尽管写LeetCode解答主要是为了自己整理思路,但是如果对您也正好有帮助,请点个赞给菜鸟一点鼓励吧 :-)
原题

解法分析
解法1使用递归法;
解法2参考了别人的思路,为迭代法,类似于广度优先搜索;
自己的迭代法使用了后序遍历来统计树的深度,较为繁琐,没有参考意义。
解法1
解法分析
递归计算左子树的深度与右子树的深度,那么树的深度为两个子树中深度的较大值+1。
代码
public class Solution104_iterator {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
stack.push(root);
int count = 0;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int size = stack.size();
while (size-- > 0) {
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
if (cur.left != null)
stack.addLast(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null)
stack.addLast(cur.right);
}
count++;
}
return count;
}
}
解法2
参考了https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/4087/simple-solution-using-java/4
解法分析
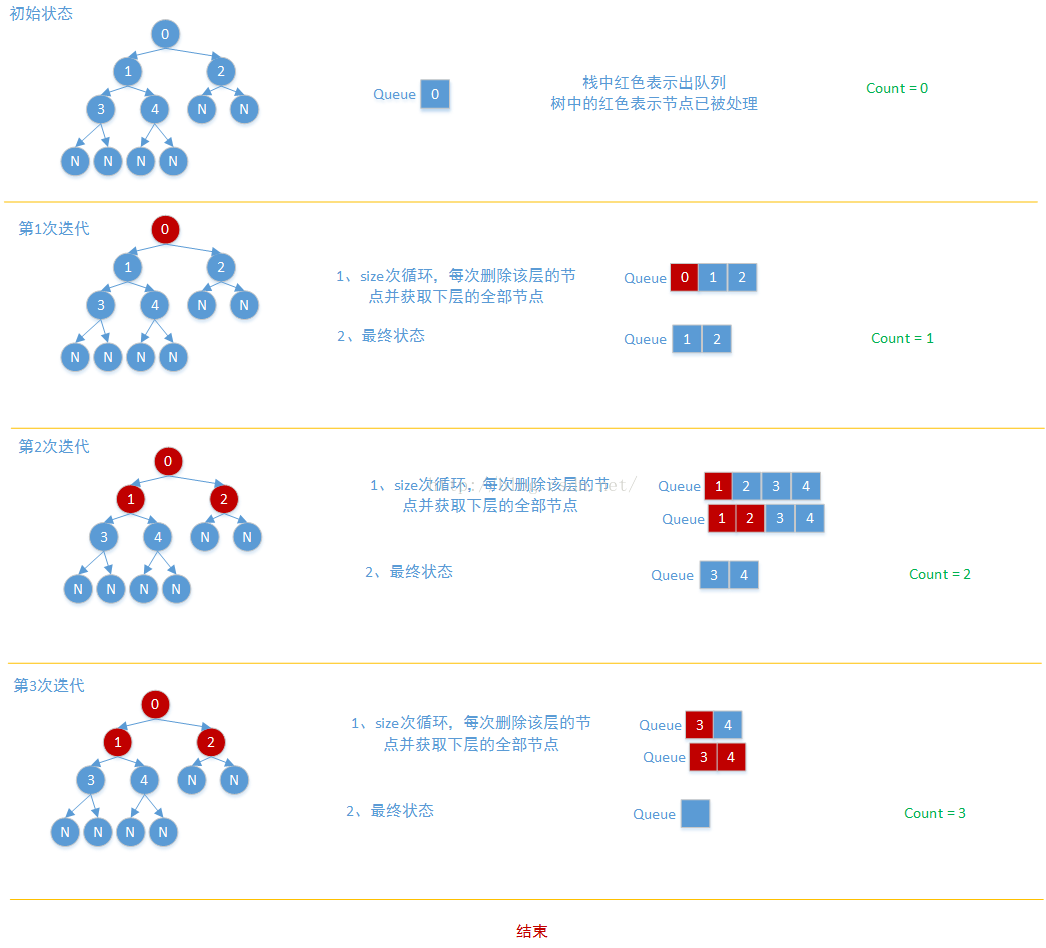
类似于广度优先搜索,使用一个队列。队列初始为空,每次都会加入第i层的所有节点,如果队列不为空,说明该层有节点,因此count++;同时,删除第i层所有的节点,加入第i+1层的所有节点,继续进行判断。如果队列为空,说明树已经到底,结束。、
图解
以下图所示的树为例,深度为3层。
代码
public class Solution104_iterator {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
stack.push(root);
int count = 0;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int size = stack.size();
while (size-- > 0) {
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
if (cur.left != null)
stack.addLast(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null)
stack.addLast(cur.right);
}
count++;
}
return count;
}
}





















 398
398

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








