原文转载自
https://blog.csdn.net/luzhouyue1024/article/details/129317402
首先需要搭建Kafka broker集群(本次实验搭建3台,伪集群单机部署3台),然后在Spring容器中启动生产者、消费者,与borker集群交互。
搭建zookeeper集群
首先,启动Kafka需要安装Zookeeper.
在官网下载Kafka对应的zookeeper版本,本Demo采用Zookeeper 3.7.1和kafka 2.13,解压缩后找到bin/目录,返回上层目录,将父目录改名为zookeeper1,并创建两个子目录data和log
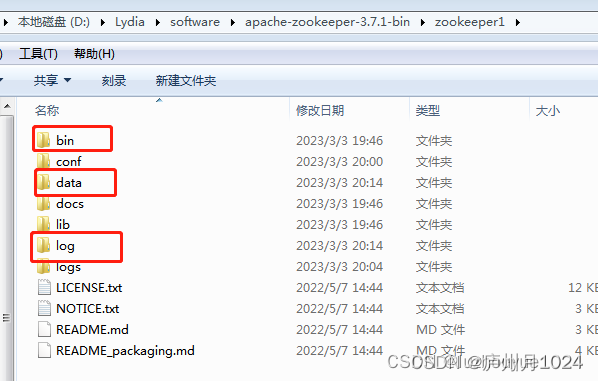
在conf/创建一个文件zoo.cfg,内容如下
tickTime=2000
initLimit=10
syncLimit=5
clientPort=2181
dataDir=D:/Lydia/software/apache-zookeeper-3.7.1-bin/zookeeper1/data
dataLogDir=D:/Lydia/software/apache-zookeeper-3.7.1-bin/zookeeper1/log
server.1=localhost:2888:3888
server.2=localhost:2889:3889
在data/目录创建文件myid,文件内容为1, 代表当前zookeeper节点的id值。
复制一份上面zookeeper1文件,修改文件夹名为zookeeper2,重复以上操作,并且修改clientPort=2182,并将data/myid设置为2
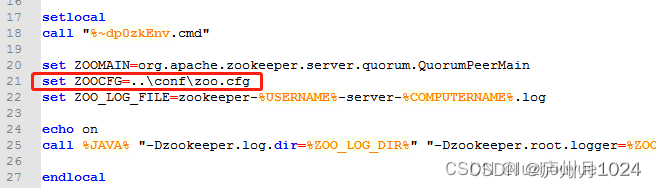
在两个zookeeper文件夹bin目录下修改zkServer.cmd
添加set ZOOCFG=..\conf\zoo.cfg,最终如下所示
依次启动zookeeper1和zookeeper2目录下的bin/zkServer.cmd,看到启动成功。
搭建Kafka
1.下载Kafka 2.13
2.解压到本地文件夹,同理,模拟两个kafka的broker,分别创建子目录kafka_2.13_1和kafka_2.13_2
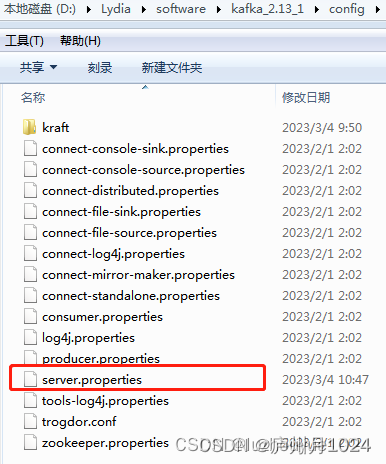
3.修改kafka_2.13_1文件夹config下的server.properties文件
主要是borker.id=1
port=9092
listners=PLAINTEXT://:9092
zookeeper.connect=localhost:2181,localhost:2182(Zookeeper刚刚用到的clientPort端口号)
broker.id=1
port=9092
listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9092
num.network.threads=3
num.io.threads=8
socket.send.buffer.bytes=102400
socket.receive.buffer.bytes=102400
socket.request.max.bytes=104857600
log.dirs=/tmp/kafka-logs
num.partitions=1
num.recovery.threads.per.data.dir=1
offsets.topic.replication.factor=1
transaction.state.log.replication.factor=1
transaction.state.log.min.isr=1
log.retention.hours=168
log.retention.check.interval.ms=300000
zookeeper.connect=localhost:2181,localhost:2182
zookeeper.connection.timeout.ms=18000
group.initial.rebalance.delay.ms=0
同理,修改kafka_2.13_2文件夹config下的server.properties文件
主要修改项是
borker.id=2
port=9093
listners=PLAINTEXT://:9093
zookeeper.connect=localhost:2181,localhost:2182
4.启动kafka1和kafka2文件夹下的bin/windows/kafka-server-start.bat,分别在两个cmd窗口启动两个broker,本Demo认为有两个borker组成集群。
SpringBoot整合Kakfa
感谢开源社区已经有了spring-kafka项目,可以方便地在Spring容器中启动和使用Kafka生产者和消费者线程。
引入依赖
打开IntelliJ, 创建一个maven工程,并引入该开源项目的maven依赖包,如下
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>创建单-生产者,双消费者Demo
生产者使用RestController建立web映射,并把收到的请求内容,通过KafkaTemplate发送给Kafka brokers.
消费者利用@KafkaListener(id = "consumer-group-id", topics = "topic-id")申明自己,代表在哪个消费者Group中,对什么topic感兴趣,如下:
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class KafkaDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(KafkaDemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate<Object, Object> kafkaTemplate;
@GetMapping("/send/{input}")
public void receiveAndSendToKafka(@PathVariable String input) {
//生产者,把收到的消息用KafkaTemplate发出去
//
this.kafkaTemplate.send("topic_hello", input);
}
@KafkaListener(id = "rest1", topics = "topic_hello")
public void listen1(String input) {
log.info("Kafka Consumer1 gets value: {}", input);
}
@KafkaListener(id = "rest2", topics = "topic_hello")
public void listen2(String input) {
log.info("Kafka Consumer2 gets value: {}", input);
}
}启动SpringBoot,然后在浏览器输入测试地址 http://localhost:8090/send/hululu,然后在控制台看到消费者收到消息:
INFO 25184 --- [ rest2-0-C-1] com.lydia.KafkaDemoApplication : Kafka Consumer2 gets value: hululu
INFO 25184 --- [ rest1-0-C-1] com.lydia.KafkaDemoApplication : Kafka Consumer1 gets value: hululu创建Topic的Demo
Kafka为了实现高可用性,对每个topic都有一个副本数量,如果某一个单点挂了,可以立刻使用其他的副本作为Leader来收发消息。
同时,每一个topic还可以分区,比如一个topic分了5个区,那么可以有5个消费者来分别监听5个区,每个消费者只会收到其中一个区的消息,那么100条消息,分到了5个区,平均只有20条消息由每个消费者接收,提高了并行度。
使用 KafkaClient 自带的 AdminClient创建消息
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class CreateTopicDemo {
@Autowired
private KafkaProperties properties;
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate<Object, Object> kafkaTemplate;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CreateTopicDemo.class, args);
}
@GetMapping("/create/{topic}/{numPartitions}")
public void createTopic(@PathVariable String topic, @PathVariable int numPartitions) {
AdminClient client = AdminClient.create(properties.buildAdminProperties());
if(client !=null){
try {
Collection<NewTopic> topics = new LinkedList<>();
short replications = 2;
log.info("Receives topic value={}, numPartition={}", topic, numPartitions);
//创建topic,含有topic名称,分区数,副本数
topics.add(new NewTopic(topic ,numPartitions,replications));
client.createTopics(topics);
}catch (Throwable e){
e.printStackTrace();
log.error("Create topic occurs with error {}", e.getCause());
}finally {
client.close();
}
}
}
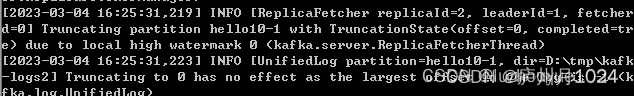
}测试创建消息: 浏览器输入http://localhost:8090/create/hello10/2, 代表想创建topic=hello10,分区数为2的主题。在Kafka服务器日志上看到类似日志,代表创建成功:
两种生产者获取Callback的方式
方法一
重写callback
测试地址http://localhost:8090/send/callback1/test1
/**
* 生产者Callback1
*/
@GetMapping("/send/callback1/{input}")
public void sendWithCallbackOne(@PathVariable String input) {
//生产者,把收到的消息用KafkaTemplate发出去
log.info("从Rest服务接收到内容:{}, 将发往topic_hello...", input);
//发到topic_hello上
this.kafkaTemplate.send("topic_hello", input).addCallback(new ListenableFutureCallback<SendResult<Object, Object>>() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable throwable) {
log.error("发送失败,{}", throwable);
log.error("发送失败,cause={}", throwable.getCause());
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(SendResult<Object, Object> objectObjectSendResult) {
log.info("Callback1发送成功:{}", objectObjectSendResult.toString());
}
});
}方法二
获取future
测试地址http://localhost:8090/send/callback2/test2
将获取如下结果:[nio-8090-exec-1] c.l.callback.KafkaProducerCallbackDemo : Callback2发送成功:SendResult [producerRecord=ProducerRecord(topic=topic_hello, partition=null, headers=RecordHeaders(headers = [], isReadOnly = true), key=null, value=test, timestamp=null), recordMetadata=topic_hello-0@13]
/**
* 生产者Callback2
*/
@GetMapping("/send/callback2/{input}")
public void sendWithCallbackTwo(@PathVariable String input) {
//生产者,把收到的消息用KafkaTemplate发出去
log.info("从Rest服务接收到内容:{}, 将发往topic_hello...", input);
//发到topic_hello上
this.kafkaTemplate.send("topic_hello", input);
ListenableFuture<SendResult<Object,Object>> future = this.kafkaTemplate.send("topic_hello", input);
try {
SendResult<Object,Object> result = future.get();
log.info("Callback2发送成功:{}", result.toString());
}catch (Throwable throwable){
log.error("发送失败,{}", throwable);
log.error("发送失败,cause={}", throwable.getCause());
}
}ReplyingKafkaTemplate
ReplyingKafkaTemplate extends KafkaTemplate,方法 sendAndReceive实现了消息回复语义,也就是说,生产者发送消息后获得一个Future, future.get能得到消费者返回的消息
JavaConfig类:
@Configuration
public class ReplayingConfig {
@Bean
public ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer<String, String> repliesContainer(ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<String, String> containerFactory) {
ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer<String, String> repliesContainer = containerFactory.createContainer("replies");
repliesContainer.getContainerProperties().setGroupId("repliesGroup");
repliesContainer.setAutoStartup(false);
return repliesContainer;
}
@Bean
public ReplyingKafkaTemplate<String, String, String> replyingTemplate(ProducerFactory<String, String> pf, ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer<String, String> repliesContainer) {
return new ReplyingKafkaTemplate(pf, repliesContainer);
}
@Bean
public KafkaTemplate kafkaTemplate(ProducerFactory<String, String> pf) {
return new KafkaTemplate(pf);
}
}启动类:
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class ReplyingKafkaTemplateDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ReplyingKafkaTemplateDemo.class, args);
}
@Autowired
private ReplyingKafkaTemplate replyingTemplate;
@GetMapping("/send/{input}")
@Transactional(rollbackFor = RuntimeException.class)
public void sendWithReplayFuture(@PathVariable String input) throws Exception {
ProducerRecord<String, String> record = new ProducerRecord<>("topic-testReplayTemplate", input);
RequestReplyFuture<String, String, String> replyFuture = replyingTemplate.sendAndReceive(record);
ConsumerRecord<String, String> consumerRecord = replyFuture.get();
log.info("获取消费者反馈: " + consumerRecord.value());
}
@KafkaListener(id = "webGroup", topics = "topic-testReplayTemplate")
@SendTo
public String consumer(String input) {
log.info("消费者收到消息: {}", input);
return "successful";
}
}测试输入http://localhost:8090/send/hello,可以看到Console打印了消费者反馈的“successful”消息
[ webGroup-0-C-1] c.l.replaying.ReplyingKafkaTemplateDemo : 消费者收到消息: hello
[ad | producer-1] org.apache.kafka.clients.Metadata : [Producer clientId=producer-1] Resetting the last seen epoch of partition replies-0 to 0 since the associated topicId changed from null to jt5w2qjBSlmBtpk9n3VDvw
[nio-8090-exec-4] c.l.replaying.ReplyingKafkaTemplateDemo : 获取消费者反馈: successful消费者确认Ack-消费成功Acknowledgment
有两个地方会用到ack确认机制,producer生产者, consumer消费者。这里演示消费者ack功能。
1.producer发送消息到指定topic的ack确认(确认kafka成功收到消息)
2.consumer从topic中消费消息,并提交ack确认。默认情况是自动ack,因此手动Ack功能需要关闭自动提交,然后设置消费者的ack模式=manual,设置属性文件加入spring.kafka.listener.ack-mode=manual
#Tomcat rest
server.port=8090
#Kafka brokers
spring.kafka.producer.bootstrap-servers=127.0.0.1:9092,127.0.0.1:9093
spring.kafka.bootstrap-servers=127.0.0.1:9092,127.0.0.1:9093
spring.kafka.consumer.enable-auto-commit=false
spring.kafka.listener.ack-mode=manual在消费Consumer端,对 @KafkaListener 的入参列表加入 Acknowledgment 即可,程序里面写 ack.acknowledge () ,运行到这行,代表向Kafka集群提交了偏移量,也就是消息被“消费”掉了.
使用Ack 手动提交偏移量时,假如 consumer 挂了重启,那它将从 committed offset 位置开始重新消费,而不是 consume offset 位置。
/**
* 消费者,当收到hulu这个消息时发送ack确认消费成功
*/
@KafkaListener(id = "ack_group", topics = "topic_ack_test")
public String ackConsumer(String input, Acknowledgment ack) {
log.info("消费者收到消息: {}", input);
if ("hulu".equals(input)) {
ack.acknowledge();
return "successful";
}
return "fail";
}Kafka死信队列
识别和处理错误对于任何可靠的数据流管道都是必不可少的。Kafka使用死信队列代表了错误流的存放位置和后续处理点。
死信队列的 Topic 的规则是,业务 Topic 名字 +“.DLT”。
如果业务命名为 “topic-hulu”,那么对应的死信队列的 Topic 就是 “topic-hulu.DLT”
可以设置消费者,为某个特定topic监听它的死信队列,也就是错误队列。
Git Repo
本Demo有Git地址,欢迎一览 https://github.com/LuzhouyueLee/Kafka_SpringBoot_Demo




















 2646
2646











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








