2.1 插入排序(增量法)
排序问题:
输入:n个数的一个序列
INSERTION-SORT(A)
1 for j=2 to A.length
key=A[j]
//Inset A[j] into the sorted sequence A[1..J-1]
i=j-1
while i>0 and A[j]>key
A[i+1]=A[i]
i=i-1
A[i+1]=key运行时间:T(n² )
2.3设计算法
2.3.1 分治法
分治法思想:将原问题分解为几个规模较小但类似于原问题的子问题,递归地求解这些子问题,然后再结合这些子问题 的解建立原问题是解。
分治模式的三步骤:
1.分解 2. 解决子问题 3. 合并
归并排序算法完全遵循分治模式:
分解:分解带排序的n个元素的序列成各具n/2个元素的两个字序列。
解决:使用归并排序递归的排序两个子序列。
合并:合并两个已排序的子序列以产生已排序的答案。
归并排序伪代码:
1.合并子程序:
Merge(A,p,q,r)
1 n1=q-p+1;
2 n2=r-q;
3 let L[1..n1+1] and R[1..n2+1] be new arrays
4 for i=1 to n1
5 L[i]=A[p+i-1]
6 for j=1 to n2+1
7 R[j]=A[q+j]
8 L[n1+1]=∞
9 R[n2+1]=∞
10 i=1
11 j=1
12 for k=p to r
13 if L[i]≤R[j]
14 A[k]=L[i]
15 i=i+1
16 else A[k]=R[j]
17 j=j+1 - 归并排序伪代码:
Merge_SORT(A,p,r)
1 if p<r
2 q=[(p+r]/2]//取整
3 Merge_SORT(A,p,q)
4 Merge_SORT(A,q+1,r)
Merge(A,p,q,r)运行时间:T(nlg(n) ,递归树的总层数:lg(n)+1.
- 归并排序算法代码实现:
3.1(C语言版)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include"compare.h"
#include "sort.h"
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int b[] = { 1, 2, 5, 8, 9, 0, 3, 4, 6, 7 }, i;
mergeSort(b,sizeof(int), 0,9, intGreater);
printf("归并排序\n");
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
printf("%d ", b[i]);
system("pause");
return 0;
}/*
file :sort.h
anther:spf
created on:2015.4.15.16:22
*/
#ifndef __sort_H__
#define __sort_H__
#ifdef _cplusplus
extern "C"{
#endif
void mergeSort(void* a, int size, int p, int r, int(*comp)(void*, void*));//归并排序
//Node* buildList(void *array,int n,int size);
#ifdef _cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /*__sort_H__*//*********************sort.c**************/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include "Sort.h"
#include "compare.h"
#include "merge.h"
/*******************归并排序**************
输入参数: a;将要排序的数组序列
size;元素数据类型所占字节
p; 数组下边界(包含)
r; 数组下边界(不包含)
*comp:比较仿函数(可调用STL库函数)
******************************************/
void mergeSort(void* a, int size, int p, int r, int(*comp)(void*, void*))
{
if (p<r)
{
int q = (p + r) / 2;
mergeSort(a, size, p, q, comp);
mergeSort(a, size, q + 1, r, comp);
merge(a, size, p, q, r, comp);
}
}/*
* File: merge.h
* Author: spf
*
* Created on 2015年 4月 16日, 11:08
*/
#ifndef _MERGE_H
#define _MERGE_H
#ifdef __cplusplus//如果是cpp文件
extern "C" { //告诉编译器{ }内部是用C写成的文件,请用C的方式来连接他们
#endif
void merge(void* a, int size, int p, int q, int r, int(*comp)(void*, void*));
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /* _MERGE_H *//*********************序列合并算法******************/
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include"merge.h"
#include"compare.h"
void merge(void* a, int size, int p, int q, int r, int(*comp)(void*, void*))
{
int i, j, k, n1 = q - p + 1, n2 = r - q;
void* L = (void*)malloc(n1*size);
void* R = (void*)malloc(n2*size);
memcpy((char*)L, (char*)a + p*size, n1*size);//将a[p......q]复制到L[1....n1]
memcpy((char*)R, (char*)a + (q + 1)*size, n2*size);//将a[q+1......r]复制到R[1....n2]
i = j = 0;
k = p;
while ((i < n1) && (j < n2))
{
if (comp((char*)L + i*size, (char*)R + j*size) <= 0)//L[i]<=R[j]
memcpy((char*)a + (k++)*size, (char*)L + (i++)*size, size);/*a[k]←L[i]*/
else
memcpy((char*)a + (k++)*size, (char*)R + (j++)*size, size);/*a[k] ←R[j]*/
}
if (i < n1)
memcpy((char*)a + k*size, (char*)L + i*size, (n1 - i)*size);/*将L[i..n1]拷贝到a[k..r]*/
if (j < n2)
memcpy((char*)a + k*size, (char*)R + j*size, (n2 - j)*size);/*将R[j..n2]拷贝到a[k..r]*/
free(L);
L = NULL;
free(R);
R = NULL;
}/*******************比较函数**********************/
#include "compare.h"
#include <string.h>
int intGreater(int *x,int *y){
return (*x)-(*y);
}
int intLess(int *x,int *y){
return intGreater(y,x);
}
int charGreater(char *x,char *y){
return (*x)-(*y);
}
int charLess(char *x,char *y){
return charGreater(y,x);
}
int strGreater(char **x,char **y){
return strcmp(*x,*y);
}
int strLess(char **x,char **y){
return strGreater(y,x);
}
int floatGreater(float *x,float *y){
if((*x-*y)>0.0)
return 1;
if((*x-*y)<0.0)
return -1;
return 0;
}
int floatLess(float *x,float *y){
return floatGreater(y,x);
}
int doubleGreater(double *x,double *y){
if((*x-*y)>0.0)
return 1;
if((*x-*y)<0.0)
return -1;
return 0;
}
int doubleLess(double *x,double *y){
return doubleGreater(y,x);
}
int dblLess(double **x,double **y){
if((**x-**y)<0.0)
return 1;
if((**x-**y)>0.0)
return -1;
return 0;
}/**************比较函数头文件**********************/
#ifndef _COMPARE_H
#define _COMPARE_H
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
//#include "../datastructure/bintree.h"
int intGreater(void *x,void *y);
int intLess(void *x,void *y);
int charGreater(void *x,void *y);
int charLess(void *x,void *y);
int strGreater(void *x,void *y);
int strLess(void *x,void *y);
int floatGreater(void *x,void *y);
int floatLess(void *x,void *y);
int doubleGreater(void *x,void *y);
int doubleLess(void *x,void *y);
int dblLess(void *x,void *y);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
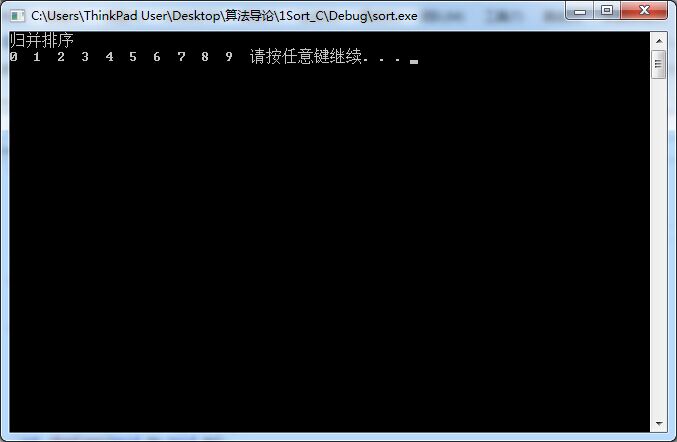
#endif /* _COMPARE_H */4.实验结果:
3.1(归并排序C++版)
/*****************test--main***************/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include<string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <vector>
#include <iterator>
#include <iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include <functional>//定义运算函数(代替运算符)
#include "sort.h"
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int a[]={1,2,5,8,9,0,3,4,6,7};
vector<int> va = vector<int>(a, a + 10);//用数组创建vector对象
mergeSort<vector<int>::iterator,greater<int> >(va.begin(),va.end());
copy(va.begin(), va.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
system("pause");
return 0;
}/*
* File: sort.h
* Author: spf
*
* Created on 2015.4.17 21:17
*/
#ifndef _SORT_H
#define _SORT_H
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
/*************归并排序***********************/
template<typename Iterator,typename Comparator>
void mergeSort(Iterator p, Iterator r)
{
int n = distance(p, r);
if (n>1)
{
Iterator q = p;
advance(q, n / 2);//移动迭代器n/2个位置
mergeSort<Iterator, Comparator>(p, q);
mergeSort<Iterator,Comparator>(q, r);
inplace_merge(p, q, r, Comparator());//STL自带序列合并函数
}
}
#endif /*sort.h*/- 快速排序
4.1 算法介绍
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/morewindows/article/details/6684558)
快速排序由于排序效率在同为O(N*logN)的几种排序方法中效率较高,因此经常被采用,再加上快速排序思想—-分治法也确实实用,因此很多软件公司的笔试面试,包括像腾讯,微软等知名IT公司都喜欢考这个,还有大大小的程序方面的考试如软考,考研中也常常出现快速排序的身影。
总的说来,要直接默写出快速排序还是有一定难度的,因为本人就自己的理解对快速排序作了下白话解释,希望对大家理解有帮助,达到快速排序,快速搞定。
快速排序是C.R.A.Hoare于1962年提出的一种划分交换排序。它采用了一种分治的策略,通常称其为分治法(Divide-and-ConquerMethod)。
该方法的基本思想是:
1.先从数列中取出一个数作为基准数。
2.分区过程,将比这个数大的数全放到它的右边,小于或等于它的数全放到它的左边。
3.再对左右区间重复第二步,直到各区间只有一个数。
快速排序的时间主要耗费在划分操作上,对长度为k的区间进行划分,共需k-1次关键字的比较。
最坏情况是每次划分选取的基准都是当前无序区中关键字最小(或最大)的记录,划分的结果是基准左边的子区间为空(或右边的子区间为空),而划分所得的另一个非空的子区间中记录数目,仅仅比划分前的无序区中记录个数减少一个。时间复杂度为O(n*n)
在最好情况下,每次划分所取的基准都是当前无序区的”中值”记录,划分的结果是基准的左、右两个无序子区间的长度大致相等。总的关键字比较次数:O(nlgn)
尽管快速排序的最坏时间为O(n2),但就平均性能而言,它是基于关键字比较的内部排序算法中速度最快者,快速排序亦因此而得名。它的平均时间复杂度为O(nlgn)。
于是,采用随机划分,是算法获得平均情形
4.2 算法代码实现
#include "stdafx.h"
#include<string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <vector>
#include <iterator>
#include <iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include <functional>//定义运算函数(代替运算符)
#include "sort.h"
#include "merge.h"
#include "partition.h"
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int a[]={1,2,5,8,9,0,3,4,6,7};
vector<int> va = vector<int>(a, a + 10);//用数组创建vector对象
quickSort(va.begin(), va.end(),greater<int>());
copy(va.begin(), va.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));
system("pause");
return 0;
}快速排序头文件:
/****************快速排序**********************/
/*
* File: sort.h
* Author: spf
*
* Created on 2015.4.17 21:17
*/
#ifndef _SORT_H
#define _SORT_H
#include "partition.h"
#include <iterator>
template<typename Iterator ,typename Comparator>
void quickSort(Iterator p, Iterator r, Comparator comp)
{
long n = distance(p, r);
if (n>1)
{
Iterator q = randomizedPartition(p, r, comp);//随机序列划分
quickSort(p, q, comp);
quickSort(q, r, comp);
}
}
#endif /*sort.h*/随机序列划分:
/*
File:partition.h
Auther:spf
Created ON:2015.4.20
*/
#ifndef _PARTITION_H
#define _PARTITION_H
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
/*返回介于p和q 之间的一个随机整数*/
int randomNumber(int p, int q)
{
return p + (int)((double)(q - p)*rand() / RAND_MAX);
}
//*随机序列划分*//
template<typename Iterator,typename Comparator>
Iterator randomizedPartition(Iterator p, Iterator r, Comparator comp)
{
int n = distance(p, r), i;
Iterator q = p, t = r;
i = randomNumber(0, n-1);
advance(q, i);
iter_swap(q, --t);
return stable_partition(p, r, bind2nd(comp, *t));
}
#endif






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








