一、文件
1.什么是文件

2.文件流

3.常用的文件操作方法
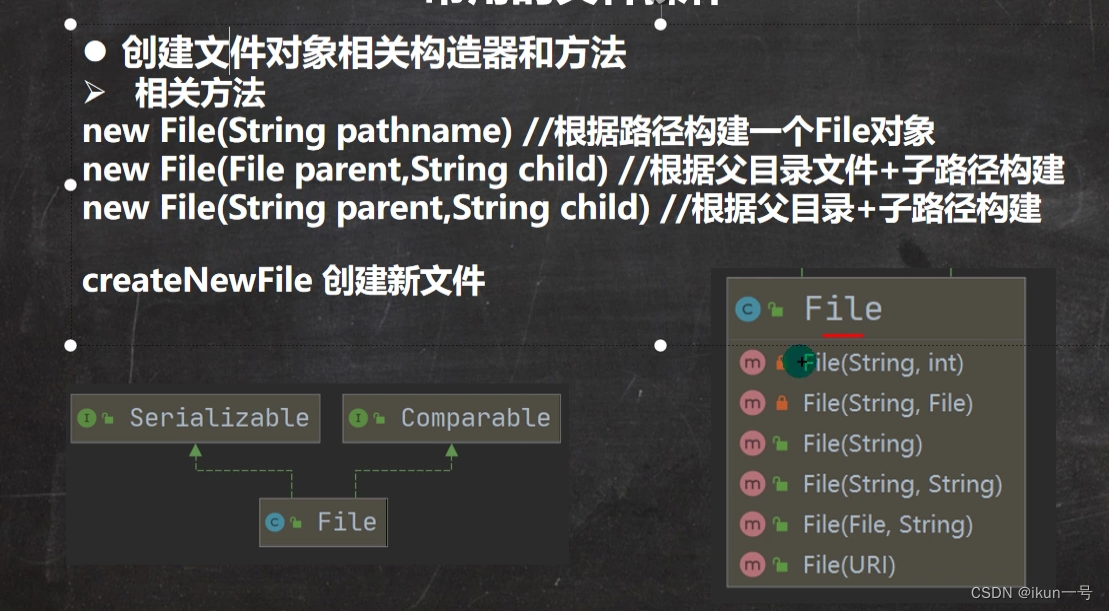
public class FileCreate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
//方式一 new File(String pathname)
@Test
public void creat01(){
String filePath = "d:\\news.txt";
File file = new File(filePath);
try {
file.createNewFile();//创建文件
System.out.println("创建成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
//方式二 new File(File parent ,String child) 根据父目录文件加子路径构建
public void creat02(){
File parentFile = new File("d:\\");
String child = "news2.txt";
File file = new File(parentFile, child);
try {
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
//方式三 new File(String parent,String child) 根据父目录加子路径创建
public void creat03(){
String parent="d:\\";
String child="news3.txt";
File file = new File(parent, child);
try {
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4.获取文件相关信息
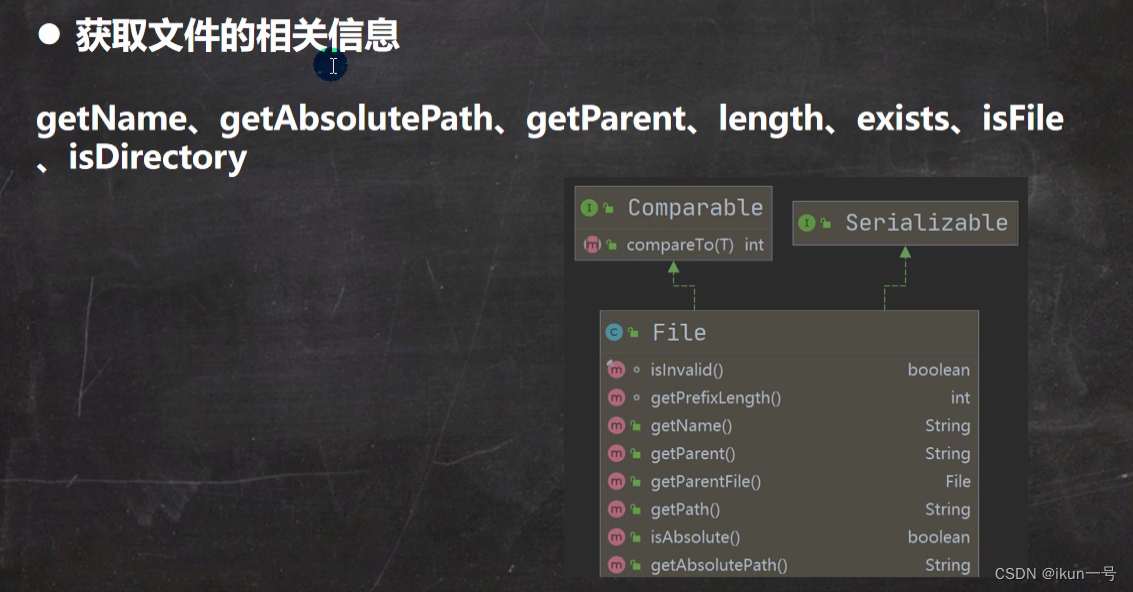
public class FileInformation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
//获取文件信息
@Test
public void info(){
//先创建文件
File file = new File("d:\\news.txt");
//调用相应方法来获取文件信息
System.out.println("===文件名字"+file.getName());
//获得绝对路径
System.out.println("===绝对路径"+file.getAbsolutePath());
//得到文件父级目录
System.out.println("===父级目录"+file.getParent());
//得到文件大小
System.out.println("===大小"+file.length());
//是否是一个文件
System.out.println("是否是一个文件"+file.isFile());
//是否是一个目录
System.out.println("是否是一个目录"+file.isDirectory());
}
}
5.目录的操作和文件删除

public class Directory_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//
}
//判断 d:\news.txt是否存在。如果存在就删除
@Test
public void m1(){
String filePath = "d:\\news.txt";
File file = new File(filePath);
if(file.exists()){//判断是否存在
if(file.delete()){//删除文件返回的是一个boolean值
System.out.println("已删除");
}
}else{
System.out.println("文件不存在");
}
}
//第二种是删除目录 d:\\demo02
@Test
public void m2(){
String filePath = "d:\\demo02";
File file = new File(filePath);
if(file.exists()){//判断是否存在
if(file.delete()){//删除文件返回的是一个boolean值
System.out.println("已删除");
}
}else{
System.out.println("目录不存在");
}
}
// 第三种是删除目录 d:\\demo\\a\\b\\c目录是否存在如果存在就提示存在否则就创建
@Test
public void m3(){
String filePath = "d:\\demo\\a\\b\\c";
File file = new File(filePath);
if(file.exists()){//判断是否存在
System.out.println("存在");
if(file.delete()){//删除文件返回的是一个boolean值
System.out.println("已删除");
}
}else{
System.out.println("目录不存在");
//创建目录
if(file.mkdirs()){//创建一级目录使用mkdir()
System.out.println("创建成功");
}
}
}
}
二、IO流原理及流的分类
1.IO流原理

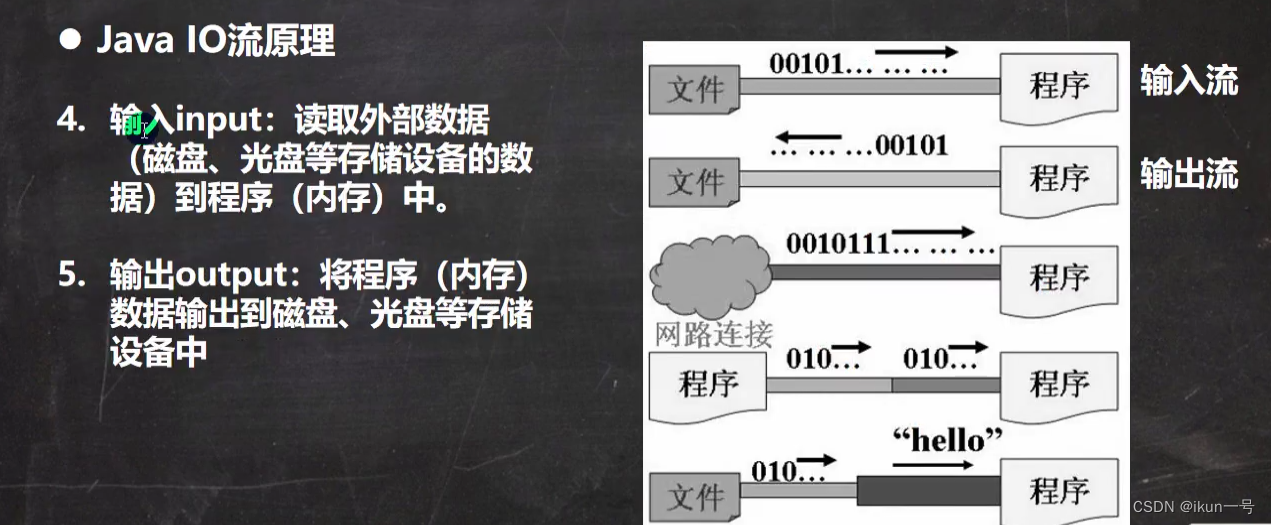
2.流的分类

三、IO流体系,常用的类
1.InputStream:字节输入流

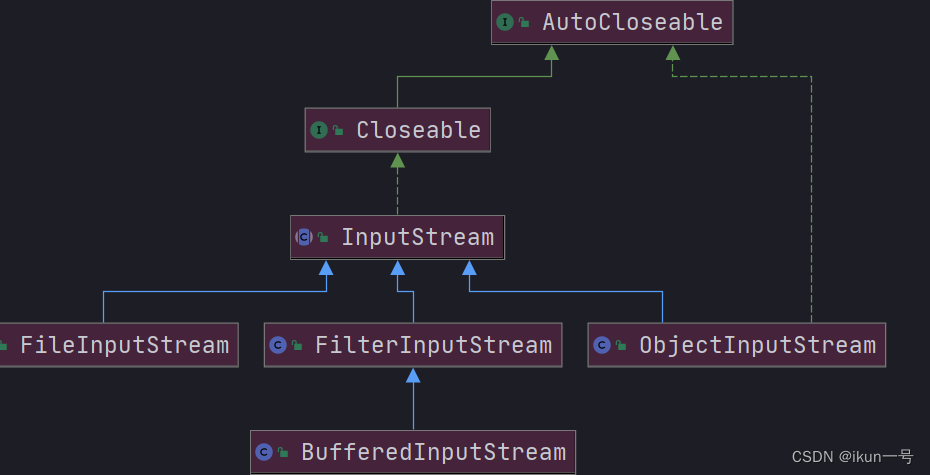
2.FileInputStream介绍
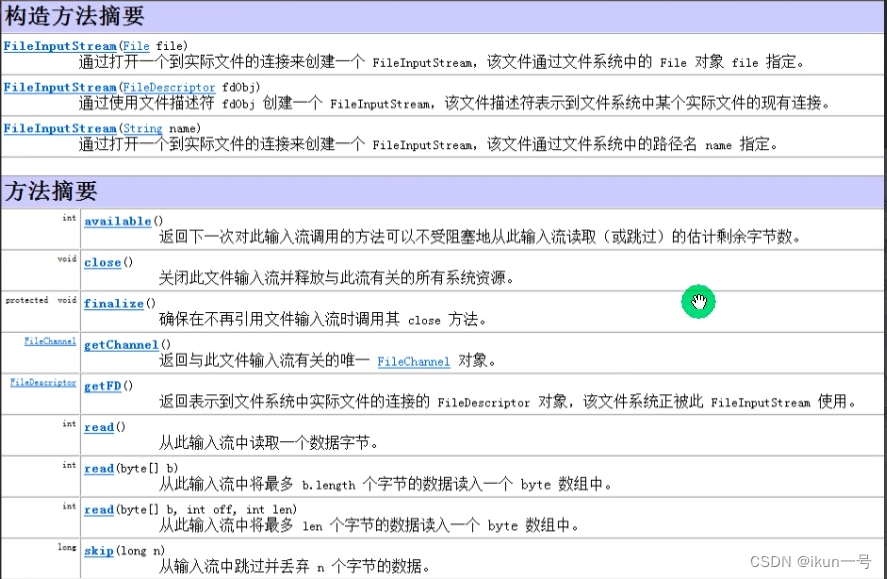
1.read()
注意这个方法因为是字节流读取的一个字节,如果想要读取汉字,而转成char类型就会出现乱码
单个字节读取效率较低
@Test
public void readFile01(){
//先定义字节输出流防止后面要finally关闭时不能使用
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
String fileread = "d:\\news.txt";
int readfile = 0;//为了存放内容
try {
//创建FileInputStream对象来读取
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(fileread);
//存放读取对象放入循环read()用来一个个读取
//读取到最后没有输入可用就返回-1
while( (readfile = fileInputStream.read()) != -1){
System.out.println((char)readfile);//因为是int类型所以读取时转成char
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileInputStream.close();//关闭流来释放空间
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.read(byte[] b)
相较于上面那个方法效率较高
@Test
public void readFile02(){
//先定义字节输出流防止后面要finally关闭时不能使用
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
String fileread = "d:\\news.txt";
byte[] buf = new byte[8];//创建一个数组来存放
int readlength = 0;//来存放数组长度
try {
//创建FileInputStream对象来读取
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(fileread);
//read(byte[] b)里面返回的是一个存放长度,没有就返回-1
while( (readlength=fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,readlength));//使用到String构造方法来输出
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileInputStream.close();//关闭流来释放空间
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3.FileOutputStream介绍
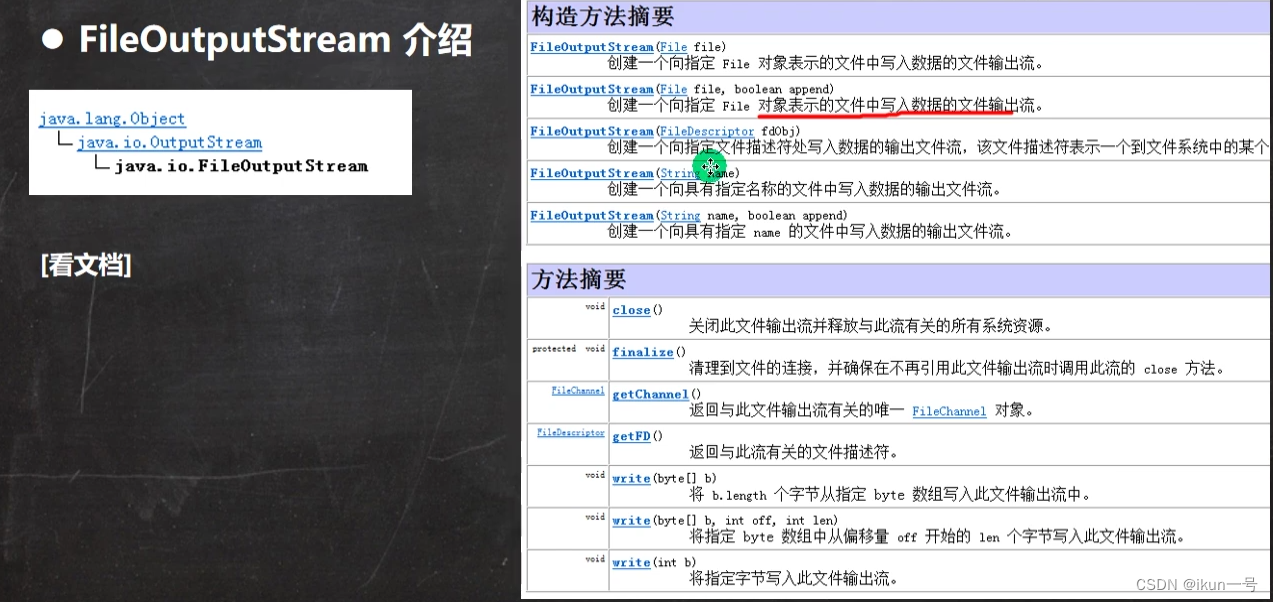
1.使用方法
@Test
//写入文件,如果没有则创建
public void writeFile(){
//先索引目录给String
String filePath = "d:\\a.txt";
//先定义FileOutputStream对象
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
//将对象FileOutputStream得到
try {
//在构造方法中可以在后面加入append的boolean值来确定是覆盖文件还是继续卸载后面
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath,true);
// fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath);
//然后写入内容
fileOutputStream.write('a');//只能写入一个数据
//第二种 write(byte[] b)
//写入字符串
String str = "sdjad";
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes());
//第三种 write(byte[] b, int off,int length)可以截取长度来输入
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(),0,3);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//记得关闭
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.拷贝文件
public class FileCopy01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
@Test
public void copy() {
//先定义拷贝对象地址和要拷贝到的地址
String srcPath = "d:\\upup.png";
String destPath = "d:\\upup2.png";
//定义输入流和输出流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
//因为是图片所以用数组效率更高
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int readlength = 0;// 判断长度
//将文件传入java程序中,用输入流
try {
//将位置传入流
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(srcPath);
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(destPath, true);
while ((readlength = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1) {//边读边写
fileOutputStream.write(buf, 0, readlength);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fileInputStream != null) {
fileInputStream.close();
}
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
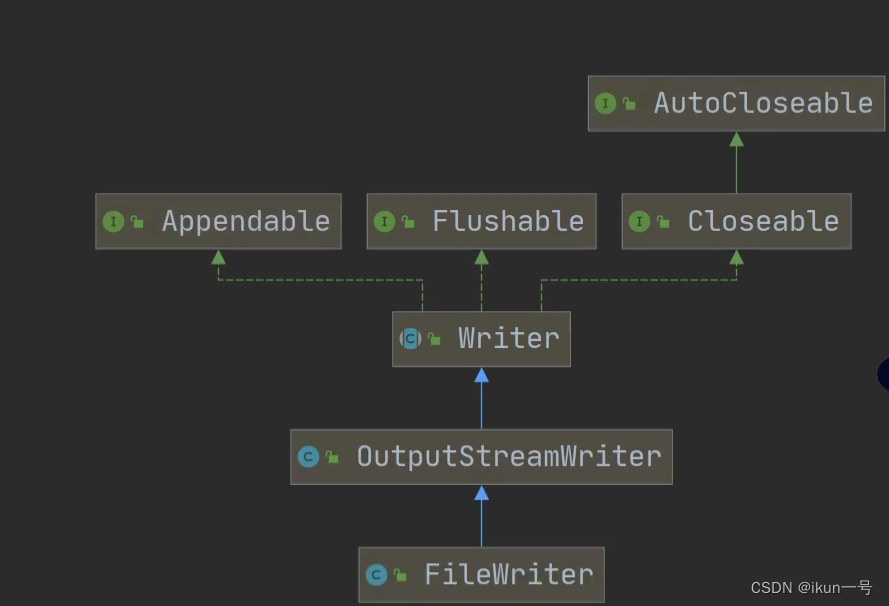
4.FileReader 和 FileWriter介绍

1.FileReader
public class FileReader01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
@Test
public void readFile(){
//先定义文件目录
String filePath = "d:\\news.txt";
//定义Reader
FileReader fileReader = null;
//定义获得读的内容
int readfile = 0;
//创建FileReader对象
try {
fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
//循环读文件
while ((readfile = fileReader.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)readfile);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(fileReader != null){
fileReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Test
public void readFile2(){
//先定义文件目录
String filePath = "d:\\news.txt";
//定义Reader
FileReader fileReader = null;
//定义长度接收
int readlength = 0;
//定义数组
char[] buf = new char[8];
//创建FileReader对象
try {
fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
//循环读文件
while ((readlength = fileReader.read(buf))!=-1){
System.out.print(new String(buf,0,readlength));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(fileReader != null){
fileReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.FileWriter

public class FileWriter_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
@Test
public void writerFile(){
//定义写入路径
String filePath = "d:\\note.txt";
//定义writer
FileWriter fileWriter = null;
//生成数组
char[] chars ={'a','b','c'};
try {
//生成对象
fileWriter = new FileWriter(filePath,true);
//write(int)写入单个字符
fileWriter.write('h');
//write(char[])写入指定数组
fileWriter.write(chars);
//write(char[],int off,int len )写入指定数组指定部分
fileWriter.write(chars,0,2);
//write(String )写入整个字符串
fileWriter.write("你好北京");
//write(String,int off,int len )写入字符串指定部分
fileWriter.write("你好北京",0, 2);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//对于FileWriter一定要关闭流或者flush才能真正把数据写入
if(fileWriter!=null){
fileWriter.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
四、字符处理流
1.基本介绍



2.BufferedReader和BufferedWriter
public class BufferedReader01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//定义文件目录
String filePath = "d:\\note.txt";
//定义每一行接受
String line = null;
//创建BufferedReader
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath));
//读取每一行效率更高,如果返回null表示没有可读取的字符
while((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(line);
}
bufferedReader.close();
}
}
public class BufferedWriter01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//定义写入路径
String filePath = "d:\\note.txt";
//创建BufferedWriter
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filePath,true));
bufferedWriter.write("hello,world");
//插入一个换行
bufferedWriter.newLine();
bufferedWriter.write("hello,world");
bufferedWriter.close();
}
}
3.BufferedCopy
public class BufferedCopy01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String srcPath = "d:\\upup.png";
String destPath = "d:\\upup3.png";
String line;
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(srcPath));
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(destPath));
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){
bufferedWriter.write(line);
}
bufferedReader.close();
bufferedWriter.close();
}
}
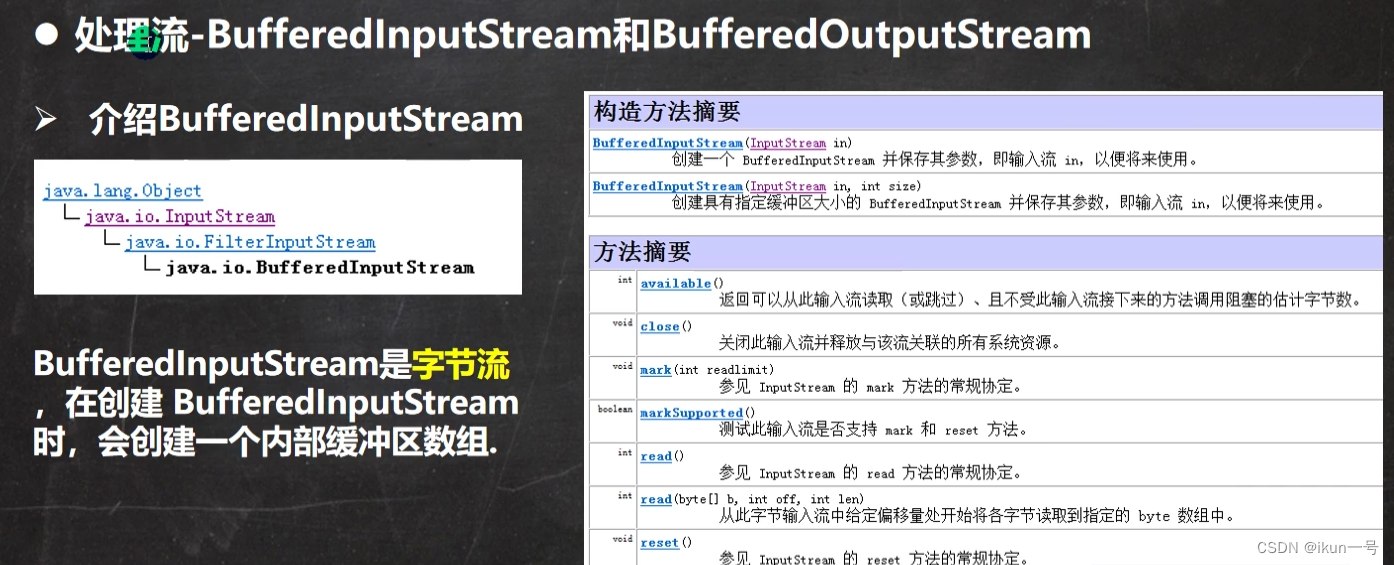
五、字节处理流
1.BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream
2.字节处理流的拷贝
public class BufferedCopy01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String srcPath = "d:\\upup.png";
String destPath = "d:\\upup3.png";
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcPath));
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destPath));
while ((len = bufferedInputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
bufferedOutputStream.write(bytes,0,len);
}
bufferedInputStream.close();
bufferedOutputStream.close();
}
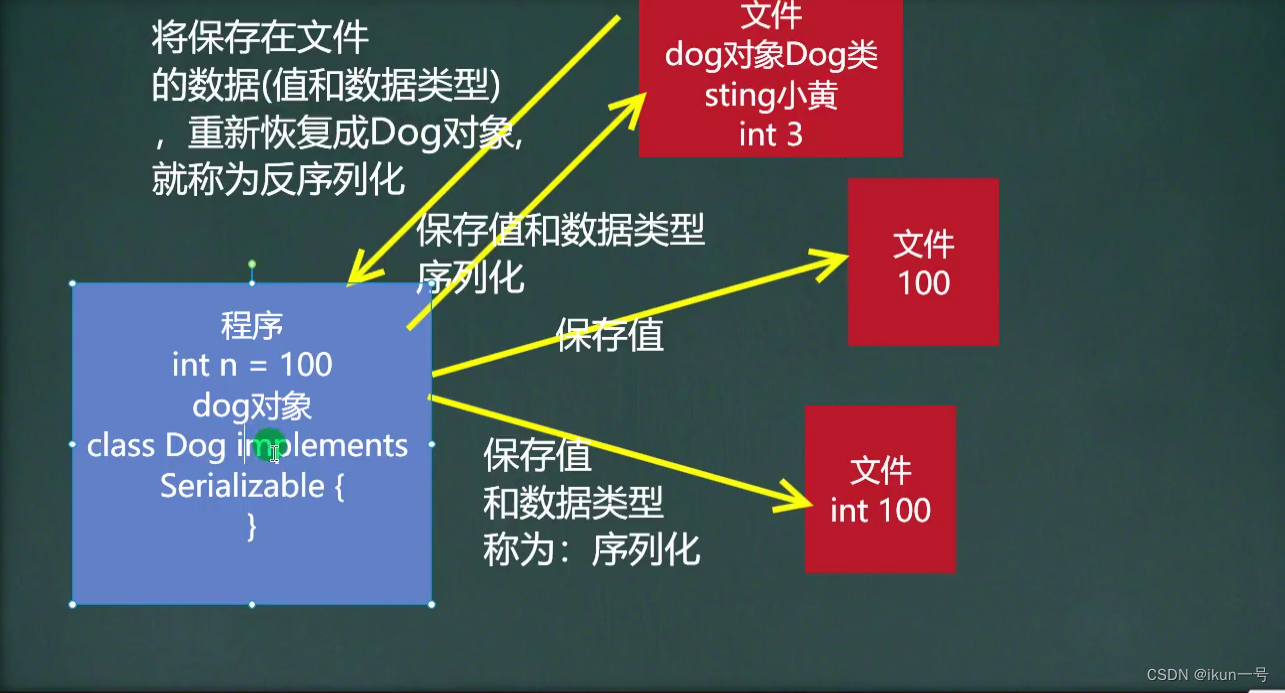
六、对象处理流
1.ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream


2.ObjectOutputStream
public class ObjectOutputStream01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//定义保存目录
String filePath = "d:\\data.dat";
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(filePath));
objectOutputStream.write(100);//int -> Integer (实现了serializable)
objectOutputStream.writeBoolean(true);//boolean ->Boolean
objectOutputStream.writeUTF("askldjklas");//String
objectOutputStream.writeObject(new Dog(12,"sd"));
objectOutputStream.close();
}
}
class Dog implements Serializable {
private int age;
private String name;
public Dog(int age, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
3.ObjectInputStream
public class ObjectInputStream01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//定义目录位置
String filePath = "d:\\data.dat";
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath));
System.out.println(objectInputStream.readInt());
System.out.println(objectInputStream.readBoolean());
System.out.println(objectInputStream.readUTF());
Object o = objectInputStream.readObject();
System.out.println(o);
Dog dog2 = (Dog)o;
System.out.println(dog2.toString());
objectInputStream.close();
}
4.细节说明

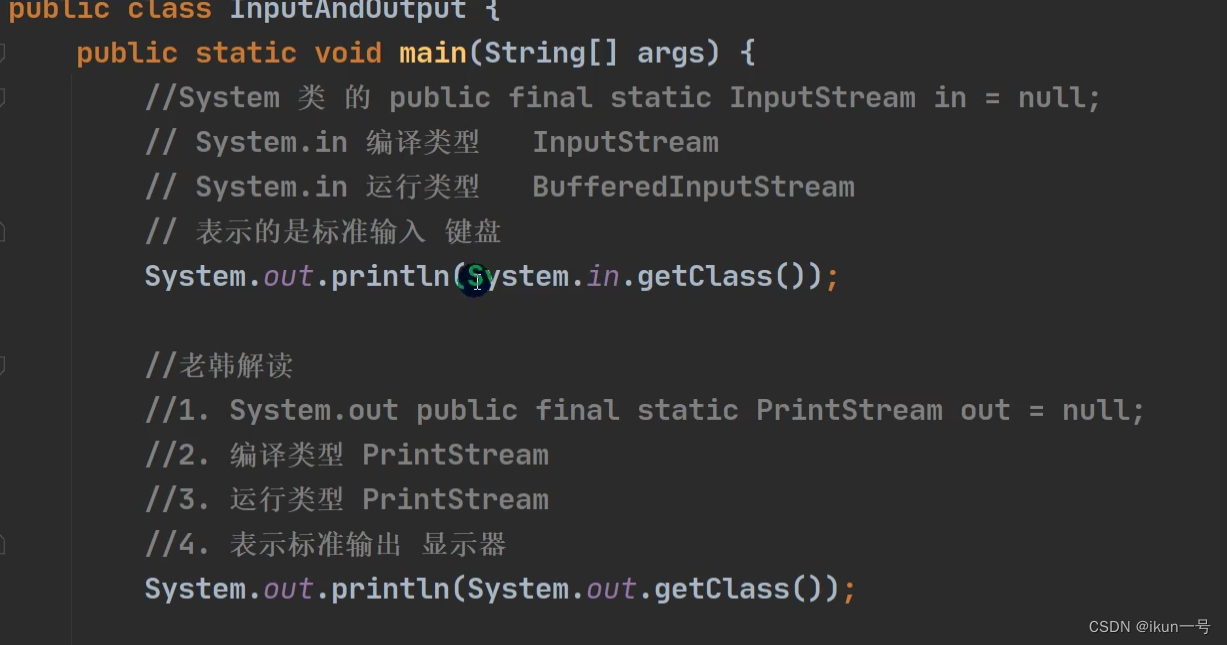
七、标准输入输出流
1.介绍

八、转换流
1.InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter

2.InputStreamReader
public class InputStreamReader01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String filePath = "d:\\news.txt";
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(filePath),"gbk");
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);
System.out.println(bufferedReader.readLine());
bufferedReader.close();
}
}
3.OutputStreamWriter
public class InputStreamReader01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String filePath = "d:\\news4.txt";
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(filePath),"gbk");
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(outputStreamWriter);
bufferedWriter.write("sd计算");
bufferedWriter.close();
}
}
九、打印流
打印流只有输出流没有输入流
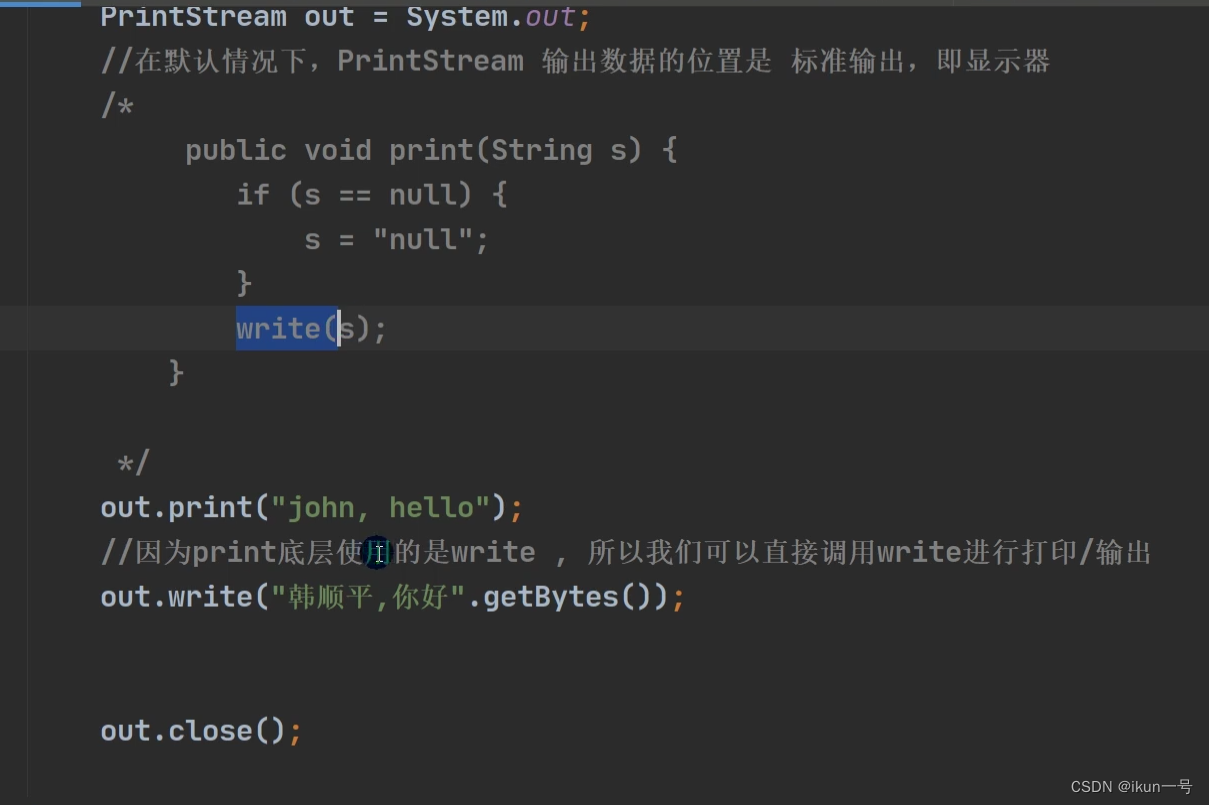
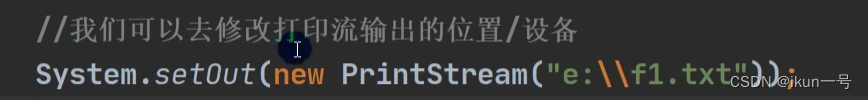
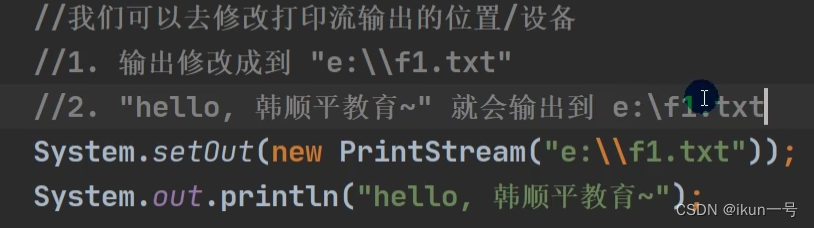
1.PrintStream
2.PrintWriter
十、properties类


public class Properties02 {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
//创建一个properties对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
//加载文件
properties.load(new FileReader("src\\mysql.properties"));
//
String ip = properties.getProperty("ip");
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
System.out.println(ip);
System.out.println(user);
}
}
public class Properties03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//创建对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
//创建
properties.setProperty("charset","utf8");
properties.setProperty("id","12345");
properties.setProperty("pwd","ae12");
//存入文件
properties.store(new FileWriter("src\\mysql2.properties"),null);
}
}






















 2296
2296











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










