Gnome排序(地精排序),起初由Hamid Sarbazi-Azad 于2000年提出,并被称为stupid排序,后来被Dick Grune描述并命名为“地精排序”,作为一个排序算法,和插入排序类似,除了移动一个元素到最终的位置,是通过交换一系列的元素实现,就像冒泡排序一样。概念上十分简单,不需要嵌套循环。时间复杂度为O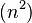 ,但是如果初始数列基本有序,时间复杂度将降为O(n)。实际上Gnome算法可以和插入排序算法一样快。平均运行时间为O
,但是如果初始数列基本有序,时间复杂度将降为O(n)。实际上Gnome算法可以和插入排序算法一样快。平均运行时间为O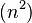 .
.
Gnome排序算法总是查找最开始逆序的一对相邻数,并交换位置,基于交换两元素后将引入一个新的相邻逆序对,并没有假定当前位置之后的元素已经有序
Description
下面gnome排序算法的伪代码,使用0起始索引数组:
procedure gnomeSort(a[])
pos := 1
while pos < length(a)
if (a[pos] >= a[pos-1])
pos := pos + 1
else
swap a[pos] and a[pos-1]
if (pos > 1)
pos := pos - 1
end if
end if
end while
end procedure实例
给定一个无序数组, a = [5, 3, 2, 4], gnome排序将在while循环中执行如下的步骤. "current position"采用加粗黑体:
| Current array | Action to take |
|---|---|
| [5, 3, 2, 4] | a[pos] < a[pos-1], swap: |
| [3, 5, 2, 4] | a[pos] >= a[pos-1], increment pos: |
| [3, 5, 2, 4] | a[pos] < a[pos-1], swap and pos > 1, decrement pos: |
| [3, 2, 5, 4] | a[pos] < a[pos-1], swap and pos <= 1, increment pos: |
| [2, 3, 5, 4] | a[pos] >= a[pos-1], increment pos: |
| [2, 3, 5, 4] | a[pos] < a[pos-1], swap and pos > 1, decrement pos: |
| [2, 3, 4, 5] | a[pos] >= a[pos-1], increment pos: |
| [2, 3, 4, 5] | a[pos] >= a[pos-1], increment pos: |
| [2, 3, 4, 5] | pos == length(a), finished. |
C代码如下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
void swap(int *a, int *b) //交换两元素的值
{
int t;
t=*a;
*a=*b;
*b=t;
}
void printArray(int a[], int count) //打印数组元素
{
int i;
for(i=0; i<count; i++)
printf("%d ",a[i]);
printf("\n");
}
void gnome_sort(int *a, int len) //gnome排序算法
{
int pos=1;
while(pos<len)
{
if(a[pos]>=a[pos-1])
{
pos++;
}
else
{
swap(&a[pos],&a[pos-1]);
if(pos>1) pos--;
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
int a[]={3, 5, 4, 6, 9, 7, 8, 0, 1};
int n=sizeof(a)/sizeof(*a);
printArray(a,n);
gnome_sort(a,n);
printArray(a,n);
return 0;
}
优化算法
gnome算法还可以通过引入一个变量,用于存储每次返回到数组前面的位置来进行优化。采用这样的优化,gnome排序将成为一个变种插入排序,下面优化后gnome排序算法的伪代码,使用0起始索引数组:
procedure optimizedGnomeSort(a[])
pos := 1
last := 0
while pos < length(a)
if (a[pos] >= a[pos-1])
if (last != 0)
pos := last
last := 0
end if
pos := pos + 1
else
swap a[pos] and a[pos-1]
if (pos > 1)
if (last == 0)
last := pos
end if
pos := pos - 1
else
pos := pos + 1
end if
end if
end while
end procedureC代码如下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
void swap(int *a, int *b) //交换两元素的值
{
int t;
t=*a;
*a=*b;
*b=t;
}
void printArray(int a[], int count) //打印数组元素
{
int i;
for(i=0; i<count; i++)
printf("%d ",a[i]);
printf("\n");
}
void optimizedGnome_Sort(int *a, int len) //优化后的gnome排序
{
int last,pos;
last=0; pos=1;
while(pos<len)
{
if(a[pos]>=a[pos-1])
{
if(last!=0)
{
pos=last;
last=0;
}
pos++;
}
else
{
swap(&a[pos],&a[pos-1]);
if(pos>1)
{
if(last==0)
last=pos;
pos--;
}
else
{
pos++;
}
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
int a[]={3, 5, 4, 6, 9, 7, 8, 0, 1};
int n=sizeof(a)/sizeof(*a);
printArray(a,n);
optimizedGnome_Sort(a,n);
printArray(a,n);
return 0;
}























 158
158











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








