进行View的修改。
二、基本使用
Handler
Handler负责我们的消息发送和处理,一般我们创建一个Handler对象,只需要重写它的handleMessage()方法进行处理我们的业务逻辑。
private Handler handler = new Handler(){
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
}
};当然Handler也给我们提供了多个发送消息的方法:
- handler.sendEmptyMessage(what);//发送空的消息
- handler.sendEmptyMessageAtTime(what, uptimeMillis);//在指定时间点发送空消息
- handler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(what, delayMillis);//延迟指定时间发送消息
- handler.sendMessage(msg);//发送消息Message
- handler.sendMessageAtTime(msg, uptimeMillis);//在指定时间发送消息Message
- handler.sendMessageDelayed(msg, delayMillis);//延迟指定时间发送消息Message
这些都是Handler提供给我们的消息发送,我们通过制定what进行区别消息的种类,用Message对象存储我们的发送数据。当然Handler不仅可以发送Message对象,也可以对我们的Runnable线程进行处理。
- handler.post(runnable)
- handler.postAtTime(runnable, uptimeMillis)
- handler.postDelayed(runnable, delayMillis)
具体功能效果与Message类似。这里我们需要强调一点,uptimeMillis时间。它取值为 SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
- SystemClock.uptimeMillis() // 从开机到现在的毫秒数(手机睡眠的时间不包括在内);
- System.currentTimeMillis() // 从1970年1月1日 UTC到现在的毫秒数;
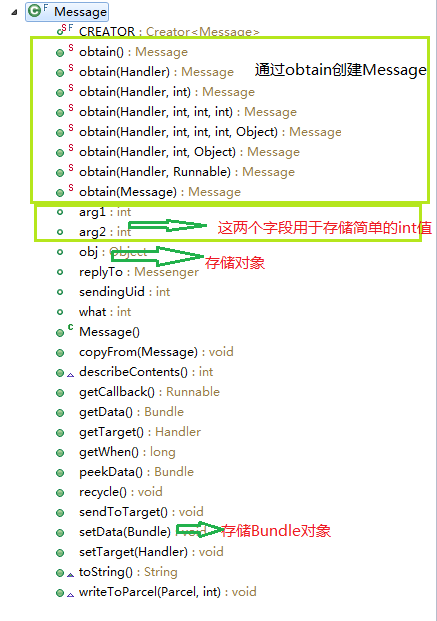
Messag对象
Message对象很简单,类似于我们的实体,用于封装我们的消息内容。
我们看下它的常用方法:
在我们的实际开发中,这两个对象我们使用最多,一般我们采用它的无参构造函数进行创建对象。
三、小小案例加深记忆
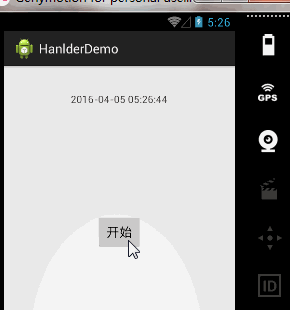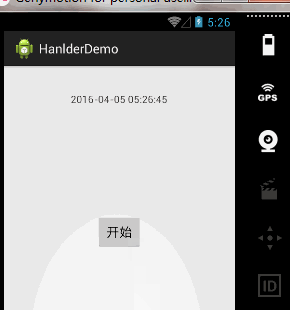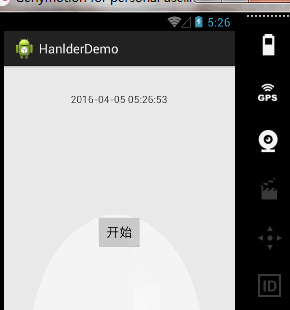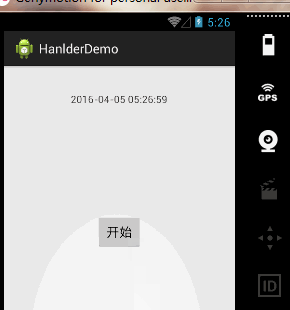
案例一、时间器工具
需求分析:
实现一个时间器,用来显示当前时间。所以我们需要不断的发送消息,来获取当前时间,我们精确到秒,所以也就是说每隔一秒,我们发送消息,来显示时间。所以呢?我们只要一个定时任务就可以了。
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private TextView tv_text;
private Button btn_ok;
private Timer timer = new Timer();;
private MyTimerTask timerTask = new MyTimerTask();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
tv_text = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text);
btn_ok = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_text);
btn_ok.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//点击开启任务
timer.schedule(timerTask, 1000,1000);
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
timer.cancel();
}
/**
* Handler处理消息
*/
private Handler handler = new Handler(){
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
tv_text.setText(refFormatNowDate());
}
};
/**
* 日期转换格式
* @return
*/
@SuppressLint("SimpleDateFormat")
public String refFormatNowDate() {
Date nowTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
SimpleDateFormat sdFormatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String retStrFormatNowDate = sdFormatter.format(nowTime);
return retStrFormatNowDate;
}
/**
* 我们的定时任务
* @author Administrator
*
*/
class MyTimerTask extends TimerTask{
@Override
public void run() {
handler.sendEmptyMessage(0);
}
}
}我们通过TimerTask定时任务去开启一个任务,然后进行消息的发送,最后在Handler中处理我们的消息。
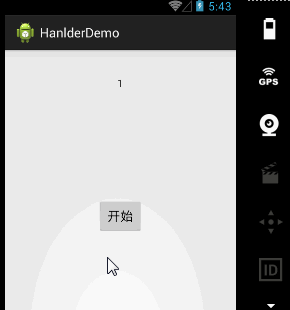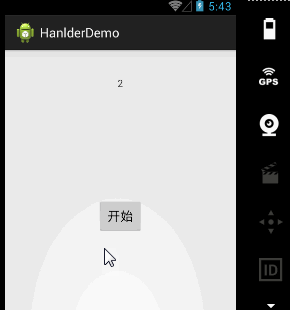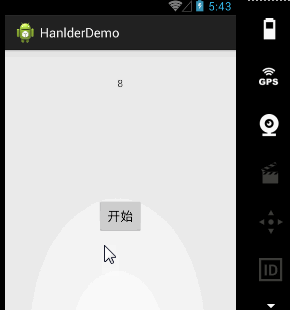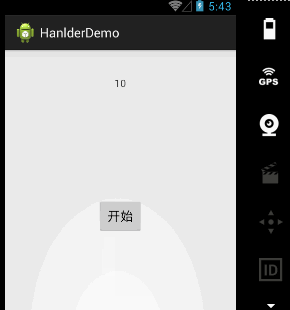
案例二、计数器工具
我们知道Handler还给我们提供了postXX系列的方法,我们这次采用这个方法写个计数器。post方法可以使我们在runnable中就行一些列更新UI的操作。
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private TextView tv_text;
private Button btn_ok;
private Timer timer = new Timer();
private int count =1;
private MyTimerTask timerTask = new MyTimerTask();
/**
* Handler处理消息
*/
private Handler handler = new Handler();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
tv_text = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text);
btn_ok = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_text);
btn_ok.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//点击开启任务
timer.schedule(timerTask, 1000,1000);
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
timer.cancel();
}
/**
* 我们的定时任务
* @author Administrator
*
*/
class MyTimerTask extends TimerTask{
@Override
public void run() {
handler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
tv_text.setText(count++ + "");
}
});
}
}
} 基本的使用就这个样子,下篇文章我们开始研究Android消息机制的原理,说说这些通讯是如何形成的,这些简单明了的方法里又做了什么?
==========================================
作者:mr_dsw
地址:http://blog.csdn.net/mr_dsw
理念:转载注明地址,进步来源于分享
==========================================






















 635
635











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








