1 主要内容:
Supervised Descent Method and its Applications to Face Alignment算法研究。
2代码彩蛋:我问了好久,xxiong好心人发给我的,希望能对你们学习有帮助:
低调下载:
http://humansensing.cs.cmu.edu/xxiong/mexintraface1.3.1%28release%29.zip。
注意杜绝一切商业用途,如果需要商业用途,请联系作者本人!!
3本文分为几个部分:
(1)解决什么问题
(2)具体理论方法是什么
(3)具体实现步骤
(1)解决什么问题
上一篇文章newton方法,请看具体实现,
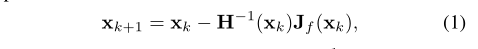
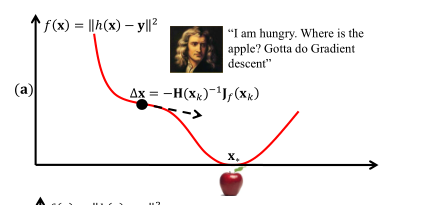
牛顿法目的是求f(x)最小值。然后改成求f’(x)=0。
迭代n次上图公式1,直到Xk+1 - Xk收敛到0.0001
or 其他非常小大于0的值。
而公式1中 f’(x)是上图中J(f(Xk))函数, 而f”(x)是H(Xk).
下图为该方法:
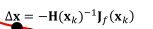
更多内容请看:上一篇牛顿法-最优方法。
我们知道牛顿法:要满足在定义域内二次可微,hession矩阵正定。
而在计算机背景下,运用newton method有三个问题:
1 Hession矩阵在最小值的局部是正定的,但在其他地方可能不正定。
因为只有Hession矩阵正定,初始值才能收敛到局部值。
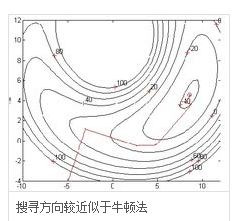
上图可知:搜索方法是凹方向,是梯度 or Hession矩阵的相反方向,只有Hession矩阵正定,即每个Hession矩阵每个特征值大于零,才会沿着梯度相反方向,即沿着曲线的凹方向(梯度方向是曲线的凸方向),收敛到局部极值点。
2Hession矩阵需要二次可微。但在计算机视觉下,x比如sift特征,是一个不可微的图像操作,即sift特征是离散的。在这种情况下,我们只能用数值逼近Hession矩阵 or 梯度,但这样做计算成本很大。
3Hession矩阵的维数可能很大。而Hession矩阵的逆矩阵计算的时间复杂度是O(n^3),空间复杂度O(n^2),n是矩阵维数,计算量和空间内存都需要很大,即使用 L-BFGS,计算成本仍然很大。
所以作者提出了a Supervised Descent Method (SDM),来求非线性的最小平方差。
在训练阶段:
通过最小化所有样本的非线性平方差函数之和,
学习许多梯度方向组成的梯度序列。
在测试阶段:
SDM minimizes 非线性平方差函数,
使用训练时训练的梯度方向,
再也不用计算 the Jacobian nor the Hessian矩阵 。
(2)Supervised Descent Method(SDM)具体理论原理是什么?
这里研究的SDM是对face alignment application.
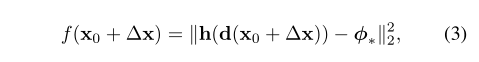
上公式中:
1 d代表一个人脸图片的m个像素,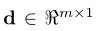
2 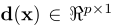
d(x)代表一个图片的66个标点。
3 h是特征抽取函数(比如sift特征抽取),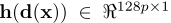
h(d(x))是在标点d(x)周围抽取的128维的sift特征。
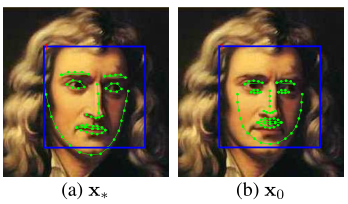
4上图
(a)图在训练期间,假设66个标记是已知,我们称之为X*
(b)图 先用检测到人脸(蓝色矩阵框),再用所有样本平均shape,作为X0,初始化位置。
人脸匹配(face alignment),是极小化公式(3).




 介绍Supervised Descent Method (SDM)算法及其在人脸对齐中的应用。SDM针对传统牛顿法在计算机视觉场景下的局限性,提出了一种新的优化方法。在训练阶段,通过最小化所有样本的非线性平方差函数之和,学习得到一系列梯度方向;在测试阶段,利用这些梯度方向进行非线性平方差函数的极小化,无需计算雅可比矩阵或海森矩阵。
介绍Supervised Descent Method (SDM)算法及其在人脸对齐中的应用。SDM针对传统牛顿法在计算机视觉场景下的局限性,提出了一种新的优化方法。在训练阶段,通过最小化所有样本的非线性平方差函数之和,学习得到一系列梯度方向;在测试阶段,利用这些梯度方向进行非线性平方差函数的极小化,无需计算雅可比矩阵或海森矩阵。
















 4540
4540










