实现安卓计时器代码
只需要用一个控件Chronometer
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<Chronometer
android:layout_width=
"wrap_content"
android:layout_height=
"wrap_content"
android:format=
"%s"
android:id=
"@+id/timer"
/>
|
是的,就这么简单。java代码同样
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
@Override
protected
void
onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super
.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
timer = (Chronometer) findViewById(R.id.timer);
}
public
void
btnClick(View view) {
timer.setBase(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());
//计时器清零
timer.start();
}
|
超简单有木有?看看运行结果:
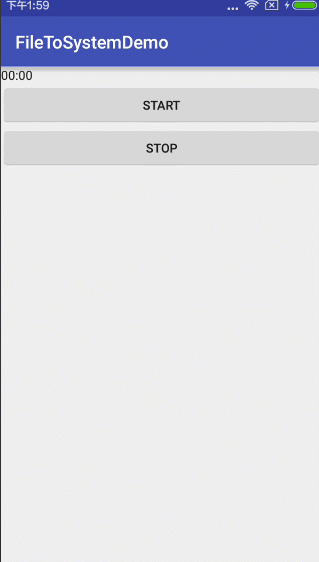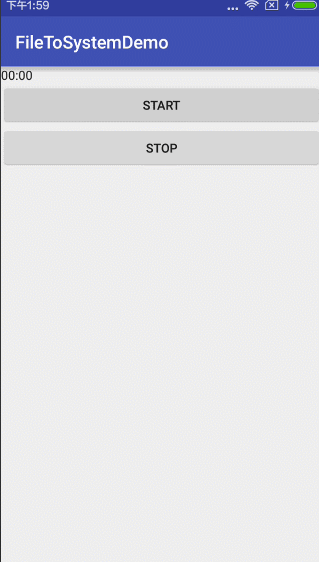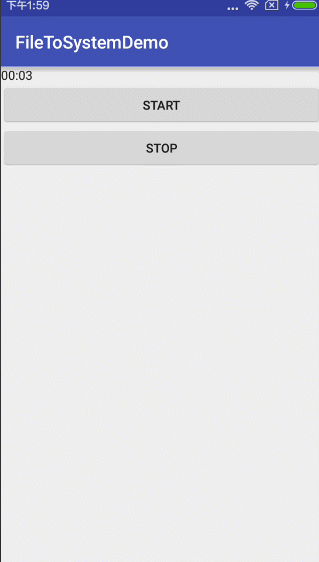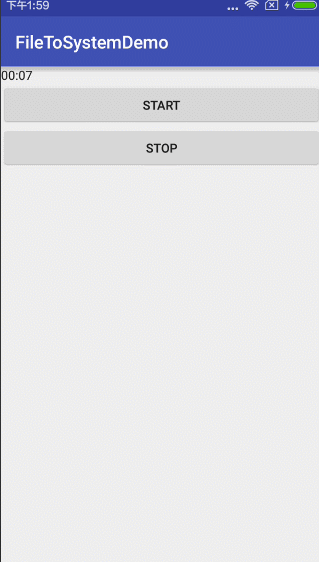
或许你会说,这个要是需要显示上时间怎么弄呢?不急不急,两行代码就能解决的事情。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public
void
btnClick(View view) {
timer.setBase(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());
//计时器清零
int
hour = (
int
) ((SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - timer.getBase()) /
1000
/
60
);
timer.setFormat(
"0"
+String.valueOf(hour)+
":%s"
);
timer.start();
}
public
void
stopClick(View view) {
timer.stop();
}
|
恩,对,就是 这么简单,不过别忘了把xml的format改一下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<Chronometer
android:layout_width=
"match_parent"
android:layout_height=
"wrap_content"
android:format=
"00:00:00"
android:gravity=
"center"
android:id=
"@+id/timer"
/>
|
是的,你没有看错,这样就可以了,不信,你看!
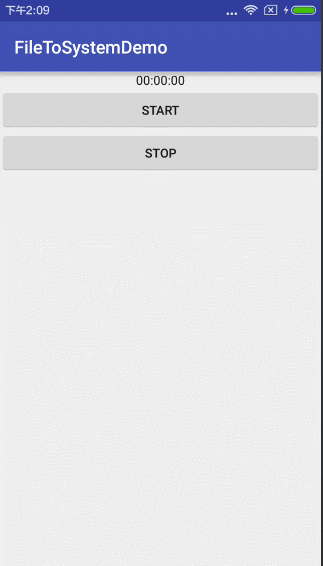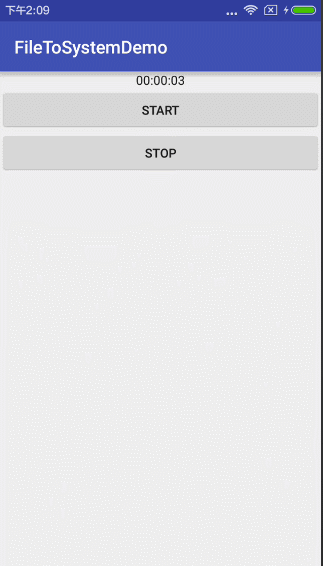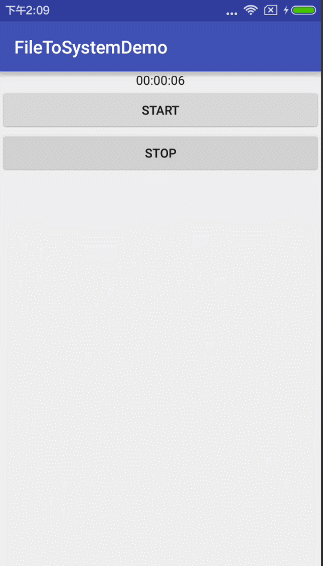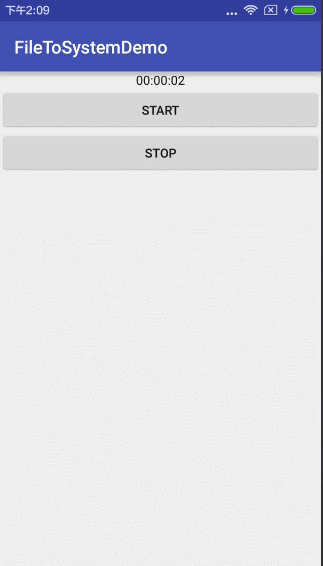
就和你想象的录像上方的时间一样有木有?恩。你前面设置一个圆圈,再设置计时器颜色就和它一样有逼格了。
而或许你并不喜欢用这种方式,当然用handler+timer+timerTask的方式也是可以的啦。由于太简单,就直接上代码了。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
|
package
com.example.nanchen.timerdemo;
import
android.os.SystemClock;
import
android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import
android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import
android.os.Bundle;
import
android.view.View;
import
android.widget.Chronometer;
import
android.widget.TextView;
import
java.util.Locale;
import
java.util.Timer;
import
java.util.TimerTask;
public
class
MainActivity
extends
AppCompatActivity {
private
Chronometer timer;
private
Timer timer1;
private
TextView textView;
private
TimerTask timerTask;
@Override
protected
void
onCreate(
@Nullable
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super
.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
timer = (Chronometer) findViewById(R.id.timer);
textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text);
timer1 =
new
Timer();
}
public
void
btnClick(View view) {
timer.setBase(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());
//计时器清零
int
hour = (
int
) ((SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - timer.getBase()) /
1000
/
60
);
timer.setFormat(
"0"
+String.valueOf(hour)+
":%s"
);
timer.start();
}
public
void
stopClick(View view) {
timer.stop();
}
public
void
startClick(View view) {
timerTask =
new
TimerTask() {
int
cnt =
0
;
@Override
public
void
run() {
runOnUiThread(
new
Runnable() {
@Override
public
void
run() {
textView.setText(getStringTime(cnt++));
}
});
}
};
timer1.schedule(timerTask,
0
,
1000
);
}
private
String getStringTime(
int
cnt) {
int
hour = cnt/
3600
;
int
min = cnt %
3600
/
60
;
int
second = cnt %
60
;
return
String.format(Locale.CHINA,
"%02d:%02d:%02d"
,hour,min,second);
}
public
void
stopClick1(View view) {
if
(!timerTask.cancel()){
timerTask.cancel();
timer1.cancel();
}
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
<?xml version=
"1.0"
encoding=
"utf-8"
?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android=
"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools=
"http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width=
"match_parent"
android:layout_height=
"match_parent"
android:orientation=
"vertical"
tools:context=
"com.example.nanchen.timerdemo.MainActivity"
>
<Chronometer
android:layout_width=
"match_parent"
android:layout_height=
"wrap_content"
android:format=
"00:00:00"
android:gravity=
"center"
android:id=
"@+id/timer"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width=
"match_parent"
android:onClick=
"btnClick"
android:text=
"start"
android:layout_height=
"wrap_content"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width=
"match_parent"
android:text=
"stop"
android:onClick=
"stopClick"
android:layout_height=
"wrap_content"
/>
<View
android:layout_width=
"match_parent"
android:layout_height=
"1dp"
android:background=
"#959393"
android:layout_marginBottom=
"20dp"
android:layout_marginTop=
"20dp"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width=
"match_parent"
android:layout_height=
"wrap_content"
android:text=
"00:00:00"
android:gravity=
"center"
android:id=
"@+id/text"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width=
"match_parent"
android:layout_height=
"wrap_content"
android:text=
"开始"
android:onClick=
"startClick"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width=
"match_parent"
android:layout_height=
"wrap_content"
android:text=
"停止"
android:onClick=
"stopClick1"
/>
</LinearLayout>
|
简单运行下方用timer实现的效果:
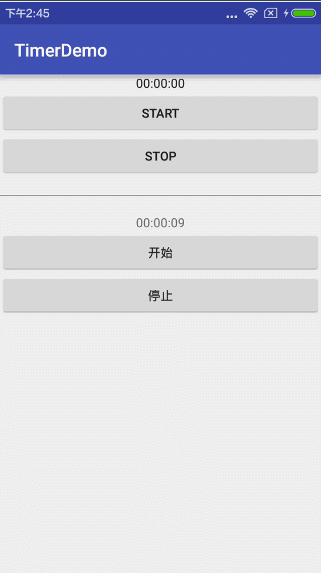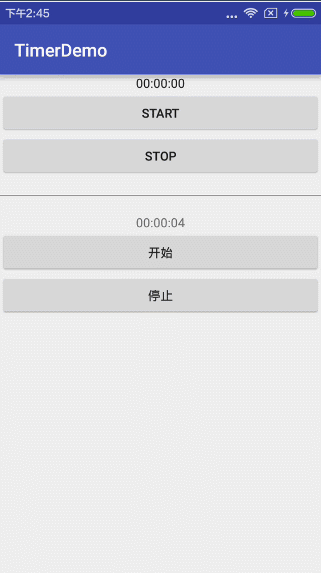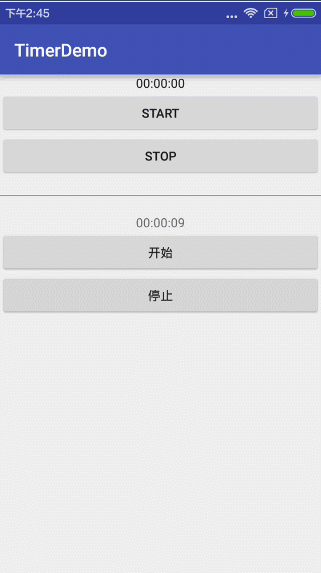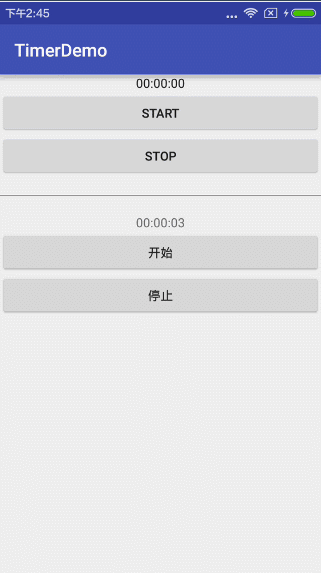
想必大家到这样都会有了自己的理解,android 官方的Chronometer方式只是为了做一个计时器,而我们采用自己用Timer和TimerTask方式可以更加自主,因为你可以想从什么时间开始计时就从什么时间开始计时,计时方式想顺计时倒计时都不是难事儿,甚至各种浮夸的隔两秒,隔三秒,隔n秒都是可以的,具体使用就看你选择咯~~





















 458
458











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








