1.意外结束和正常结束的概念
正常结束:按照语句的顺序执行完毕。
意外结束:例如break,continue等阻止程序按顺序执行下面的语句。
public class PuzzlerDemo36{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println(decision());
}
public static boolean decision(){
try{
return true;
}
finally{
return false;
}
}
}2.try-finally规则
特点:
(1)当try语句块和finally语句块都意外结束时,则try语句块引发意外结束的原因将被丢弃。
忠告:
(1)不要在finally语句块中意外结束,即不能在finally中使用return、break、continue跳出finally语句块,并且不要让受检查异常传播到finally之外。
(2)注意:只有try语句结束后才会进入finally语句块,因此如果try语句没有结束,是永远都不会进入finally的。
(3)System.exit(0);就是能够让try语句块不能结束的语句。
当调用这个语句后,(1)JVM将停止当前线程和死亡线程。(2)关闭挂钩(3)关闭终结器
(4)System.halt();在不关闭挂钩的前提停止VM.
public class PuzzleDemo39{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Hello");
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(){
public void run(){
System.out.println("GoodBye");
}
});
System.exit(0);
}
}3.try-catch规则
特性:
(1)如果一个catch子句捕获一个受检查异常,则在try语句中一定要能够抛出这个受检查异常,否则会编译错误。
(2)如果在catch中捕获Exception或Throwable,则try语句任意。
4.方法抛出异常规定
一个方法可以抛出的受检查异常集合是他所声明的所有要抛出的受检查异常集合的交集。
简单的来说,A方法是多个继承而来的throws的交集,
举例,
| interface A { public void fun() throws CloneNotSupportedException,InterruptedException; } interface B{ public void fun() throws InterruptedException; } class C{ public void fun() throws InterruptedException{ //继承方法throws的交集 } } |
//一个方法可以抛出的异常集合是他所适用的类型声明要抛出的已检查异常的交集!
import java.io.*;
public class PuzzleDemo37 implements Type3{
public void f(){
System.out.println("Hello");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Type3 t3 = new PuzzleDemo37();
t3.f();
}
}
class Arcane1{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
System.out.println("Hello world");
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("Error1");
}
}
}
class Arcane2{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("Error2");
}
}
}
interface Type1{
void f() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
}
interface Type2{
void f() throws InterruptedException;
}
interface Type3 extends Type1,Type2{
}
//一个方法可以抛出的异常集合是他所适用的类型声明要抛出的已检查异常的交集!
import java.io.*;
public class PuzzleDemo37 implements Type3{
public void f(){
System.out.println("Hello");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Type3 t3 = new PuzzleDemo37();
t3.f();
}
}
class Arcane1{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
System.out.println("Hello world");
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("Error1");
}
}
}
class Arcane2{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("Error2");
}
}
}
interface Type1{
void f() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
}
interface Type2{
void f() throws InterruptedException;
}
interface Type3 extends Type1,Type2{
}
5.final变量的规定
空的final变量只有在他的确没有赋过值的地方才可以被赋值。
即如果

则不能通过编译,因为编译器采取保守态度,即使你确定是安全的。
解决方案:利用辅助函数:
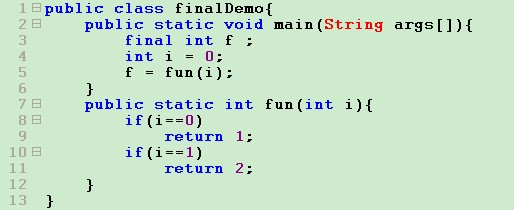
结论:
如果必须重构一个程序,消除明确赋值引发的错误,则必须考虑添加一个新的方法。
public class PuzzleDemo38{
public static final long GUEST_USER_ID = -1L;
private static final long USER_ID;
static{
try{
USER_ID = getUserIdFromEnvironment();
}
catch(IdUnavailableException e){
USER_ID = GUEST_USER_ID;
System.out.println("Logging in as guest");
}
}
private static long getUserIdFromEnvironment() throws IdUnavailableException{
throw new IdUnavailableException();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("user_id:"+USER_ID);
}
}
class IdUnavailableException extends Exception{
IdUnavailableException(){}
}6.类的规定
(1)实例变量初始化优先于构造器的程序体运行。
(2)构造器必须声明实例变量可能抛出的所有受检查异常。
7.流的规定
对于在finally中可能抛出的异常,都需要进行处理,不能任意传播。
对于finally中的close()方法,必须要对其进行捕获。
import java.io.*;
public class PuzzleDemo41{
public static void main(String args[])throws Exception{
copy("src.txt","des.txt");
}
public static void copy(String src,String des)throws IOException{
InputStream in = null;
OutputStream out = null;
try{
in = new FileInputStream(src);
out = new FileOutputStream(des);
byte[]b = new byte[1024];
int n;
while((n=in.read(b))>=0){
out.write(b,0,n);
}
}finally{
try{
if(in!=null)
in.close();
}
catch(IOException e){
System.out.println("in");
}
try{
if(out!=null)
out.close();
}
catch(IOException e){
System.out.println("out");
}
}
}
}
8.&与&&等一系列逻辑和条件操作符
a&b:规定不管a是true还是false,b都要计算,并得出结果。
a&&b:规定如果a为false,则b可以不用计算,并直接返回false。
a|b:规定不管a是true还是false,b都要计算,并得出结果。
a||b:规定如果a为true,则b可以不用计算,并直接返回true。
9.StackOverFlowError介绍
通常是由无限递归引起的。
在JVM中有一个调用栈,他预设了一个深度,当超出了这个深度,则会抛出StackOverflowError。
因此我们要避免无限递归调用。
import java.io.*;
public class PuzzleDemo40{
public static void main(String args[])throws Exception{
try{
PuzzleDemo40 pd2 = new PuzzleDemo40();
System.out.println("1");
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("异常发生");
}
}
private PuzzleDemo40 pd1 = new PuzzleDemo40();
public PuzzleDemo40() throws Exception{
throw new Exception("故意为之");
}
}





















 118
118

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








