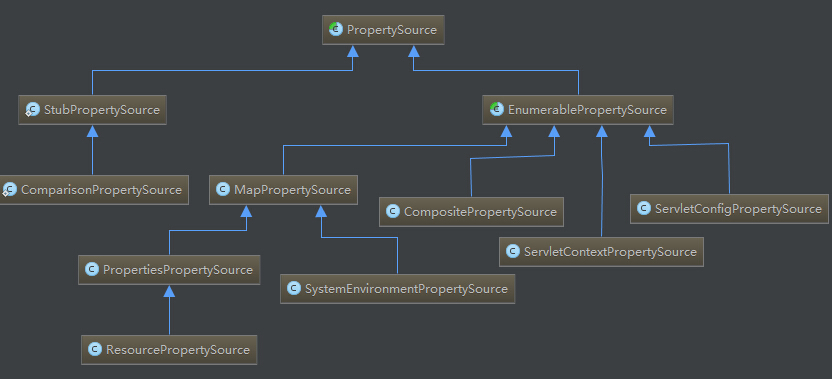
一 、抽象类PropertySource及子类
PropertySource是一个抽象类,它包含一个source和一个name。source可以是map或其他,通常是一组键值对。
这个类结构简化如下:
public abstract class PropertySource<T> {protected final
String name;//属性源名称
protected final T source;//属性源(比如来自Map,那就是一个Map对象)
public String getName(); //获取属性源的名字
public T getSource(); //获取属性源
public boolean containsProperty(String name); //是否包含某个属性
public abstract Object getProperty(String name); //得到属性名对应的属性值
} 主要类体系:
实现类1:MapPropertySource
MapPropertySource的source来自于一个Map,这个类结构很简单,这里不说。
用法如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("name","wang");
map.put("age",23);
MapPropertySource source_1=new MapPropertySource("person",map);
System.out.println(source_1.getProperty("name"));//wang
System.out.println(source_1.getProperty("age"));//23
System.out.println(source_1.getName());//person
System.out.println(source_1.containsProperty("class"));//false
}实现类2:PropertiesPropertySource
source是一个Properties对象,继承自MapPropertySource。与MapPropertySource用法相同
实现类3:ResourcePropertySource
继承自PropertiesPropertySource,它的source来自于一个Resource资源。
实现类4:ServletConfigPropertySource
source为ServletConfig对象
实现类5:ServletContextPropertySource
source为ServletContext对象
实现类6 StubPropertySource
临时作为一个PropertySource的占位,后期会被真实的PropertySource取代。
实现类7 SystemEnvironmentPropertySource
继承自MapPropertySource,它的source也是一个map,但来源于系统环境。
【重点】与MapPropertySource不同的是,取值时它将会忽略大小写,”.”和”_”将会转化。遇到转化情况会打印出日志。用法如下:
SystemEnvironmentPropertySource source =
new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource("systemEnvironment",(Map)System.getenv());
System.out.println(source.getProperty("PROCESSOR_LEVEL"));
System.out.println(source.getProperty("PROCESSOR_LEVEL".toLowerCase()));
System.out.println(source.getProperty("PROCESSOR.LEVEL"));输出如下:
6
09:23:38.833 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.core.env.SystemEnvironmentPropertySource - PropertySource [systemEnvironment] does not contain 'processor_level', but found equivalent 'PROCESSOR_LEVEL'
6
09:23:38.836 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.core.env.SystemEnvironmentPropertySource - PropertySource [systemEnvironment] does not contain 'PROCESSOR.LEVEL', but found equivalent 'PROCESSOR_LEVEL'
6实现类9 CompositePropertySource
内部可以保存多个PropertySource
private final Set<PropertySource<?>> propertySources = new LinkedHashSet<PropertySource<?>>();取值时依次遍历这些PropertySource
二、PropertySources
包含多个PropertySource,继承了Iterable接口,所以它的子类还具有迭代的能力。
接口定义:
public interface PropertySources extends Iterable<PropertySource<?>> {
boolean contains(String name);//是否包含某个PropertySource
PropertySource<?> get(String name);//获取某个PropertySource
}实现类 MutablePropertySources
它包含了一个CopyOnWriteArrayList集合,用来包含多个PropertySource
private final List<PropertySource<?>> propertySourceList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<PropertySource<?>>();这个类还具有几个比较重要的方法,用来向集合中加减PropertySource
addFirst
addLast
addBefore
addAfter
remove
三、PropertyResolver接口
实现这个类的接口具有解析PropertySource、根据PropertySource转换文本中的占位符的能力
public interface PropertyResolver {
//是否包含某个属性
boolean containsProperty(String key);
//获取属性值 如果找不到返回null
String getProperty(String key);
//获取属性值,如果找不到返回默认值
String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue);
//获取指定类型的属性值,找不到返回null
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType);
//获取指定类型的属性值,找不到返回默认值
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType, T defaultValue);
//获取属性值为某个Class类型,找不到返回null,如果类型不兼容将抛出ConversionException
<T> Class<T> getPropertyAsClass(String key, Class<T> targetType);
//获取属性值,找不到抛出异常IllegalStateException
String getRequiredProperty(String key) throws IllegalStateException;
//获取指定类型的属性值,找不到抛出异常IllegalStateException
<T> T getRequiredProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) throws IllegalStateException;
//替换文本中的占位符(${key})到属性值,找不到不解析
String resolvePlaceholders(String text);
//替换文本中的占位符(${key})到属性值,找不到抛出异常IllegalArgumentException
String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException;
} 它的实现类主要有两种:
1 各种Resolver:主要是PropertySourcesPropertyResolver
2 各种Evironment:下一节介绍
## PropertySourcesPropertyResolver示例
MutablePropertySources sources = new MutablePropertySources();
sources.addLast(new MapPropertySource("map", new HashMap<String, Object>() {
{
put("name", "wang");
put("age", 12);
}
}));//向MutablePropertySources添加一个MapPropertySource
PropertyResolver resolver = new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(sources);
System.out.println(resolver.containsProperty("name"));//输出 true
System.out.println(resolver.getProperty("age"));//输出 12
System.out.println(resolver.resolvePlaceholders("My name is ${name} .I am ${age}."));
//输出 My name is wang .I am 12.四、Environment
开发环境,比如JDK环境,系统环境;每个环境都有自己的配置数据,如System.getProperties()可以拿到JDK环境数据、System.getenv()可以拿到系统变量,ServletContext.getInitParameter()可以拿到Servlet环境配置数据。
Spring抽象了一个Environment来表示Spring应用程序环境配置,它整合了各种各样的外部环境,并且提供统一访问的方法。
public interface Environment extends PropertyResolver {
//得到当前明确激活的剖面
String[] getActiveProfiles();
//得到默认激活的剖面,而不是明确设置激活的
String[] getDefaultProfiles();
//是否接受某些剖面
boolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles);
} 从API上可以看出,除了可以解析相应的属性信息外,还提供了剖面相关的API,目的是: 可以根据剖面有选择的进行注册组件/配置。比如对于不同的环境注册不同的组件/配置(正式机、测试机、开发机等的数据源配置)
我们再看看它的继承关系:
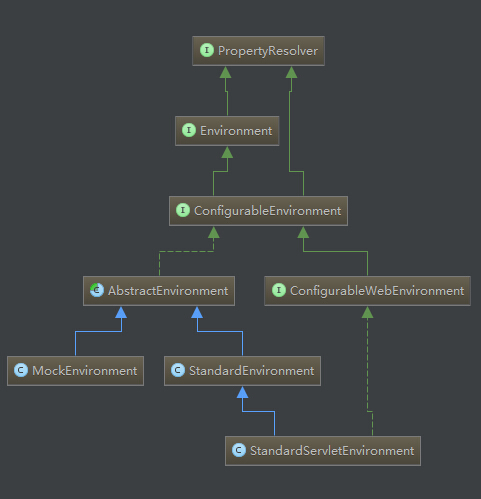
抛开复杂的继承关系,发现它的实现类主要有两个:
StandardEnvironment:标准环境,普通Java应用时使用,会自动注册System.getProperties() 和 System.getenv()到环境;
StandardServletEnvironment:标准Servlet环境,其继承了StandardEnvironment,Web应用时使用,除了StandardEnvironment外,会自动注册ServletConfig(DispatcherServlet)、ServletContext及有选择性的注册JNDI实例到环境;
使用示例如下:
//会自动注册 System.getProperties() 和 System.getenv()
Environment environment = new StandardEnvironment();
System.out.println(environment.getProperty("file.encoding")); Profile
profile,剖面,大体意思是:我们程序可能从某几个剖面来执行应用,比如正式机环境、测试机环境、开发机环境等,每个剖面的配置可能不一样(比如开发机可能使用本地的数据库测试,正式机使用正式机的数据库测试)等;因此呢,就需要根据不同的环境选择不同的配置;
profile有两种:
默认的:通过环境中“spring.profiles.default”属性获取,如果没有配置默认值是“default”
明确激活的:通过环境中“spring.profiles.active”获取
查找顺序是:先进性明确激活的匹配,如果没有指定明确激活的(即集合为空)就找默认的;配置属性值从Environment读取。
@Profile()的使用
可以使用在类或方法上,表示这个bean或方法属于哪个剖面
示例:
@Configuration
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
System.setProperty("spring.profiles.active","dev");
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Test.class);
System.out.println(Arrays.asList(context.getBeanNamesForType(String.class)));
}
@Bean()
@Profile("test")
public String str1() {
return "str1";
}
@Bean
@Profile("dev")
public String str2() {
return "str2";
}
@Bean
public String str3() {
return "str3";
}
}将会输出[str2, str3]
因为str1的剖面为test,既不是激活的dev–str2,也不是默认的default—str3
@PropertySource()
Java Config方式的注解,其属性会自动注册到相应的Environment
@Configuration
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:resources.properties", ignoreResourceNotFound = false)
public class AppConfig {
} 























 5万+
5万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








