传智扫地僧课程学习笔记。
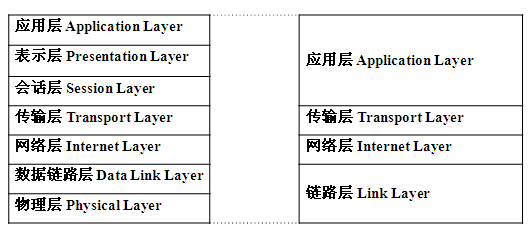
ISO的开放互联网模型OSI,
应用层,提供应用程序间通信,
表示层,处理数据格式,数据加密等,
会话层,建立,维护和管理会话,
传输层,建立端到端链接,
网络层,数据包,寻址和路由选择,
数据链路层,数据帧,介质访问,链路管理,
物理层,比特流传输,
重要结论:传输层做差错处理,对IP包进行排序,IP路由,
图片来自传智扫地僧老师课件,
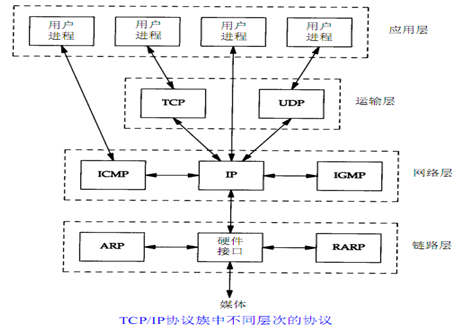
实际中使用的协议TCP/IP,4层,
主要协议有这些,
dm9k.c,
帮助你理解,
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#define DM9K_ADDR 0x28000300
#define DM9K_DATA 0x28000304
#define VIDL 0x28
#define PHR 0x10
#define WAKEST (1 << 5)
#define TX2END (1 << 3)
#define TX1END (1 << 2)
#define IP_START 14
#define UDP_START (14 + 20)
#define ARP_START 14
#define DATA_START (14 + 20 + 8)
#define ICMP_START (14 + 20)
enum {ARP_REQUEST = 1, ARP_REPLY};
char *io_addr = NULL;
char *io_data = NULL;
static dev_t dev;
struct cdev my_dev;
struct udp_hdr {
unsigned short src_port;
unsigned short dest_port;
unsigned short len;
unsigned short chksum;
};
struct ip_hdr {
char ver_hl;
char tos;
unsigned short len;
unsigned short id;
unsigned short fragment;
char ttl;
char protocol;
unsigned short hdr_chksum;
char src_ip [4];
char dest_ip [4];
};
struct ethernet_hdr {
char dest_mac[6];
char src_mac[6];
short protocol;
};
struct arp_hdr {
unsigned short hwtype; // 固定1
unsigned short protype; // 固定0x0800(代表为IP协议做请求)
unsigned char hwaddrlen; // 固定6(即MAC地址长度)
unsigned char proaddrlen; // 固定4 (即IP地址长度)
unsigned short opcode; // Request - 1, Reply - 0x0002
unsigned char sender_mac[6]; // 发送者MAC
unsigned char sender_ip[4]; // 发送者IP
unsigned char dest_mac[6]; // 接收者MAC
unsigned char dest_ip[4]; // 接收者IP
};
struct icmp_hdr {
char type; // ICMP报文类型
char code; // “子类型”
unsigned short icmpchksum; // 校验和
};
static int ipid;
static char MyIP[4] = {192, 168, 0, 250};
static char DestIP[4] = {192, 168, 0, 253};
static char MyMAC[6] = {0x12, 0x34, 0x56, 0x78, 0x90, 0xAB};
static char DestMAC[6] = {0x00, 0x1c, 0x25, 0xdb, 0x3e, 0x7e};
int ior(int reg)
{
writeb(reg, io_addr);
return readb(io_data);
}
void iow(int reg, int value)
{
writeb(reg, io_addr);
writeb(value, io_data);
}
int chksum16(void *buf1, short len, int chksum, char complement)
{
unsigned short * buf = buf1;
int chksum16;
while (len > 0) {
chksum16 = (len == 1) ? ((*buf)&0x00FF) : (*buf);
chksum = chksum + htons(chksum16);
*buf++;
len -=2;
}
if (complement)
return (~(chksum + ((chksum & 0xFFFF0000) >> 16))&0xFFFF);
return chksum;
}
void hardware_init()
{
int i;
io_addr = ioremap(DM9K_ADDR, 4);
io_data = ioremap(DM9K_DATA, 40);
if(ior(VIDL) != 0x46)
printk("VIDL mismatch!");
printk(KERN_ALERT "Mac:");
for (i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
printk("%x ", ior(PHR + i));
}
printk("\n");
/* PHY initialization */
iow(0x1E, ior(0x1E) | 0x01); /* GPCR */
iow(0x1F, ior(0x1F) & (~1)); /* GPR */
printk("PHY initialized\n");
mdelay(200); /* mdelay */
/* Soft reset */
iow(0x00, 3); /* NCR */
mdelay(20); /* mdelay */
iow(0x00, 0); /* NCR */
mdelay(20); /* mdelay */
iow(0x00, 3); /* NCR */
mdelay(20); /* mdelay */
iow(0x00, 0); /* NCR */
/* Flags */
iow(0x01, 0x2c); /* NSR */
iow(0xFE, 0x3F); /* ISR */
iow(0xFF, 0x81); /* IMR */
}
int hardware_recv(char *buf, int max_len)
{
int flag, status, len;
int i;
printk("hardware_recv begin\n");
ior(0xF0); /* MRCMDX */
ior(0xF4); /* MRRH */
ior(0xF5); /* MRRL */
if ((flag = ior(0xF0)) == 0) /* MRCMDX */
{
printk("No unread data\n");
return 0;
}
writeb(0xF2, io_addr); /* MRCMD */
status = readw(io_data);
len = readw(io_data);
for (i = 0; i < len; i += 2)
*((unsigned short *)(buf + i)) = *((unsigned short *)io_data);
printk("hardware_recv end=%d\n", len);
return len;
}
void hardware_send(char *buf, int len)
{
int i;
printk("hardware_send len=%d\n", len);
writeb(0xF8, io_addr); /* MWCWD */
for (i = 0; i < len; i += 2) /* 批量数据写入 */
{
*((unsigned short *)io_data) = *((unsigned short *)(buf + i));
printk("%x ", *((unsigned short *)(buf + i)));
}
printk("\n");
iow(0xFC, len & 0xff); /* low */
iow(0xFD, len >> 8); /* high */
iow(0x02, 1); /* TCR */
}
int dm9k_open(struct inode *node, struct file *f)
{
printk(KERN_ALERT "dm9k_open\n");
iow(0x2, 0); /* TCR */
iow(0x08, 0x3f); /* BPTR */
iow(0x0A, 0xff); /* FCR */
iow(0x2F, 0); /* SMCR */
iow(0x01, WAKEST | TX2END | TX1END); /* NSR */
iow(0xFE, (1<<3) | (1<<2) | (1<<1) | 1); /* ISR */
iow(0x5, (1<<5) | (1<<4) | (1<<1) | 1); /* RCR */
iow(0xFF, (1<<7) | (1<<5) | (1<<1) | 1); /* IMR */
return 0;
}
ssize_t dm9k_write(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
{
int total_len = DATA_START + count;
char frame[1024];
struct udp_hdr * UDPt = (struct udp_hdr * )(frame + UDP_START);
struct ip_hdr * IPt = (struct ip_hdr * )(frame + IP_START);
struct ethernet_hdr * eth_hdr = (struct ethernet_hdr * )frame;
printk("write:\n");
memset(frame, 0, total_len);
copy_from_user(frame + DATA_START, buf, count);
/* udp */
UDPt->src_port = htons(3000);
UDPt->dest_port = htons(3000);
UDPt->chksum = 0;
UDPt->len = htons(count + sizeof(struct udp_hdr));
/* ip */
IPt->ver_hl = 0x45;
IPt->tos = 0x00;
IPt->len=htons(count + sizeof(struct udp_hdr) + sizeof(struct ip_hdr));
ipid++;
IPt->id = htons(ipid);
IPt->fragment =htons(0x4000);
IPt->ttl = 64;
IPt->protocol =17;
IPt->hdr_chksum = 0;
memcpy(IPt->src_ip, MyIP, 4);
memcpy(IPt->dest_ip, DestIP, 4);
IPt->hdr_chksum = htons(chksum16(IPt, sizeof(struct ip_hdr), 0, 1));
printk("write1\n");
/* eth */
memcpy(eth_hdr->dest_mac, DestMAC, 6);
memcpy(eth_hdr->src_mac, MyMAC, 6);
eth_hdr->protocol = htons((short)0x0800);
printk("total_len=%d\n", total_len);
/* hardware send */
hardware_send(frame, total_len);
return count;
}
ssize_t dm9k_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
{
char frame[1024];
int len;
struct ip_hdr * IPt = (struct ip_hdr * )(frame + IP_START);
struct ethernet_hdr * eth_hdr = (struct ethernet_hdr * )frame;
struct arp_hdr * ARPt = (struct arp_header * )(frame + ARP_START);
struct icmp_hdr * ICMPt = (struct icmp_header * )(frame + ICMP_START);
if ((len = hardware_recv(frame, 1024)) == 0)
return 0;
char *p = frame + 6;
printk("Sender MAC: %x:%x:%x:%x:%x:%x\n", p[0], p[1], p[2], p[3], p[4], p[5]);
if(eth_hdr->protocol == htons((short)0x0800))
{
printk("IP received\n");
if(IPt->protocol == 17) /* UDP */
{
printk("UDP received: %s\n", frame + DATA_START);
}
else if(IPt->protocol == 1) /* ICMP */
{
printk("ICMP received!\n");
ICMPt->type = 0;
ICMPt->icmpchksum = 0;
ICMPt->icmpchksum = htons(chksum16(ICMPt, sizeof(struct icmp_hdr), 0, 1));
memcpy(IPt->dest_ip, IPt->src_ip, 4);
memcpy(IPt->src_ip, MyIP, 4);
IPt->hdr_chksum = 0;
IPt->hdr_chksum = htons(chksum16(IPt, sizeof(struct ip_hdr), 0, 1));
memcpy(eth_hdr->dest_mac, eth_hdr->src_mac, 6);
memcpy(eth_hdr->src_mac, MyMAC, 6);
hardware_send(frame, len);
printk("ICMP replied!\n");
}
}
else if(eth_hdr->protocol == htons((short)0x0806))
{
printk("ARP received\n");
p = ARPt->sender_ip;
printk("\tSender IP: %d.%d.%d.%d\n", p[0], p[1], p[2], p[3]);
printk("\topcode=%d\n", ARPt->opcode);
if (ARPt->opcode == htons(ARP_REQUEST))
{
ARPt->opcode= htons(ARP_REPLY);
memcpy(ARPt->dest_mac, ARPt->sender_mac, 6);
memcpy(ARPt->dest_ip, ARPt->sender_ip, 4);
memcpy(ARPt->sender_mac, MyMAC, 6);
memcpy(ARPt->sender_ip, MyIP, 4);
memcpy(eth_hdr->dest_mac, eth_hdr->src_mac, 6);
memcpy(eth_hdr->src_mac, MyMAC, 6);
hardware_send(frame, IP_START + sizeof(struct arp_hdr));
}
}
else
{
printk("Unknown protocol: %x\n", eth_hdr->protocol);
}
printk(KERN_ALERT "dm9k_read\n");
return 0;
}
struct file_operations dm9k_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = dm9k_read,
.write = dm9k_write,
.open = dm9k_open
};
void init_chrdev()
{
alloc_chrdev_region(&dev, 0, 1, "dm9k");
printk(KERN_ALERT "major=%d\n", MAJOR(dev));
cdev_init(&my_dev, &dm9k_fops);
if (cdev_add(&my_dev, dev, 1))
printk(KERN_DEBUG "cdev_add error");
}
int dm9k_init()
{
init_chrdev();
hardware_init();
printk(KERN_ALERT "Dm9k init!\n");
return 0;
}
void dm9k_exit()
{
unregister_chrdev_region(dev, 1);
cdev_del(&my_dev);
printk(KERN_ALERT "Dm9k exit!\n");
}
module_init(dm9k_init);
module_exit(dm9k_exit);
以前学习tcp/ip的时候,
只是单纯的把这些协议分了下层,这样分也对,
但也不全是,挺有意思,
注意分支走向,
以太网是主流,
这里也有上面相印证,
简单说,以前总觉得arp包得和应用层有直接联系,
实际可能,它就是用于链路层,
MTU,最大传输单元,
多个网络的以太网MTU中最小的那个就是路径MTU,
ICMP协议说明
ICMP协议用于传递差错信息、时间、回显、网络信息等控制数据
当你ping 一台主机想看它是否运行时,就产生了一条ICMP 信息。远程主机将用它自己的ICMP 信息对ping 请求作出回应。
TCP数据包里面有6个标志位,
URG,ACK,PSH,RST,SYN,FIN,
有没有感觉有几个很熟悉啊?
ACK:为1表示确认号有效,为0表示该TCP数据包不包含确认信息,
SYN:用于建立连接,连接请求时SYN=1,ACK=0;响应连接请求时SYN=1,ACK=1,
步骤a:应用程序ping会判断发送的是主机名还是IP地址,调用函数gethostbyname()解析主机机B,将主机名转换成一个32位的IP地址。这个过程叫做DNS域名解析
步骤b:ping程序向目的IP地址发送一个ICMP的ECHO包
步骤c:将目标主机的IP地址转换为48位硬件地址,在局域网内发送ARP请求广播,查找主机B的硬件地址。
步骤d:主机B的ARP协议层接收到主机A的ARP请求后,将本机的硬件地址填充到应答包,发送ARP应答到主机A。
步骤e:发送ICMP数据包到主机B
步骤f:主机B接收到主机A的ICMP包,发送响应包。
步骤g:主机A接收到主机B的ICMP包响应包。




























 311
311

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








