题目来自于:http://hihocoder.com/problemset/problem/1066
时间限制:20000ms
单点时限:1000ms
内存限制:256MB
描述
这天天气晴朗、阳光明媚、鸟语花香,空气中弥漫着春天的气息……额,说远了,总之,小Hi和小Ho决定趁着这朗朗春光出去玩。
但是刚刚离开居住的宾馆不久,抄近道不小心走入了一条偏僻小道的小Hi和小Ho就发现自己的前方走来了几个彪形大汉,定睛一看还都是地地道道的黑人兄弟!小Hi和小Ho这下就慌了神,捡肥皂事小,这一身百把来斤别一不小心葬身他乡可就没处说去了。
就在两人正举足无措之时,为首的黑叔叔从怀里掏出了一件东西——两张花花绿绿的纸,分别递给了小Hi和小Ho。
小Hi和小Ho接过来,只见上面写道(译为中文):“本地最大的帮派——青龙帮,诚邀您的加入!”下面还详细的列出了加入青龙帮的种种好处。
于是两人略感心安,在同黑叔叔们交谈一番之后,已是均感相见恨晚。同时,在小Hi和小Ho表示自己不日便将回国之后,黑叔叔们也没有再提加入帮派之事,但是那为首的黑叔叔思索一会,开口道(译为中文):“我现在有一个难题,思索了很久也没法子解决,既然你们俩都是高材生,不如来帮我看看。”
小Hi和小Ho点了点头表示没问题,于是黑叔叔继续说道:“这个问题是这样的,我们帮派最近混进了许多警察的卧底,但是在我们的调查过程中只能够知道诸如‘某人和另一个人是同阵营的’这样的信息,虽然没有办法知道他们具体是哪个阵营的,但是这样的信息也是很重要的,因为我们经常会想要知道某两个人究竟是不是同一阵营的。”
小Hi和小Ho赞同的点了点头,毕竟无间道也都是他们看过的。
黑叔叔接着说道:“于是现在问题就来了,我希望你们能写出这样一个程序,我会有两种操作,一种是告诉它哪两个人是同一阵营的,而另一种是询问某两个人是不是同一阵营的……既然你们就要回国了,不如现在就去我们帮派的总部写好这个程序再走把。”
为了生命安全与……小Hi和小Ho都不得不解决这个问题!那么他们究竟从何下手呢?
提示:说起来其实就是不断的合并集合嘛~
输入
每个测试点(输入文件)有且仅有一组测试数据。
每组测试数据的第1行为一个整数N,表示黑叔叔总共进行的操作次数。
每组测试数据的第2~N+1行,每行分别描述黑叔叔的一次操作,其中第i+1行为一个整数op_i和两个由大小写字母组成的字符串Name1_i, Name2_i,其中op_i只可能为0或1,当op_i=0时,表示黑叔叔判定Name1_i和Name2_i是同一阵营的,当op_i=1时,表示黑叔叔希望知道Name1_i和Name2_i是否为同一阵营的。
对于100%的数据,满足N<=10^5, 且数据中所有涉及的人物中不存在两个名字相同的人(即姓名唯一的确定了一个人),对于所有的i,满足Name1_i和Name2_i是不同的两个人。
输出
对于每组测试数据,对于黑叔叔每次op_i=1的操作,输出一行,表示查询的结果:如果根据已知信息(即这次操作之前的所有op_i=0的操作),可以判定询问中的两个人是同一阵营的,则输出yes,否则输出no。
样例输入
10
0 Steven David
0 Lcch Dzx
1 Lcch Dzx
1 David Dzx
0 Lcch David
0 Frank Dzx
1 Steven Dzx
1 Frank David
0 Steven Dzx
0 Dzx Frank
样例输出
yes
no
yes
yes
解法一:使用c++的set进行的求解
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<set<string>> vset;
int op;
string name1, name2;
int pos1,pos2;
for(int ye=0;ye<n;++ye)
{
pos1=pos2=-1;
cin>>op>>name1>>name2;
if(op==0)
{
for(int i=0;i<vset.size();++i)
{
if(vset[i].find(name1)!=vset[i].end())
pos1=i;
if(vset[i].find(name2)!=vset[i].end())
pos2=i;
}
if(pos1==pos2&&pos1==-1)//两个都不在集合当中
{
set<string> tmpSet;
tmpSet.insert(name1);
tmpSet.insert(name2);
vset.push_back(tmpSet);
}
else if(pos1==-1||pos2==-1)//有一个不在已知的集合中,插入已知的集合
{
if(pos1==-1)
vset[pos2].insert(name1);
else
vset[pos1].insert(name2);
}
else if(pos1!=pos2)//两个都在不同集合中
{
vset[pos1].insert(vset[pos2].begin(),vset[pos2].end());
vset.erase(vset.begin()+pos2);
}
}
else
{
bool flag=false;
for(int i=0;i<vset.size();++i)
{
if(vset[i].find(name1)!=vset[i].end()&&vset[i].find(name2)!=vset[i].end())
flag=true;
}
if(flag)
cout<<"yes\n";
else
cout<<"no\n";
}
}
}解法二采用map的并查集实现
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
void PutInMap(string& str,map<string,string>&father)
{
if(father.find(str)==father.end())
father.insert(make_pair(str,str));
return ;
}
string getfather(string&str,map<string,string>&father)
{
if(father[str]!=str)
father[str]=getfather(father[str],father);
return father[str];
}
void union_set(string &str1,string&str2,map<string,string>&father)
{
string f1=getfather(str1,father);
string f2=getfather(str2,father);
if(f2!=f1)
father[f1]=f2;
}
bool same(string &str1,string&str2,map<string,string>&father)
{
return getfather(str1,father)==getfather(str2,father);
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
int op;
map<string,string> father;
int curPos=0;
string name1, name2;
for(int ye=0;ye<n;++ye)
{
cin>>op>>name1>>name2;
PutInMap(name1,father);
PutInMap(name2,father);
if(op==0)
{
union_set(name1,name2,father);
}
else
{
if(same(name1,name2,father))
cout<<"yes\n";
else
cout<<"no\n";
}
}
}解法三采用unordered_map的并查集实现
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<map>
#include <tr1/unordered_map>
using namespace std;
void PutInMap(string& str,std::tr1::unordered_map<string,string>&father)
{
if(father.find(str)==father.end())
father.insert(make_pair(str,str));
return ;
}
string getfather(string&str,std::tr1::unordered_map<string,string>&father)
{
if(father[str]!=str)
father[str]=getfather(father[str],father);
return father[str];
}
void union_set(string &str1,string&str2,std::tr1::unordered_map<string,string>&father)
{
string f1=getfather(str1,father);
string f2=getfather(str2,father);
if(f2!=f1)
father[f1]=f2;
}
bool same(string &str1,string&str2,std::tr1::unordered_map<string,string>&father)
{
return getfather(str1,father)==getfather(str2,father);
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
int op;
std::tr1::unordered_map<string,string> father;
int curPos=0;
string name1, name2;
for(int ye=0;ye<n;++ye)
{
cin>>op>>name1>>name2;
PutInMap(name1,father);
PutInMap(name2,father);
if(op==0)
{
union_set(name1,name2,father);
}
else
{
if(same(name1,name2,father))
cout<<"yes\n";
else
cout<<"no\n";
}
}
}三种方法的时间对比
解法四采用rank合并的并查集方法
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<map>
#include <tr1/unordered_map>
using namespace std;
void PutInMap(string& str,std::tr1::unordered_map<string,string>&father,std::tr1::unordered_map<string,int> & rank)
{
if(father.find(str)==father.end())
{
father.insert(make_pair(str,str));
rank.insert(make_pair(str,0));
}
return ;
}
string getfather(string&str,std::tr1::unordered_map<string,string>&father)
{
if(father[str]!=str)
father[str]=getfather(father[str],father);
return father[str];
}
void union_set(string &str1,string&str2,std::tr1::unordered_map<string,string>&father,std::tr1::unordered_map<string,int> & rank)
{
string f1=getfather(str1,father);
string f2=getfather(str2,father);
if(f2==f1)
return;
if(rank[f1]>rank[f2])
father[f2]=f1;
else if(rank[f1]<rank[f2])
father[f1]=f2;
else
{
father[f1]=f2;
++rank[f2];
}
}
bool same(string &str1,string&str2,std::tr1::unordered_map<string,string>&father)
{
return getfather(str1,father)==getfather(str2,father);
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
int op;
std::tr1::unordered_map<string,string> father;
std::tr1::unordered_map<string,int> rank;
int curPos=0;
string name1, name2;
for(int ye=0;ye<n;++ye)
{
cin>>op>>name1>>name2;
PutInMap(name1,father,rank);
PutInMap(name2,father,rank);
if(op==0)
{
union_set(name1,name2,father,rank);
}
else
{
if(same(name1,name2,father))
cout<<"yes\n";
else
cout<<"no\n";
}
}
}耗时:










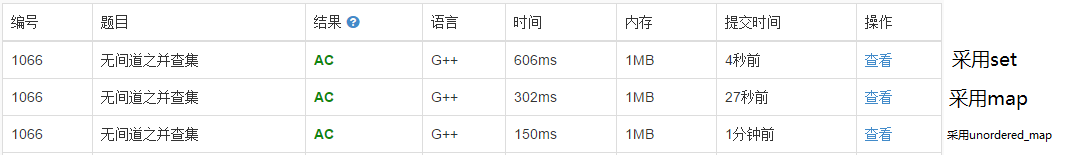















 1341
1341

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








