传送门
In most professional sporting events, cheerleaders play a major role in entertaining the spectators. Their
roles are substantial during breaks and prior to start of play. The world cup soccer is no exception.
Usually the cheerleaders form a group and perform at the centre of the field. In addition to this group,
some of them are placed outside the side line so they are closer to the spectators. The organizers would
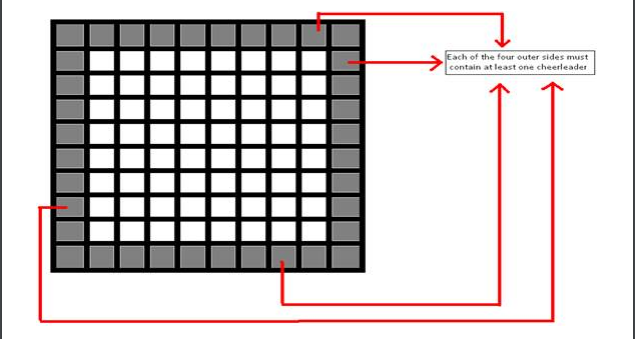
like to ensure that at least one cheerleader is located on each of the four sides. For this problem, we
will model the playing ground as an M × N rectangular grid. The constraints for placing cheerleaders
are described below:
• There should be at least one cheerleader on each of the four sides. Note that, placing a cheerleader
on a corner cell would cover two sides simultaneously.
• There can be at most one cheerleader in a cell.
• All the cheerleaders available must be assigned to a cell. That is, none of them can be left out.
The organizers would like to know, how many ways they can place the cheerleaders while maintaining
the above constraints. Two placements are different, if there is at least one cell which contains a
cheerleader in one of the placement but not in the other.
Input
The first line of input contains a positive integer T ≤ 50, which denotes the number of test cases. T
lines then follow each describing one test case. Each case consists of three nonnegative integers, 2 ≤ M,
N ≤ 20 and K ≤ 500. Here M is the number of rows and N is the number of columns in the grid. K
denotes the number of cheerleaders that must be assigned to the cells in the grid.
Output
For each case of input, there will be one line of output. It will first contain the case number followed by
the number of ways to place the cheerleaders as described earlier. Look at the sample output for exact
formatting. Note that, the numbers can be arbitrarily large. Therefore you must output the answers
modulo 1000007.
Sample Input
2
2 2 1
2 3 2
Sample Output
Case 1: 0
Case 2: 2
题目大意:
给你一个
n∗m
的方格,现在有
k
个相同石子,我们要将这
解题思路:
我们来分析一下这个题目,因为题目中要求的是第一行、第一列、最后一行和最后一列中必须有石子,那么我们现在应该从反面考虑也就是利用容斥原理解决这个问题,这个是很容易想到的,那么现在我们设
4
个事件:
B:表示的是第一列中没有石子的方案数
C:表示的是最后一行中没有石子的方案数
D:表示的是最后一列中没有石子的方案数
那么我们要求的方案数就是:
|A∪B∪C∪D|=|A|+|B|+|C|+|D|−|A∩B|−|A∩C|−|A∩D|−|B∩C|−|B∩D|−|C∩D|+|A∩B∩C|+|A∩B∩D|+|A∩C∩D|+|B∩C∩D|−|A∩B∩C∩D|
然后利用二进制枚举总的状态就可以了(都是容斥原理的一些套路:)
My Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
const int INF = 1e9+5;
const int MAXN = 5e2+5;
const LL MOD = 1000007;
const double eps = 1e-7;
const double PI = acos(-1);
using namespace std;
LL c[MAXN][MAXN];
void Init(){
for(int i=0; i<MAXN; i++)
c[i][0] = c[i][i] = 1;
for(int i=1; i<MAXN; i++)
for(int j=1; j<=i; j++)
c[i][j] = (c[i-1][j-1]+c[i-1][j]) % MOD;
}
int main()
{
Init();
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
for(int cas=1; cas<=T; cas++){
int n, m, k;
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k);
LL ans = 0;
for(int i=0; i<16; i++){
int cnt = 0, cc = n, r = m;
if(i & 1){
cnt++;
cc--;
}
if(i & 2){
cnt++;
r--;
}
if(i & 4){
cnt++;
cc--;
}
if(i & 8){
cnt++;
r--;
}
if(cnt & 1)
ans = (ans-c[r*cc][k]+MOD)%MOD;
else
ans = (ans+c[r*cc][k])%MOD;
}
printf("Case %d: %lld\n",cas,ans);
}
return 0;
}

























 412
412

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








