欢迎转载,转载请注明:http://blog.csdn.net/zhgxhuaa
init启动过程
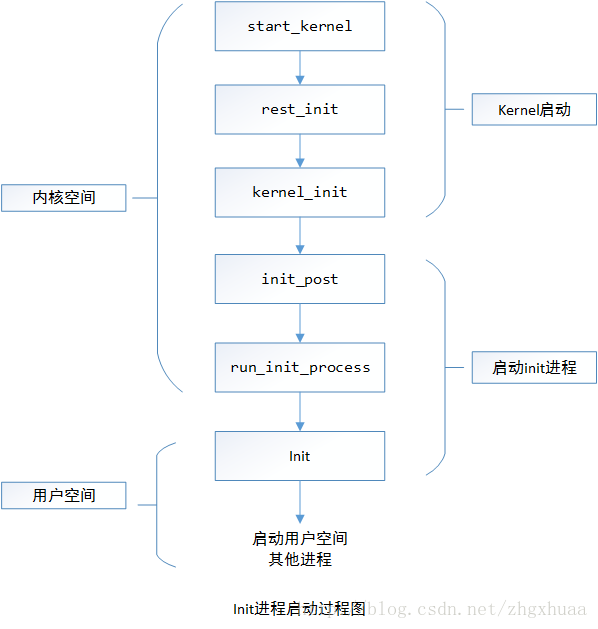
众所周知,Linux中的所有进程都是有init进程创建并运行的。首先Linux内核启动,然后在用户空间中启动init进程,再启动其他系统进程。在系统启动完成完成后,init将变为守护进程监视系统其他进程。Android是基于Linux的操作系统,所以init也是Android系统中用户空间的第一个进程,它的进程号是1。下面先简单的看一下init进程的启动过程。
@/kernel/goodfish/init/main.c
static int __init kernel_init(void * unused)
{
/*
* Wait until kthreadd is all set-up.
*/
wait_for_completion(&kthreadd_done);
/*
* init can allocate pages on any node
*/
set_mems_allowed(node_states[N_HIGH_MEMORY]);
/*
* init can run on any cpu.
*/
set_cpus_allowed_ptr(current, cpu_all_mask);
cad_pid = task_pid(current);
smp_prepare_cpus(setup_max_cpus);
do_pre_smp_initcalls();
lockup_detector_init();
smp_init();
sched_init_smp();
do_basic_setup();
/* Open the /dev/console on the rootfs, this should never fail */
if (sys_open((const char __user *) "/dev/console", O_RDWR, 0) < 0)
printk(KERN_WARNING "Warning: unable to open an initial console.\n");
(void) sys_dup(0);
(void) sys_dup(0);
/*
* check if there is an early userspace init. If yes, let it do all
* the work
*/
if (!ramdisk_execute_command)
ramdisk_execute_command = "/init";
if (sys_access((const char __user *) ramdisk_execute_command, 0) != 0) {
ramdisk_execute_command = NULL;
prepare_namespace();
}
/*
* Ok, we have completed the initial bootup, and
* we're essentially up and running. Get rid of the
* initmem segments and start the user-mode stuff..
*/
init_post();
return 0;
}/* This is a non __init function. Force it to be noinline otherwise gcc
* makes it inline to init() and it becomes part of init.text section
*/
static noinline int init_post(void)
{
/* need to finish all async __init code before freeing the memory */
async_synchronize_full();
free_initmem();
mark_rodata_ro();
system_state = SYSTEM_RUNNING;
numa_default_policy();
current->signal->flags |= SIGNAL_UNKILLABLE;
if (ramdisk_execute_command) {
run_init_process(ramdisk_execute_command);
printk(KERN_WARNING "Failed to execute %s\n",
ramdisk_execute_command);
}
/*
* We try each of these until one succeeds.
*
* The Bourne shell can be used instead of init if we are
* trying to recover a really broken machine.
*/
if (execute_command) {
run_init_process(execute_command);
printk(KERN_WARNING "Failed to execute %s. Attempting "
"defaults...\n", execute_command);
}
run_init_process("/sbin/init");
run_init_process("/etc/init");
run_init_process("/bin/init");
run_init_process("/bin/sh");
panic("No init found. Try passing init= option to kernel. "
"See Linux Documentation/init.txt for guidance.");
}static void run_init_process(const char *init_filename)
{
argv_init[0] = init_filename;
kernel_execve(init_filename, argv_init, envp_init);
}在init_post()中会判断execute_command是否为空,如果不为空则执行run_init_process调用。execute_command的赋值在init_setup()中,所以这里应该注意在设置内核启动选项时,应设置为“ init=/init”,以便正常启动init进程,因为编译完Android后生成的文件系统中,init位于最顶层目录。
<span style="font-size:14px;">static const char * argv_init[MAX_INIT_ARGS+2] = { "init", NULL, };</span>static int __init init_setup(char *str)
{
unsigned int i;
execute_command = str;
/*
* In case LILO is going to boot us with default command line,
* it prepends "auto" before the whole cmdline which makes
* the shell think it should execute a script with such name.
* So we ignore all arguments entered _before_ init=... [MJ]
*/
for (i = 1; i < MAX_INIT_ARGS; i++)
argv_init[i] = NULL;
return 1;
}
__setup("init=", init_setup);
了解了init进程的启动过程后,接下来看一下init进程都干了些什么?Android中的init进程与Linux不同,其职责可以归结如下:
- 作为守护进程
- 解析和执行init.rc文件
- 生成设备驱动节点
- 属性服务
init源码分析
init进程的入口函数是main,它的代码如下:
@/system/core/init/init.c
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd_count = 0;





 本文介绍了Android系统的init进程启动过程,从Linux内核启动到用户空间的init进程,讲解了init如何成为用户空间的第一个进程,其主要职责包括解析init.rc、生成设备驱动节点和属性服务。此外,还分析了main函数,包括启动ueventd进程和创建关键目录如/dev、/proc、/sys等。
本文介绍了Android系统的init进程启动过程,从Linux内核启动到用户空间的init进程,讲解了init如何成为用户空间的第一个进程,其主要职责包括解析init.rc、生成设备驱动节点和属性服务。此外,还分析了main函数,包括启动ueventd进程和创建关键目录如/dev、/proc、/sys等。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 4512
4512

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








