0:扯淡
对这个openwrt的细节方面了解的还比较欠缺,故从实际中的经常用的功能说起,研究研究,可以了解更多的细节。
在openwrt的页面中已经涉及到下面的内容如:
其中在更新系统时候有进行配置保存及恢复的功能。
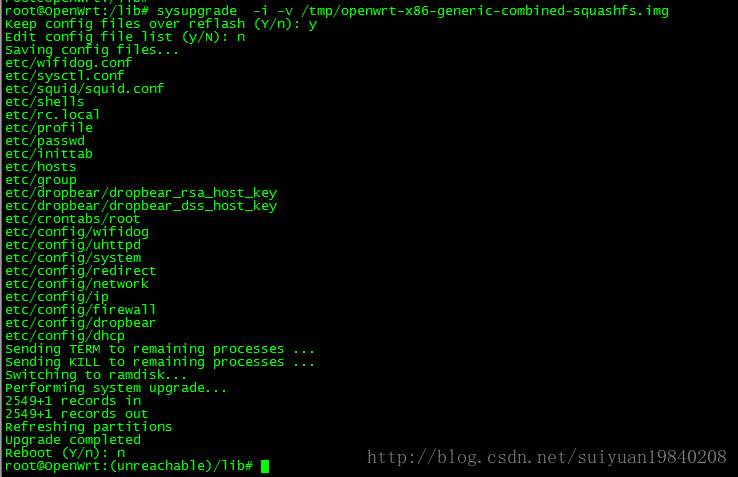
1:sysupgrade是的交互式使用命令如下:
经过上面的系统更新之后,会保存上面显示的配置文件中的内容,故更新系统不会影响配置的丢失。
3:脚本分析
脚本有点多,其中分析主要的脚本就可以了,其他的加一些打印信息可以帮助分析执行流程。
上面就是通过openwrt系统提供的sysupgrade命令来对系统进行更新的。
root@OpenWrt:~# which sysupgrade
/sbin/sysupgrade
看看脚本中的主要内容,
include /lib/upgrade
do_save_conffiles() {
local conf_tar="${1:-$CONF_TAR}"
[ -z "$(rootfs_type)" ] && {
echo "Cannot save config while running from ramdisk."
ask_bool 0 "Abort" && exit
return 0
}
run_hooks "$CONFFILES" $sysupgrade_init_conffiles
ask_bool 0 "Edit config file list" && vi "$CONFFILES"
v "Saving config files..."
[ "$VERBOSE" -gt 1 ] && TAR_V="v" || TAR_V=""
tar c${TAR_V}zf "$conf_tar" -T "$CONFFILES" 2>/dev/null
}
其中run_hooks函数的定义如下,其主要是执行钩子函数,即,第一个参数为:函数参数,第二个参数之后为:调用函数。
run_hooks() {
local arg="$1"; shift
for func in "$@"; do
eval "$func $arg"
done
}
run_hooks "$CONFFILES" $sysupgrade_init_conffiles 的作用就是将需要保存的文件名字保存到"$CONFFILES"文件中,保存那些文件了
定义在add_uci_conffiles()和add_overlayfiles()函数中。
add_uci_conffiles() {
local file="$1"
( find $(sed -ne '/^[[:space:]]*$/d; /^#/d; p' \
/etc/sysupgrade.conf /lib/upgrade/keep.d/* 2>/dev/null) \
-type f 2>/dev/null;
opkg list-changed-conffiles ) | sort -u > "$file"
return 0
}
add_overlayfiles() {
local file="$1"
find /overlay/etc/ -type f | sed \
-e 's,^/overlay/,/,' \
-e '\,/META_[a-zA-Z0-9]*$,d' \
-e '\,/functions.sh$,d' \
-e '\,/[^/]*-opkg$,d' \
> "$file"
return 0
}
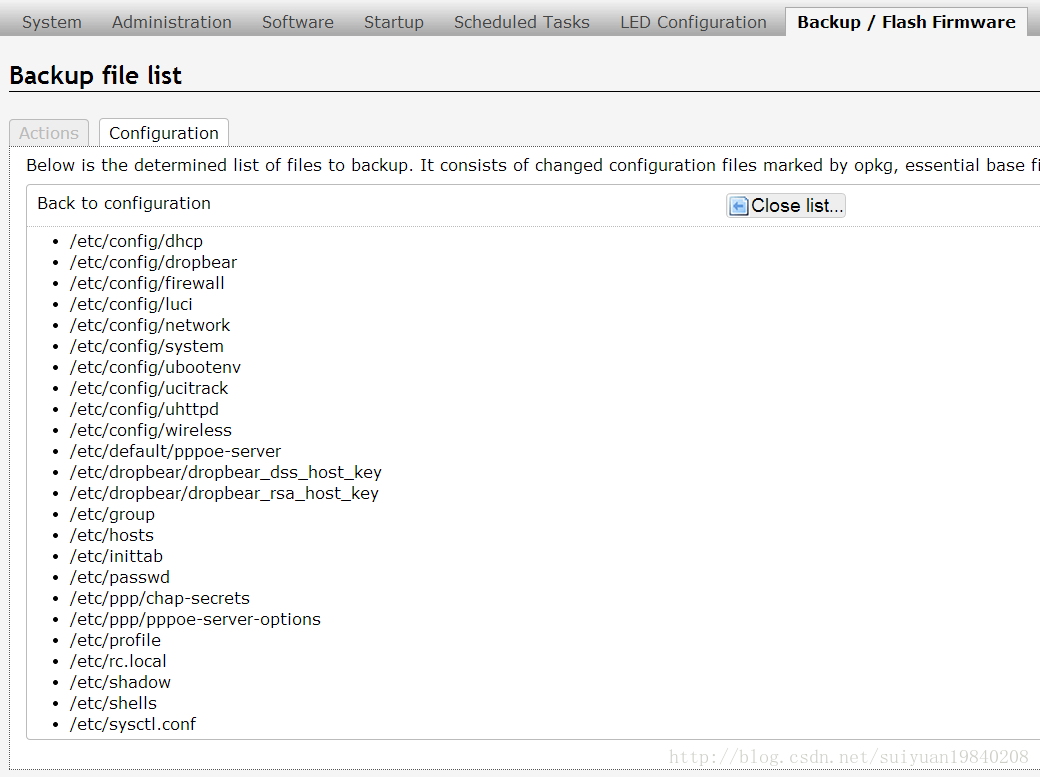
默认保存的文件内容如下:如果需要对自定
etc/wifidog.conf
etc/sysctl.conf
etc/squid/squid.conf
etc/shells
etc/rc.local
etc/profile
etc/passwd
etc/inittab
etc/hosts
etc/group
etc/dropbear/dropbear_rsa_host_key
etc/dropbear/dropbear_dss_host_key
etc/crontabs/root
etc/config/wifidog
etc/config/uhttpd
etc/config/system
etc/config/redirect
etc/config/network
etc/config/ip
etc/config/firewall
etc/config/dropbear
etc/config/dhcp
函数ask_bool()实现是否与命令行进行交互式的处理。
v "Saving config files..."
[ "$VERBOSE" -gt 1 ] && TAR_V="v" || TAR_V=""
tar c${TAR_V}zf "$conf_tar" -T "$CONFFILES" 2>/dev/null
实现对上面的数据文件进行压缩处理,其文件名称为:/tmp/sysupgrade.tgz
if [ -n "$CONF_IMAGE" ]; then
case "$(get_magic_word $CONF_IMAGE cat)" in
# .gz files
1f8b) ;;
*)
echo "Invalid config file. Please use only .tar.gz files"
exit 1
;;
esac
get_image "$CONF_IMAGE" "cat" > "$CONF_TAR"
export SAVE_CONFIG=1
elif ask_bool $SAVE_CONFIG "Keep config files over reflash"; then
do_save_conffiles
export SAVE_CONFIG=1
else
export SAVE_CONFIG=0
fi
上面的条件判断执行的是elif,即默认是保存更改过的配置文件。 export SAVE_CONFIG=1
其中语句
kill_remaining TERM
sleep 3
kill_remaining KILL
实现对进程的term和kill操作
kill_remaining() { # [ <signal> ]
local sig="${1:-TERM}"
echo -n "Sending $sig to remaining processes ... "
local stat
for stat in /proc/[0-9]*/stat; do
[ -f "$stat" ] || continue
local pid name state ppid rest
read pid name state ppid rest < $stat
name="${name#(}"; name="${name%)}"
local cmdline
read cmdline < /proc/$pid/cmdline
# Skip kernel threads
[ -n "$cmdline" ] || continue
case "$name" in
# Skip essential services
*ash*|*init*|*watchdog*|*ssh*|*dropbear*|*telnet*|*login*|*hostapd*|*wpa_supplicant*) : ;;
# Killable process
*)
if [ $pid -ne $$ ] && [ $ppid -ne $$ ]; then
echo -n "$name "
kill -$sig $pid 2>/dev/null
fi
;;
esac
done
echo ""
}
在升级操作之前有一个run_ramfs(),将一个最小能运行的系统mount到内存中去。为后的操作提供运行环境。
run_ramfs() { # <command> [...]
install_bin /bin/busybox /bin/ash /bin/sh /bin/mount /bin/umount \
/sbin/pivot_root /usr/bin/wget /sbin/reboot /bin/sync /bin/dd \
/bin/grep /bin/cp /bin/mv /bin/tar /usr/bin/md5sum "/usr/bin/[" \
/bin/vi /bin/ls /bin/cat /usr/bin/awk /usr/bin/hexdump \
/bin/sleep /bin/zcat /usr/bin/bzcat /usr/bin/printf /usr/bin/wc
install_bin /sbin/mtd
for file in $RAMFS_COPY_BIN; do
install_bin $file
done
install_file /etc/resolv.conf /lib/functions.sh /lib/functions.sh /lib/upgrade/*.sh $RAMFS_COPY_DATA
pivot $RAM_ROOT /mnt || {
echo "Failed to switch over to ramfs. Please reboot."
exit 1
}
mount -o remount,ro /mnt
umount -l /mnt
grep /overlay /proc/mounts > /dev/null && {
mount -o remount,ro /overlay
umount -l /overlay
}
# spawn a new shell from ramdisk to reduce the probability of cache issues
exec /bin/busybox ash -c "$*"
}
在整整操作之前先看看 mtd,sysupgrade 更新过程实际使用的就是mtd命令
root@OpenWrt:/overlay/etc#mtd
Usage: mtd [<options> ...] <command> [<arguments> ...] <device>[:<device>...]
The device is in the format of mtdX (eg: mtd4) or its label.
mtd recognizes these commands:
unlock unlock the device
refresh refresh mtd partition
erase erase all data on device
write <imagefile>|- write <imagefile> (use - for stdin) to device
jffs2write <file> append <file> to the jffs2 partition on the device
Following options are available:
-q quiet mode (once: no [w] on writing,
twice: no status messages)
-n write without first erasing the blocks
-r reboot after successful command
-f force write without trx checks
-e <device> erase <device> before executing the command
-d <name> directory for jffs2write, defaults to "tmp"
-j <name> integrate <file> into jffs2 data when writing an image
-p write beginning at partition offset
Example: To write linux.trx to mtd4 labeled as linux and reboot afterwards
mtd -r write linux.trx linux
do_upgrade() {
v "Performing system upgrade..."
if type 'platform_do_upgrade' >/dev/null 2>/dev/null; then
platform_do_upgrade "$ARGV"
else
default_do_upgrade "$ARGV"
fi
[ "$SAVE_CONFIG" -eq 1 -a -n "$USE_REFRESH" ] && {
v "Refreshing partitions"
if type 'platform_refresh_partitions' >/dev/null 2>/dev/null; then
platform_refresh_partitions
else
refresh_mtd_partitions
fi
if type 'platform_copy_config' >/dev/null 2>/dev/null; then
platform_copy_config
else
jffs2_copy_config
fi
}
v "Upgrade completed"
[ -n "$DELAY" ] && sleep "$DELAY"
ask_bool 1 "Reboot" && {
v "Rebooting system..."
reboot -f
sleep 5
echo b 2>/dev/null >/proc/sysrq-trigger
}
}
default_do_upgrade() {
sync
if [ "$SAVE_CONFIG" -eq 1 -a -z "$USE_REFRESH" ]; then
get_image "$1" | mtd -j "$CONF_TAR" write - "${PART_NAME:-image}"
else
get_image "$1" | mtd write - "${PART_NAME:-image}"
fi
}
platform_do_upgrade() {
local rootfs="$(x86_get_rootfs)"
local rootfsdev="${rootfs##*:}"
sync
[ -b ${rootfsdev%[0-9]} ] && get_image "$@" | dd of=${rootfsdev%[0-9]} bs=4096 conv=fsync
sleep 1
}
x86_get_rootfs() {
local rootfsdev
local rootfstype
rootfstype="$(awk 'BEGIN { RS=" "; FS="="; } ($1 == "rootfstype") { print $2 }' < /proc/cmdline)"
case "$rootfstype" in
squashfs|jffs2)
rootfsdev="$(awk 'BEGIN { RS=" "; FS="="; } ($1 == "block2mtd.block2mtd") { print substr($2,1,index($2, ",")-1) }' < /proc/cmdline)";;
ext4)
rootfsdev="$(awk 'BEGIN { RS=" "; FS="="; } ($1 == "root") { print $2 }' < /proc/cmdline)";;
esac
echo "$rootfstype:$rootfsdev"
}
jffs2_copy_config() {
if grep rootfs_data /proc/mtd >/dev/null; then
# squashfs+jffs2
mtd -e rootfs_data jffs2write "$CONF_TAR" rootfs_data
else
# jffs2
mtd jffs2write "$CONF_TAR" rootfs
fi
}
refresh_mtd_partitions() {
mtd refresh rootfs
}其中需要注意的是不同的平台如,Atheros和x86的各个平台的执行过程有所不同,最终一点是需要将$CONF_TAR保存到系统的rootfs_data或者rootfs_data分区数据中去。





 本文详细介绍了OpenWRT系统中的sysupgrade命令使用方法及其背后的工作原理,包括配置文件的保存与恢复流程、脚本分析等内容,并针对不同平台的升级过程进行了说明。
本文详细介绍了OpenWRT系统中的sysupgrade命令使用方法及其背后的工作原理,包括配置文件的保存与恢复流程、脚本分析等内容,并针对不同平台的升级过程进行了说明。

















 226
226

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










