说明:当前kafka的版本为2.8.11,Spring Boot的版本为2.7.6。
第一步:在pom.xml中引入下述依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
<version>2.8.11</version>
</dependency>第二步:在yml配置文件进行如下配置
spring:
kafka:
# kafka服务的地址
bootstrap-servers: 127.0.0.1:9092
producer:
# key-value序列化
key-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
value-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
consumer:
# 设置默认的消费者所属组id
group-id: 0
# key-value反序列化
key-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
value-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer第三步:创建生产者
package com.example.demo.kafka;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
import org.springframework.kafka.support.SendResult;
import org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFuture;
import org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFutureCallback;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("kafka")
public class KafkaProducer {
// 自定义topic
public static final String TOPIC_NAME="topic.one";
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate;
@RequestMapping("send")
public String send(@RequestParam("msg")String msg) {
log.info("准备发送消息为:{}",msg);
// 1.发送消息
ListenableFuture<SendResult<String,String>> future=kafkaTemplate.send(TOPIC_NAME,msg);
future.addCallback(new ListenableFutureCallback<SendResult<String, String>>() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable throwable) {
// 2.发送失败的处理
log.error("生产者 发送消息失败:"+throwable.getMessage());
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(SendResult<String, String> stringObjectSendResult) {
// 3.发送成功的处理
log.info("生产者 发送消息成功:"+stringObjectSendResult.toString());
}
});
return "接口调用成功";
}
}注意:当kafka中没有名为topic.one的主题时程序会自动创建,其实这里的主题就相当于rabbitmq中的队列。
第四步:创建消费者
package com.example.demo.kafka;
import java.util.Optional;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecord;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.KafkaListener;
import org.springframework.kafka.support.KafkaHeaders;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Header;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class KafkaConsumer {
// 自定义topic
public static final String TOPIC_NAME="topic.one";
@KafkaListener(topics = TOPIC_NAME, groupId = "ONE")
public void topic_one(ConsumerRecord<?, ?> record, @Header(KafkaHeaders.RECEIVED_TOPIC) String topic) {
Optional message = Optional.ofNullable(record.value());
if (message.isPresent()) {
Object msg = message.get();
log.info("消费者One消费了: +++++++++++++++ Topic:" + topic + ",Record:" + record + ",Message:" + msg);
}
}
@KafkaListener(topics = TOPIC_NAME, groupId = "TWO")
public void topic_two(ConsumerRecord<?, ?> record, @Header(KafkaHeaders.RECEIVED_TOPIC) String topic) {
Optional message = Optional.ofNullable(record.value());
if (message.isPresent()) {
Object msg = message.get();
log.info("消费者TwO消费了: +++++++++++++++ Topic:" + topic + ",Record:" + record + ",Message:" + msg);
}
}
}第五步:启动项目,在postman中访问请求下述接口
http://127.0.0.1:8080/kafka/send?msg=测试数据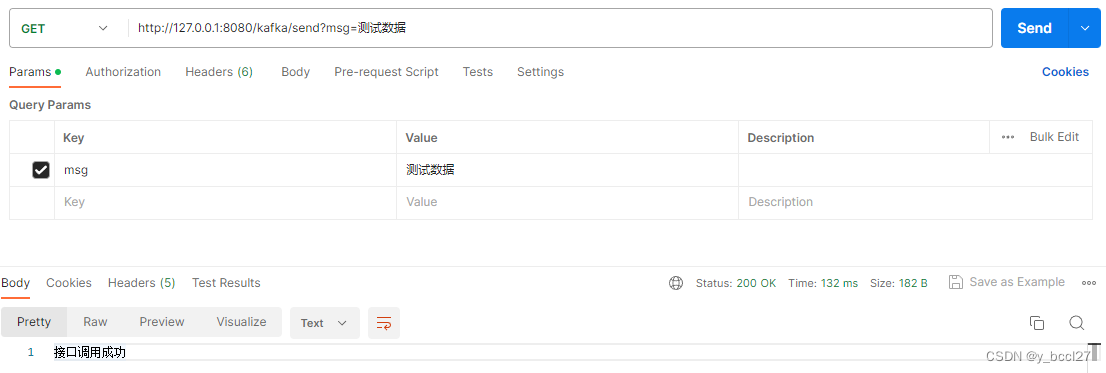
项目启动后首次调用该接口控制台会输出如下日志:
2023-05-31 22:09:50.935 INFO 20036 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring DispatcherServlet 'dispatcherServlet'
2023-05-31 22:09:50.935 INFO 20036 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Initializing Servlet 'dispatcherServlet'
2023-05-31 22:09:50.936 INFO 20036 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Completed initialization in 1 ms
2023-05-31 22:09:50.963 INFO 20036 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] com.example.demo.kafka.KafkaProducer : 准备发送消息为:测试数据
2023-05-31 22:09:50.966 INFO 20036 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.a.k.clients.producer.ProducerConfig : ProducerConfig values:
acks = -1
batch.size = 16384
bootstrap.servers = [127.0.0.1:9092]
buffer.memory = 33554432
client.dns.lookup = use_all_dns_ips
client.id = producer-1
compression.type = none
connections.max.idle.ms = 540000
delivery.timeout.ms = 120000
enable.idempotence = true
interceptor.classes = []
key.serializer = class org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
linger.ms = 0
max.block.ms = 60000
max.in.flight.requests.per.connection = 5
max.request.size = 1048576
metadata.max.age.ms = 300000
metadata.max.idle.ms = 300000
metric.reporters = []
metrics.num.samples = 2
metrics.recording.level = INFO
metrics.sample.window.ms = 30000
partitioner.class = class org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.DefaultPartitioner
receive.buffer.bytes = 32768
reconnect.backoff.max.ms = 1000
reconnect.backoff.ms = 50
request.timeout.ms = 30000
retries = 2147483647
retry.backoff.ms = 100
sasl.client.callback.handler.class = null
sasl.jaas.config = null
sasl.kerberos.kinit.cmd = /usr/bin/kinit
sasl.kerberos.min.time.before.relogin = 60000
sasl.kerberos.service.name = null
sasl.kerberos.ticket.renew.jitter = 0.05
sasl.kerberos.ticket.renew.window.factor = 0.8
sasl.login.callback.handler.class = null
sasl.login.class = null
sasl.login.connect.timeout.ms = null
sasl.login.read.timeout.ms = null
sasl.login.refresh.buffer.seconds = 300
sasl.login.refresh.min.period.seconds = 60
sasl.login.refresh.window.factor = 0.8
sasl.login.refresh.window.jitter = 0.05
sasl.login.retry.backoff.max.ms = 10000
sasl.login.retry.backoff.ms = 100
sasl.mechanism = GSSAPI
sasl.oauthbearer.clock.skew.seconds = 30
sasl.oauthbearer.expected.audience = null
sasl.oauthbearer.expected.issuer = null
sasl.oauthbearer.jwks.endpoint.refresh.ms = 3600000
sasl.oauthbearer.jwks.endpoint.retry.backoff.max.ms = 10000
sasl.oauthbearer.jwks.endpoint.retry.backoff.ms = 100
sasl.oauthbearer.jwks.endpoint.url = null
sasl.oauthbearer.scope.claim.name = scope
sasl.oauthbearer.sub.claim.name = sub
sasl.oauthbearer.token.endpoint.url = null
security.protocol = PLAINTEXT
security.providers = null
send.buffer.bytes = 131072
socket.connection.setup.timeout.max.ms = 30000
socket.connection.setup.timeout.ms = 10000
ssl.cipher.suites = null
ssl.enabled.protocols = [TLSv1.2]
ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm = https
ssl.engine.factory.class = null
ssl.key.password = null
ssl.keymanager.algorithm = SunX509
ssl.keystore.certificate.chain = null
ssl.keystore.key = null
ssl.keystore.location = null
ssl.keystore.password = null
ssl.keystore.type = JKS
ssl.protocol = TLSv1.2
ssl.provider = null
ssl.secure.random.implementation = null
ssl.trustmanager.algorithm = PKIX
ssl.truststore.certificates = null
ssl.truststore.location = null
ssl.truststore.password = null
ssl.truststore.type = JKS
transaction.timeout.ms = 60000
transactional.id = null
value.serializer = class org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
2023-05-31 22:09:50.973 INFO 20036 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.a.k.clients.producer.KafkaProducer : [Producer clientId=producer-1] Instantiated an idempotent producer.
2023-05-31 22:09:50.982 INFO 20036 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.a.kafka.common.utils.AppInfoParser : Kafka version: 3.1.2
2023-05-31 22:09:50.982 INFO 20036 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.a.kafka.common.utils.AppInfoParser : Kafka commitId: f8c67dc3ae0a3265
2023-05-31 22:09:50.982 INFO 20036 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.a.kafka.common.utils.AppInfoParser : Kafka startTimeMs: 1685542190982
2023-05-31 22:09:50.991 INFO 20036 --- [ad | producer-1] org.apache.kafka.clients.Metadata : [Producer clientId=producer-1] Resetting the last seen epoch of partition topic.one-0 to 0 since the associated topicId changed from null to A8Lfh0GZQ3GR6fUo-OvcAQ
2023-05-31 22:09:50.991 INFO 20036 --- [ad | producer-1] org.apache.kafka.clients.Metadata : [Producer clientId=producer-1] Cluster ID: 0YMM4442QOyhnWsg0zfjig
2023-05-31 22:09:50.992 INFO 20036 --- [ad | producer-1] o.a.k.c.p.internals.TransactionManager : [Producer clientId=producer-1] ProducerId set to 4 with epoch 0
2023-05-31 22:09:51.020 INFO 20036 --- [ad | producer-1] com.example.demo.kafka.KafkaProducer : 生产者 发送消息成功:SendResult [producerRecord=ProducerRecord(topic=topic.one, partition=null, headers=RecordHeaders(headers = [], isReadOnly = true), key=null, value=测试数据, timestamp=null), recordMetadata=topic.one-0@7]
2023-05-31 22:09:51.025 INFO 20036 --- [ntainer#1-0-C-1] com.example.demo.kafka.KafkaConsumer : 消费者TwO消费了: +++++++++++++++ Topic:topic.one,Record:ConsumerRecord(topic = topic.one, partition = 0, leaderEpoch = 0, offset = 7, CreateTime = 1685542190992, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size = 12, headers = RecordHeaders(headers = [], isReadOnly = false), key = null, value = 测试数据),Message:测试数据
2023-05-31 22:09:51.025 INFO 20036 --- [ntainer#0-0-C-1] com.example.demo.kafka.KafkaConsumer : 消费者One消费了: +++++++++++++++ Topic:topic.one,Record:ConsumerRecord(topic = topic.one, partition = 0, leaderEpoch = 0, offset = 7, CreateTime = 1685542190992, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size = 12, headers = RecordHeaders(headers = [], isReadOnly = false), key = null, value = 测试数据),Message:测试数据
第二次调用该接口,其输出日志则比较简洁:
2023-05-31 22:11:13.130 INFO 20036 --- [nio-8080-exec-3] com.example.demo.kafka.KafkaProducer : 准备发送消息为:测试数据
2023-05-31 22:11:13.135 INFO 20036 --- [ad | producer-1] com.example.demo.kafka.KafkaProducer : 生产者 发送消息成功:SendResult [producerRecord=ProducerRecord(topic=topic.one, partition=null, headers=RecordHeaders(headers = [], isReadOnly = true), key=null, value=测试数据, timestamp=null), recordMetadata=topic.one-0@8]
2023-05-31 22:11:13.144 INFO 20036 --- [ntainer#0-0-C-1] com.example.demo.kafka.KafkaConsumer : 消费者One消费了: +++++++++++++++ Topic:topic.one,Record:ConsumerRecord(topic = topic.one, partition = 0, leaderEpoch = 0, offset = 8, CreateTime = 1685542273130, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size = 12, headers = RecordHeaders(headers = [], isReadOnly = false), key = null, value = 测试数据),Message:测试数据
2023-05-31 22:11:13.144 INFO 20036 --- [ntainer#1-0-C-1] com.example.demo.kafka.KafkaConsumer : 消费者TwO消费了: +++++++++++++++ Topic:topic.one,Record:ConsumerRecord(topic = topic.one, partition = 0, leaderEpoch = 0, offset = 8, CreateTime = 1685542273130, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size = 12, headers = RecordHeaders(headers = [], isReadOnly = false), key = null, value = 测试数据),Message:测试数据
如上面代码所示,程序创建了两个消息消费者,每个消费者都监听来自主题topic_one的消息,唯一不同的是两个消费者分别属于不同的组别,即groupId设置不同。由此可见一条消息分别被两个不同的消费者消费,由此达到了广播的效果。
如果不需要每个消费者都读取到重复的消息该如何配置?
答案:采用相同消费组唯一消费模式
package com.example.demo.kafka;
import java.util.Optional;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecord;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.KafkaListener;
import org.springframework.kafka.support.KafkaHeaders;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Header;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class KafkaConsumer {
// 自定义topic
public static final String TOPIC_NAME="topic.one";
@KafkaListener(topics = TOPIC_NAME, groupId = "ONE")
public void topic_one(ConsumerRecord<?, ?> record, @Header(KafkaHeaders.RECEIVED_TOPIC) String topic) {
Optional message = Optional.ofNullable(record.value());
if (message.isPresent()) {
Object msg = message.get();
log.info("消费者One消费了: +++++++++++++++ Topic:" + topic + ",Record:" + record + ",Message:" + msg);
}
}
@KafkaListener(topics = TOPIC_NAME, groupId = "ONE")
public void topic_two(ConsumerRecord<?, ?> record, @Header(KafkaHeaders.RECEIVED_TOPIC) String topic) {
Optional message = Optional.ofNullable(record.value());
if (message.isPresent()) {
Object msg = message.get();
log.info("消费者TwO消费了: +++++++++++++++ Topic:" + topic + ",Record:" + record + ",Message:" + msg);
}
}
}上述代码与前段代码唯一的区别在于,两个消费者的组别设置成了一样的。再次调用上述接口,查看程序日志如下:
2023-05-31 22:19:31.953 INFO 17084 --- [nio-8080-exec-5] com.example.demo.kafka.KafkaProducer : 准备发送消息为:测试数据
2023-05-31 22:19:31.956 INFO 17084 --- [ad | producer-1] com.example.demo.kafka.KafkaProducer : 生产者 发送消息成功:SendResult [producerRecord=ProducerRecord(topic=topic.one, partition=null, headers=RecordHeaders(headers = [], isReadOnly = true), key=null, value=测试数据, timestamp=null), recordMetadata=topic.one-0@11]
2023-05-31 22:19:31.957 INFO 17084 --- [ntainer#0-0-C-1] com.example.demo.kafka.KafkaConsumer : 消费者One消费了: +++++++++++++++ Topic:topic.one,Record:ConsumerRecord(topic = topic.one, partition = 0, leaderEpoch = 0, offset = 11, CreateTime = 1685542771953, serialized key size = -1, serialized value size = 12, headers = RecordHeaders(headers = [], isReadOnly = false), key = null, value = 测试数据),Message:测试数据
从日志可以看出无论访问多少次,只会有一个消费者消费了消息,因此达到了不重复消费的目的。





















 2618
2618











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








