为什么学习string类?
C语言中,字符串是以’\0’结尾的一些字符的集合,为了操作方便,C标准库中提供了一些str系列的库函数,但是这些库函数与字符串是分离开的,不太符合OOP的思想,而且底层空间需要用户自己管理,稍不留神可能还会越界访问。
标准库中的string类
重要构造
下面介绍几个重要的string构造:
(constructor)函数名称 功能说明
string() (重点) 构造空的string类对象,即空字符串
string(const char s) (重点) 用C-string来构造string类对象
string(size_t n, char c) string类对象中包含n个字符c
string(const string&s) (重点) 拷贝构造函数
看下面的代码立即代码功能:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>
void string1()
{
string s0;//构造空串
string s1("hello world");//用C语言字符串格式构造s1
string s2(s1);//拷贝构造s1
string s3(s1, 5, 3);//从目标字符串的第5个字符处开始拷贝3个字符
string s4(s1, 5, 10);//从目标字符串的第5个字符处开始拷贝10个字符,若目标字符串数量不够,那么拷贝完剩下的字符串结束
string s5(s1, 5);
cout << s0 << endl;
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s3 << endl;
cout << s4 << endl;
cout << s5 << endl;
}
int main()
{
string1();
return 0;
}
遍历字符串
方法一:for循环常规便利
void string2()
{
string s1 = "hello world";
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1[i] << " ";
}
}
以上这种遍历方式可以等效替代下面这种方式:
void string2()
{
string s1 = "hello world";
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout<<s1.operator[](i)<<" ";
}
}
第二种便利方式:使用迭代器
void string2()
{
string s1 = "hello world";
string::iterator it1 = s1.begin();//si.begin()表示字符串首元素
while (it1 != s1.end())//s1.end()表示字符串最后一个元素的下一个元素
{
cout << *it1 << " ";
++it1;
}
cout << endl;
}
当然我们之前学习的auto关键字也可以遍历这个数组:
void string2()
{
string s1 = "hello world";
for (auto e : s1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
这里的auto关键字的底层是迭代器的使用。
迭代器也可以让我们实现反向遍历字符串:
void test_string1()
{
string s1 = "hello world";
string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin();
while (rit != s1.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
rit++;
}
}
int main()
{
test_string1();
return 0;
}
这里画图解析:
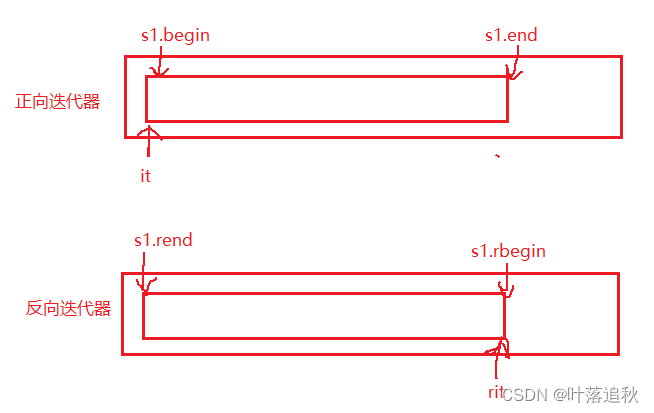
下面介绍另一种迭代器:const修饰的迭代器,下面看代码:
void test_string1()
{
string s1 = "hello world";
string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin();
while (rit != s1.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
rit++;
}
cout << endl;
const string s2 = "hello world";
string::const_iterator it = s2.begin();
while (it != s2.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
}
这里没有const修饰会报错:

报错:

当然这里也有反向的const修饰的迭代器。
整体来说,迭代器分为两类:
一类是没有const修饰的,一类是const修饰的;
功能也分为两种,一种是正向遍历,一种是反向遍历。
string类对象的容量操作
size和length
这两个操作功能实质上是一样的,都是返回字符串的有效长度,下面我们先看代码:
void test_string2()
{
string s1 = "hello world";
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.length() << endl;
}
结果:

capacity
作用:返回空间总大小。 下面看代码:
void test_string2()
{
string s1 = "hello world";
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.length() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
}

通过这个操作我们可以了解一下当前编译器(VS)的扩容机制,下面看代码:
void test_string2()
{
//查看扩容机制
string s;
size_t sz = s.capacity();
cout << "capacity changed:" << sz << '\n';
cout << "making s grow:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
s.push_back('c');
if (sz != s.capacity())
{
sz = s.capacity();
cout << "capacity changed:" << sz << '\n';
}
}
}
下面我们看运行结果:

clear
作用:清楚有效字符
下面看代码:
void test_string2()
{
string s1 = "hello world";
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
s1.clear();
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
}

reserve
作用:为字符串预留空间
场景一:预留空间大于原有空间:
这里原有的空间大小为15,我们这里利用reverse手动进行扩容,空间大小发生改变。
场景二:原有空间大于预留空间;

原有空间大于预留空间,这里编译器并没有将该空间缩小,还是保留的原有的空间。
resize
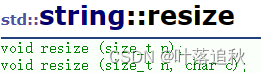
作用:将有效字符的个数该成n个,多出的空间用字符c填充
以上有两个重载函数,功能类似的,下面我们来看:
void test_string4()
{
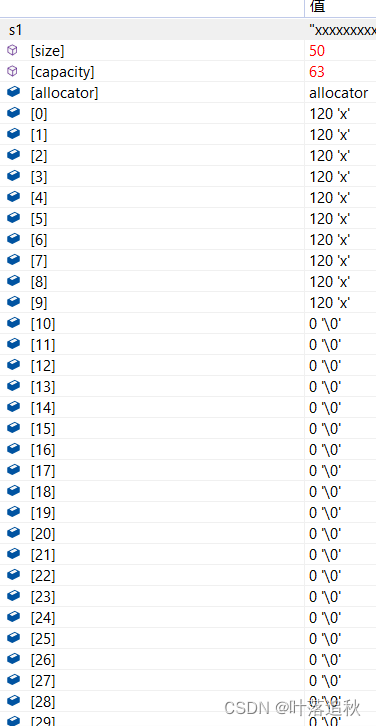
string s1("xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx");
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl << endl;
s1.resize(10);
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl << endl;
s1.resize(30);
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl << endl;
s1.resize(50);
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl << endl;
}

我们通过调试发现,插入的是字符 ‘\0’ ;
string类对象的访问及遍历操作
operator[]
void test_string5()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1[6] << endl;
}

string类对象的修改操作
operator+=
在字符串后追加一个字符串str
void test_string6()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1 << endl;
s1 += "xxxxxx";
cout << s1 << endl;
string s2 = "abcdefg";
s1 += s2;
cout << s1 << endl;
}
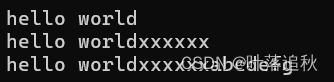
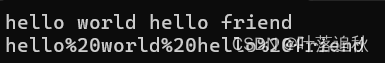
replace + find
void test_string7()
{
string s("hello world hello friend");
cout << s << endl;
size_t pos = s.find(' ');
while (pos != string::npos)
{
s.replace(pos, 1, "%20");
pos = s.find(' ');
}
cout << s << endl;
}
这里类似的操作还有 insert 和 erase ,该操作需要挪动数据,能不用就不用。
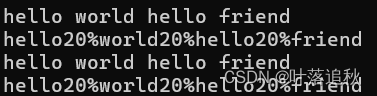
上面的操作还有一种方便一点的写法:
void test_string8()
{
string s1("hello world hello friend");
cout << s1 << endl;
string s2;
s2.reserve(s1.size());
for (auto ch : s1)
{
if (ch != ' ')
{
s2 += ch;
}
else
{
s2 += "20%";
}
}
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.swap(s2);
cout << s1 << endl;
}
find+substr


void test_string1()
{
string s1("file.cpp");
//拿到文件后缀
size_t pos1 = s1.find('.');
if (pos1 != string::npos)
{
string suffix = s1.substr(pos1);
//string suffix = s1.substr(pos1, s1.size() - pos1);
cout << suffix << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没有后缀" << endl;
}
}

输出字符串的一部分:
void test_string2()
{
string url1("https://cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/substr/");
string protocol, domain, uri;
size_t i1 = url1.find(':');
if (i1 != string::npos)
{
protocol = url1.substr(0, i1 - 0);
cout << protocol << endl;
}
}

查找字符串
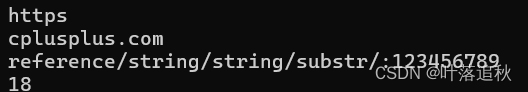
void test_string2()
{
string url1("https://cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/substr/:123456789");
string protocol, domain, uri;
size_t i1 = url1.find(':');
if (i1 != string::npos)
{
protocol = url1.substr(0, i1 - 0);
cout << protocol << endl;
}
//strchar
size_t i2 = url1.find('/', i1 + 3);
if (i2 != string::npos)
{
domain = url1.substr(i1 + 3, i2 - (i1 + 3));
cout << domain << endl;
uri = url1.substr(i2 + 1);
cout << uri << endl;
}
//查找特定字符/字符串的地址
size_t i3 = url1.find("com");
cout << i3 << endl;
}






















 31万+
31万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








