先自我介绍一下,小编浙江大学毕业,去过华为、字节跳动等大厂,目前阿里P7
深知大多数程序员,想要提升技能,往往是自己摸索成长,但自己不成体系的自学效果低效又漫长,而且极易碰到天花板技术停滞不前!
因此收集整理了一份《2024年最新网络安全全套学习资料》,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助到想自学提升又不知道该从何学起的朋友。
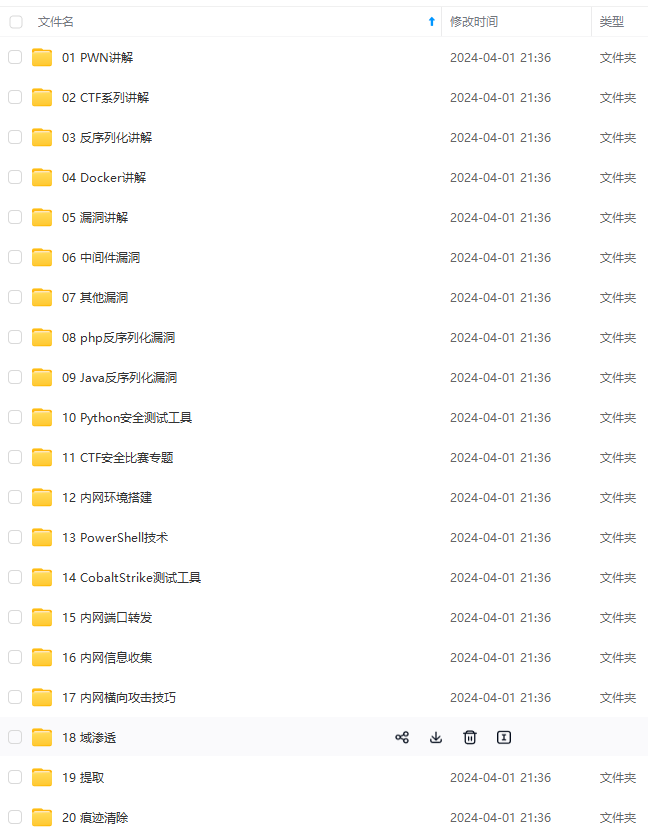
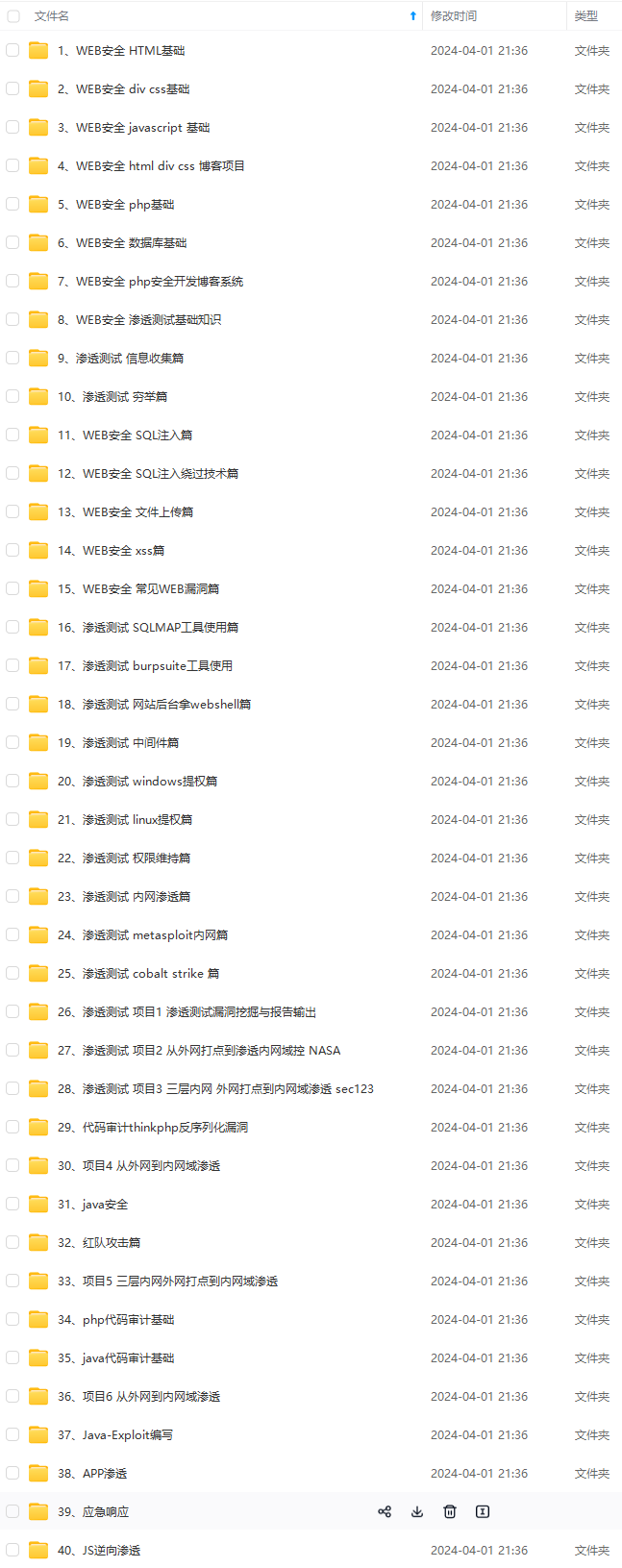
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上网络安全知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
如果你需要这些资料,可以添加V获取:vip204888 (备注网络安全)

正文
@Override
public Session findSession(String id) throws IOException {
if (id == null) {
return null;
}
return sessions.get(id);
}
创建好session后,需要进行随时的维护:我们看下tomcat是如何刷新访问时间的?可能比预想的简单,其仅是更新一个访问时间字段,再无其他。
// org.apache.catalina.session.StandardSession#access
/**
- Update the accessed time information for this session. This method
- should be called by the context when a request comes in for a particular
- session, even if the application does not reference it.
*/
@Override
public void access() {
// 更新访问时间
this.thisAccessedTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 访问次数统计,默认不启用
if (ACTIVITY_CHECK) {
accessCount.incrementAndGet();
}
}
最后,还需要看下 HttpSession 是如何被包装返回的?
// org.apache.catalina.session.StandardSession#getSession
/**
- Return the
HttpSessionfor which this object - is the facade.
*/
@Override
public HttpSession getSession() {
if (facade == null){
if (SecurityUtil.isPackageProtectionEnabled()){
final StandardSession fsession = this;
facade = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction(){
@Override
public StandardSessionFacade run(){
return new StandardSessionFacade(fsession);
}
});
} else {
// 直接使用 StandardSessionFacade 包装即可
facade = new StandardSessionFacade(this);
}
}
return (facade);
}
再最后,要说明的是,整个sessions的管理使用一个 ConcurrentHashMap 来存放全局会话信息,sessionId->session实例。
对于同一次http请求中,该session会被存储在当前的Request栈org.apache.catalina.connector.Request#session字段中,从而无需每次深入获取。每个请求进来后,会将session保存在当前的request信息中。
3. 过期session清理?
会话不可能不过期,不过期的也不叫会话了。
会话过期的触发时机主要有三个:1. 每次进行会话调用时,会主动有效性isValid()验证,此时如果发现过期可以主动清理: 2. 后台定时任务触发清理; 3. 启动或停止应用的时候清理;(这对于非内存式的存储会更有用些)
// case1. 请求时验证,如前面所述
// org.apache.catalina.connector.Request#doGetSession
protected Session doGetSession(boolean create) {
…
// Return the current session if it exists and is valid
if ((session != null) && !session.isValid()) {
session = null;
}
if (session != null) {
return (session);
}
…
}
// case2. 后台定时任务清理
// org.apache.catalina.session.ManagerBase#backgroundProcess
@Override
public void backgroundProcess() {
// 并非每次定时任务到达时都会进行清理,而是要根据其清理频率设置来运行
// 默认是 6
count = (count + 1) % processExpiresFrequency;
if (count == 0)
processExpires();
}
/**
- Invalidate all sessions that have expired.
*/
public void processExpires() {
long timeNow = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 找出所有的sessions, 转化为数组遍历
Session sessions[] = findSessions();
int expireHere = 0 ;
if(log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Start expire sessions " + getName() + " at " + timeNow + " sessioncount " + sessions.length);
for (int i = 0; i < sessions.length; i++) {
// 事实上后台任务也是调用 isValid() 方法 进行过期任务清理的
if (sessions[i]!=null && !sessions[i].isValid()) {
expireHere++;
}
}
long timeEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();
if(log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("End expire sessions " + getName() + " processingTime " + (timeEnd - timeNow) + " expired sessions: " + expireHere);
processingTime += ( timeEnd - timeNow );
}
//case3. start/stop 时触发过期清理(生命周期事件)
// org.apache.catalina.session.StandardManager#startInternal
/**
- Start this component and implement the requirements
- of {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
- @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error
- that prevents this component from being used
*/
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.startInternal();
// Load unloaded sessions, if any
try {
// doLoad() 调用
load();
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString(“standardManager.managerLoad”), t);
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
}
/**
- Load any currently active sessions that were previously unloaded
- to the appropriate persistence mechanism, if any. If persistence is not
- supported, this method returns without doing anything.
- @exception ClassNotFoundException if a serialized class cannot be
- found during the reload
- @exception IOException if an input/output error occurs
*/
protected void doLoad() throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(“Start: Loading persisted sessions”);
}
// Initialize our internal data structures
sessions.clear();
// Open an input stream to the specified pathname, if any
File file = file();
if (file == null) {
return;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString(“standardManager.loading”, pathname));
}
Loader loader = null;
ClassLoader classLoader = null;
Log logger = null;
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file.getAbsolutePath());
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis)) {
Context c = getContext();
loader = c.getLoader();
logger = c.getLogger();
if (loader != null) {
classLoader = loader.getClassLoader();
}
if (classLoader == null) {
classLoader = getClass().getClassLoader();
}
// Load the previously unloaded active sessions
synchronized (sessions) {
try (ObjectInputStream ois = new CustomObjectInputStream(bis, classLoader, logger,
getSessionAttributeValueClassNamePattern(),
getWarnOnSessionAttributeFilterFailure())) {
Integer count = (Integer) ois.readObject();
int n = count.intValue();
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(“Loading " + n + " persisted sessions”);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
StandardSession session = getNewSession();
session.readObjectData(ois);
session.setManager(this);
sessions.put(session.getIdInternal(), session);
session.activate();
if (!session.isValidInternal()) {
// If session is already invalid,
// expire session to prevent memory leak.
// 主动调用 expire
session.setValid(true);
session.expire();
}
sessionCounter++;
}
} finally {
// Delete the persistent storage file
if (file.exists()) {
file.delete();
}
}
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(“No persisted data file found”);
}
return;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(“Finish: Loading persisted sessions”);
}
}
// stopInternal() 事件到达时清理 sessions
/**
- Save any currently active sessions in the appropriate persistence
- mechanism, if any. If persistence is not supported, this method
- returns without doing anything.
- @exception IOException if an input/output error occurs
*/
protected void doUnload() throws IOException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(sm.getString(“standardManager.unloading.debug”));
if (sessions.isEmpty()) {
log.debug(sm.getString(“standardManager.unloading.nosessions”));
return; // nothing to do
}
// Open an output stream to the specified pathname, if any
File file = file();
if (file == null) {
return;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString(“standardManager.unloading”, pathname));
}
// Keep a note of sessions that are expired
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file.getAbsolutePath());
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos)) {
synchronized (sessions) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(“Unloading " + sessions.size() + " sessions”);
}
// Write the number of active sessions, followed by the details
oos.writeObject(Integer.valueOf(sessions.size()));
for (Session s : sessions.values()) {
StandardSession session = (StandardSession) s;
list.add(session);
session.passivate();
session.writeObjectData(oos);
}
}
}
// Expire all the sessions we just wrote
// 将所有session失效,实际上应用即将关闭,失不失效的应该也无所谓了
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(“Expiring " + list.size() + " persisted sessions”);
}
for (StandardSession session : list) {
try {
session.expire(false);
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
} finally {
session.recycle();
}
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(“Unloading complete”);
}
}
接下来我们看下具体如何清理过期的会话?实际应该就是一个remove的事。
// org.apache.catalina.session.StandardSession#isValid
/**
- Return the
isValidflag for this session.
*/
@Override
public boolean isValid() {
if (!this.isValid) {
return false;
}
if (this.expiring) {
return true;
}
if (ACTIVITY_CHECK && accessCount.get() > 0) {
return true;
}
// 超过有效期,主动触发清理
if (maxInactiveInterval > 0) {
int timeIdle = (int) (getIdleTimeInternal() / 1000L);
if (timeIdle >= maxInactiveInterval) {
expire(true);
}
}
return this.isValid;
}
// org.apache.catalina.session.StandardSession#expire(boolean)
/**
- Perform the internal processing required to invalidate this session,
- without triggering an exception if the session has already expired.
- @param notify Should we notify listeners about the demise of
- this session?
*/
public void expire(boolean notify) {
// Check to see if session has already been invalidated.
// Do not check expiring at this point as expire should not return until
// isValid is false
if (!isValid)
return;
// 上锁保证线程安全
synchronized (this) {
// Check again, now we are inside the sync so this code only runs once
// Double check locking - isValid needs to be volatile
// The check of expiring is to ensure that an infinite loop is not
// entered as per bug 56339
if (expiring || !isValid)
return;
if (manager == null)
return;
// Mark this session as “being expired”
expiring = true;
// Notify interested application event listeners
// FIXME - Assumes we call listeners in reverse order
Context context = manager.getContext();
// The call to expire() may not have been triggered by the webapp.
// Make sure the webapp’s class loader is set when calling the
// listeners
if (notify) {
ClassLoader oldContextClassLoader = null;
try {
oldContextClassLoader = context.bind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, null);
Object listeners[] = context.getApplicationLifecycleListeners();
if (listeners != null && listeners.length > 0) {
HttpSessionEvent event =
new HttpSessionEvent(getSession());
for (int i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++) {
int j = (listeners.length - 1) - i;
if (!(listeners[j] instanceof HttpSessionListener))
continue;
HttpSessionListener listener =
(HttpSessionListener) listeners[j];
try {
context.fireContainerEvent(“beforeSessionDestroyed”,
listener);
listener.sessionDestroyed(event);
context.fireContainerEvent(“afterSessionDestroyed”,
listener);
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
try {
context.fireContainerEvent(
“afterSessionDestroyed”, listener);
} catch (Exception e) {
// Ignore
}
manager.getContext().getLogger().error
(sm.getString(“standardSession.sessionEvent”), t);
}
}
}
} finally {
context.unbind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, oldContextClassLoader);
}
}
if (ACTIVITY_CHECK) {
accessCount.set(0);
}
// Remove this session from our manager’s active sessions
// 从ManagerBase 中删除
manager.remove(this, true);
// Notify interested session event listeners
if (notify) {
fireSessionEvent(Session.SESSION_DESTROYED_EVENT, null);
}
// Call the logout method
if (principal instanceof TomcatPrincipal) {
TomcatPrincipal gp = (TomcatPrincipal) principal;
try {
gp.logout();
} catch (Exception e) {
manager.getContext().getLogger().error(
sm.getString(“standardSession.logoutfail”),
e);
}
}
// We have completed expire of this session
setValid(false);
expiring = false;
// Unbind any objects associated with this session
String keys[] = keys();
ClassLoader oldContextClassLoader = null;
try {
oldContextClassLoader = context.bind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, null);
for (int i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
removeAttributeInternal(keys[i], notify);
}
} finally {
context.unbind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, oldContextClassLoader);
}
}
}
// org.apache.catalina.session.ManagerBase#remove(org.apache.catalina.Session, boolean)
@Override
public void remove(Session session, boolean update) {
// If the session has expired - as opposed to just being removed from
// the manager because it is being persisted - update the expired stats
if (update) {
long timeNow = System.currentTimeMillis();
int timeAlive =
(int) (timeNow - session.getCreationTimeInternal())/1000;
updateSessionMaxAliveTime(timeAlive);
expiredSessions.incrementAndGet();
SessionTiming timing = new SessionTiming(timeNow, timeAlive);
synchronized (sessionExpirationTiming) {
sessionExpirationTiming.add(timing);
sessionExpirationTiming.poll();
}
}
// 从sessions中移除session
if (session.getIdInternal() != null) {
sessions.remove(session.getIdInternal());
}
}
清理工作的核心任务没猜错,还是进行remove对应的session, 但作为框架必然会设置很多的扩展点,为各监听器接入的机会。这些点的设计,直接关系到整个功能的好坏了。
4. session如何保证线程安全?
实际是废话,前面已经明显看出,其使用一个 ConcurrentHashMap 作为session的管理容器,而ConcurrentHashMap本身就是线程安全的,自然也就保证了线程安全了。
不过需要注意的是,上面的线程安全是指的不同客户端间的数据是互不影响的。然而对于同一个客户端的重复请求,以上实现并未处理,即可能会生成一次session,也可能生成n次session,不过实际影响不大,因为客户端的状态与服务端的状态都是一致的。
5. 使用持久化方案的session管理实现
默认情况使用内存作为session管理工具,一是方便,二是速度相当快。但是最大的缺点是,其无法实现持久化,即可能停机后信息就丢失了(虽然上面有在停机时做了持久化操作,但仍然是不可靠的)。
所以就有了与之相对的存储方案了:Persistent,它有一个基类 PersistentManagerBase 继承了 ManagerBase,做了些特别的实现:
// 1. session的添加
// 复用 ManagerBase
// 2. session的查找
// org.apache.catalina.session.PersistentManagerBase#findSession
/**
- {@inheritDoc}
-
- This method checks the persistence store if persistence is enabled,
- otherwise just uses the functionality from ManagerBase.
*/
@Override
public Session findSession(String id) throws IOException {
// 复用ManagerBase, 获取Session实例
Session session = super.findSession(id);
// OK, at this point, we’re not sure if another thread is trying to
// remove the session or not so the only way around this is to lock it
// (or attempt to) and then try to get it by this session id again. If
// the other code ran swapOut, then we should get a null back during
// this run, and if not, we lock it out so we can access the session
// safely.
if(session != null) {
synchronized(session){
session = super.findSession(session.getIdInternal());
if(session != null){
// To keep any external calling code from messing up the
// concurrency.
session.access();
session.endAccess();
}
}
}
if (session != null)
return session;
// See if the Session is in the Store
// 如果内存中找不到会话信息,从存储中查找,这是主要的区别
session = swapIn(id);
return session;
}
// org.apache.catalina.session.PersistentManagerBase#swapIn
/**
- Look for a session in the Store and, if found, restore
- it in the Manager’s list of active sessions if appropriate.
- The session will be removed from the Store after swapping
- in, but will not be added to the active session list if it
- is invalid or past its expiration.
- @param id The id of the session that should be swapped in
- @return restored session, or {@code null}, if none is found
- @throws IOException an IO error occurred
*/
protected Session swapIn(String id) throws IOException {
if (store == null)
return null;
Object swapInLock = null;
/*
- The purpose of this sync and these locks is to make sure that a
- session is only loaded once. It doesn’t matter if the lock is removed
- and then another thread enters this method and tries to load the same
- session. That thread will re-create a swapIn lock for that session,
- quickly find that the session is already in sessions, use it and
- carry on.
*/
// 额,总之就是有点复杂
synchronized (this) {
swapInLock = sessionSwapInLocks.get(id);
if (swapInLock == null) {
swapInLock = new Object();
sessionSwapInLocks.put(id, swapInLock);
}
}
Session session = null;
synchronized (swapInLock) {
// First check to see if another thread has loaded the session into
// the manager
session = sessions.get(id);
if (session == null) {
Session currentSwapInSession = sessionToSwapIn.get();
try {
if (currentSwapInSession == null || !id.equals(currentSwapInSession.getId())) {
// 从存储中查找session
session = loadSessionFromStore(id);
sessionToSwapIn.set(session);
if (session != null && !session.isValid()) {
log.error(sm.getString(“persistentManager.swapInInvalid”, id));
session.expire();
removeSession(id);
session = null;
}
// 重新加入到内存 sessions 中
if (session != null) {
reactivateLoadedSession(id, session);
}
}
} finally {
sessionToSwapIn.remove();
}
}
}
// Make sure the lock is removed
synchronized (this) {
sessionSwapInLocks.remove(id);
}
return session;
}
private Session loadSessionFromStore(String id) throws IOException {
try {
if (SecurityUtil.isPackageProtectionEnabled()){
return securedStoreLoad(id);
} else {
// 依赖于store的实现了,比如 file, jdbc…
return store.load(id);
本人从事网路安全工作12年,曾在2个大厂工作过,安全服务、售后服务、售前、攻防比赛、安全讲师、销售经理等职位都做过,对这个行业了解比较全面。
最近遍览了各种网络安全类的文章,内容参差不齐,其中不伐有大佬倾力教学,也有各种不良机构浑水摸鱼,在收到几条私信,发现大家对一套完整的系统的网络安全从学习路线到学习资料,甚至是工具有着不小的需求。
最后,我将这部分内容融会贯通成了一套282G的网络安全资料包,所有类目条理清晰,知识点层层递进,需要的小伙伴可以点击下方小卡片领取哦!下面就开始进入正题,如何从一个萌新一步一步进入网络安全行业。
学习路线图
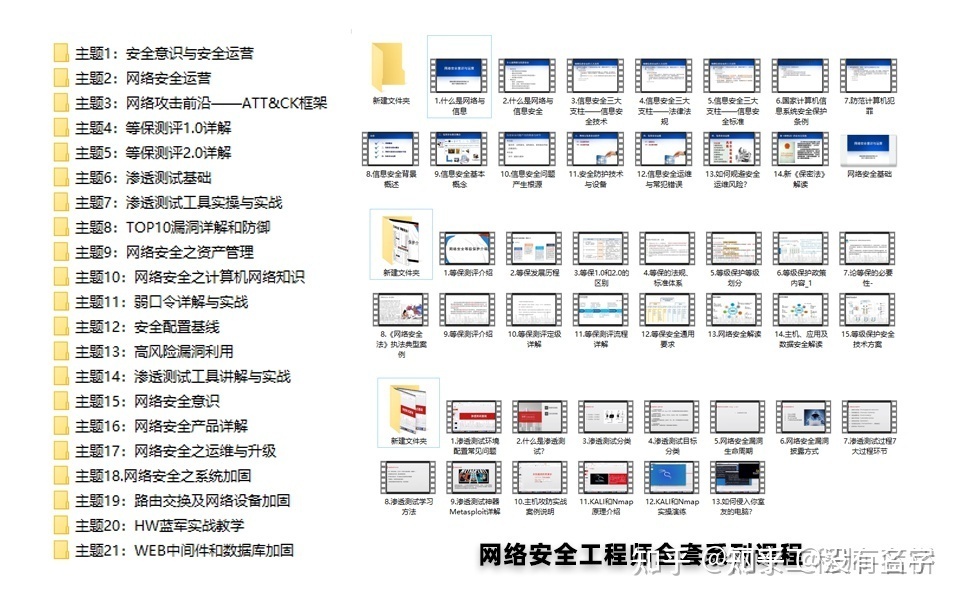
其中最为瞩目也是最为基础的就是网络安全学习路线图,这里我给大家分享一份打磨了3个月,已经更新到4.0版本的网络安全学习路线图。
相比起繁琐的文字,还是生动的视频教程更加适合零基础的同学们学习,这里也是整理了一份与上述学习路线一一对应的网络安全视频教程。
网络安全工具箱
当然,当你入门之后,仅仅是视频教程已经不能满足你的需求了,你肯定需要学习各种工具的使用以及大量的实战项目,这里也分享一份我自己整理的网络安全入门工具以及使用教程和实战。
项目实战
最后就是项目实战,这里带来的是SRC资料&HW资料,毕竟实战是检验真理的唯一标准嘛~

面试题
归根结底,我们的最终目的都是为了就业,所以这份结合了多位朋友的亲身经验打磨的面试题合集你绝对不能错过!
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以添加V获取:vip204888 (备注网络安全)

一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
网络安全工具箱
当然,当你入门之后,仅仅是视频教程已经不能满足你的需求了,你肯定需要学习各种工具的使用以及大量的实战项目,这里也分享一份我自己整理的网络安全入门工具以及使用教程和实战。

项目实战
最后就是项目实战,这里带来的是SRC资料&HW资料,毕竟实战是检验真理的唯一标准嘛~

面试题
归根结底,我们的最终目的都是为了就业,所以这份结合了多位朋友的亲身经验打磨的面试题合集你绝对不能错过!
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以添加V获取:vip204888 (备注网络安全)
[外链图片转存中…(img-R1yyk1Jg-1713410771797)]
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!





















 522
522











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








