Object类
介绍:
○ Object类是所有Java类的祖先(根基类),每个类都使用 Object 作为超类(父类),所有对象(包括数组)都继承实现这个类的方法。
new int[10].hashCode(); //数组也继承Object类○ 如果在类的声明中未使用extends关键字指明其基类,则默认基类为Object类
○ public class Person {...} 等价于: public class Person extends Object {...}
常用方法:
1. toString方法
- Object类中定义有public String toString()方法,其返回值是 String 类型,描述当前对象的有关息;当需要通过输出语句输出一个对象时,如System.out.println(person),将自动调用该对象类的 toString()方法,如果该类中没有重写toString(),那么默认调用Object类中toString(),默认输出对象hashCode值。我们可以根据需要在用户自定义类型中重写toString()方法。
public class Person {
private String name ;
private int age;
public Person(){
}
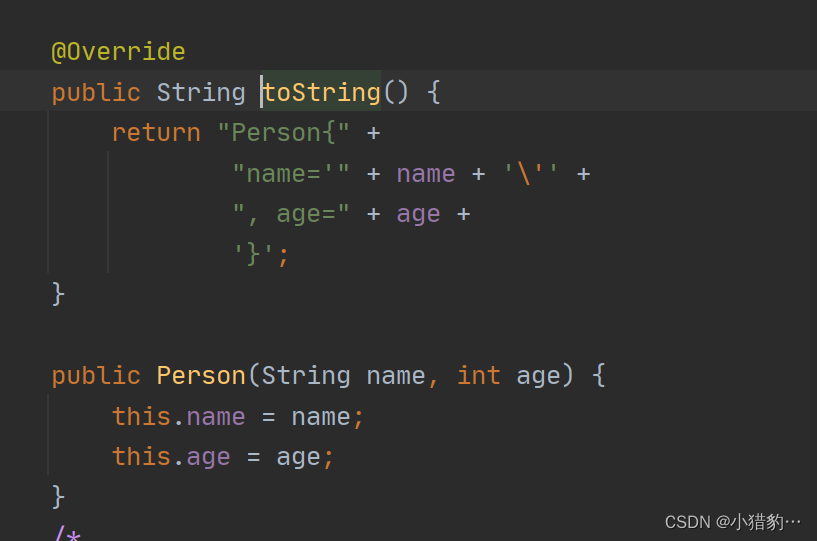
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
/*
* 当输出一个对象时会默认调用此对象的toString().
* 如果类中没有定义toString(),会调用Object类中toString(),
* Object类中toString()是吧对象在内存的哈希值返回(以16进制返回)
* 把对象信息通过字符串形式输出
*/
//重写toString()
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1=new Person("小魏",18);
System.out.println(p1);
}○ 当我们重写toString方法后就可以把对象信息通过字符串形式输出了 。
 (重写后的结果)
(重写后的结果)
○ 如果不重写的话会默认调用Object类中toString(),把对象在内存的哈希值返回(以16进制返回)。
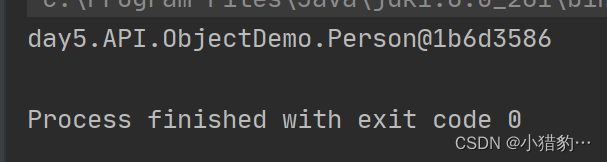 (没重写的结果)
(没重写的结果)
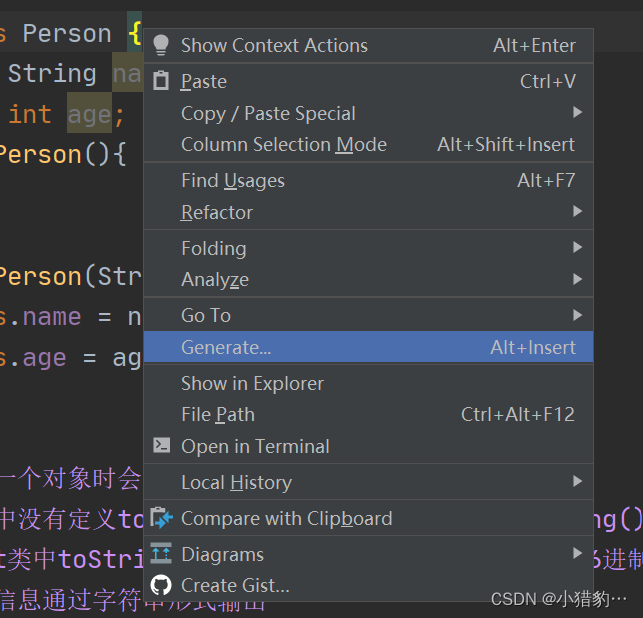
快速生成toString重写方法:
○ 右键选择Generate,点击toString()即可。


2. equals方法
○ boolean equals(Object obj) 判断两个对象是否相等
注意:
○ Object类中的equals默认比较的是两个对象的地址是否相等, 我们就可以使用 == 代替它,在其他类中,一般都重写了equals(), 把它改造为比较对象中的内容是否相等
public class Test_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person("小魏",16);
Person p2 = new Person("小魏",16);
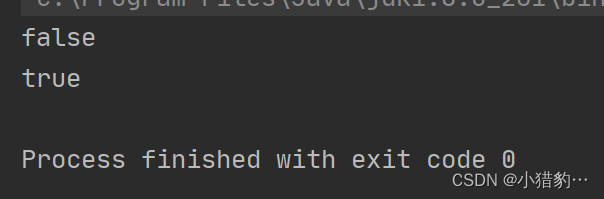
System.out.println(p1==p2); //比较的是地址
System.out.println(p1.equals(p2)); //已经对equals方法进行了重写,使其比较的是两对象内容是否相等
}
}(Object 中的 equals 方法默认使用==比较,比较的是对象地址,这点需要注意 )
○ 在Person类中对equals方法进行重写,使其比较的是对象中的内容是否相等
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(obj instanceof Person){
Person other =(Person)obj;
return name.equals(other.name) && age ==other.age;
}
return false;
}
○ 关于 " == " :
- "==" 比较等号两边是否相等
○ 当==用于基本类型比较时,比较的是变量值是否相等。
○ 当==用于引用类型比较时,比较的是对象的地址是否相等。
( JDK提供的一些类,如String,Date等,重写了Object的equals方法,调用这些类的equals方法, x.equals (y) ,当x和y所引用的对象是同一类对象且属性内容相等返回 true 否则返回 false )
Arrays类
○ 常用方法:
1. equals( )方法
• 比较两个数组内容是否相等,返回值为boolean类型.
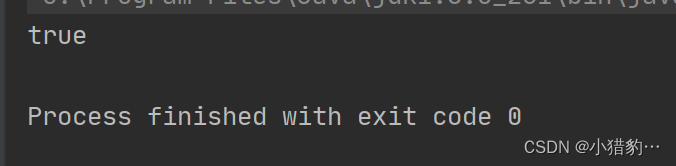
public class Null {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
比较两个数组内容是否相等
*/
int[] a={1,2,3,4};
int[] b={1,2,3,4};
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(a,b));
}
}
2. copyOf( ) 方法
• 数组复制,将原数组内容复制到一个指定长度新数组中.
public class Null {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] c=new int[3];
c[0]=0;
c[1]=1;
c[2]=2;
int[]d=Arrays.copyOf(c,6);//将原数组c复制到长度为6的新数组d中
//(原数组,新数组长度)
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(d));
}
}
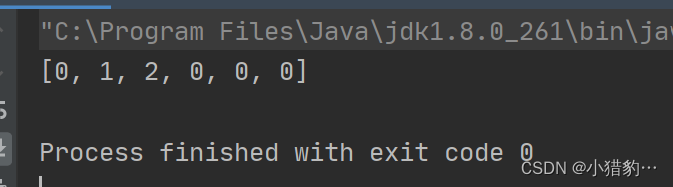
3. fill( ) 方法.
• 用指定的值 ,将指定数组中的值进行填充.
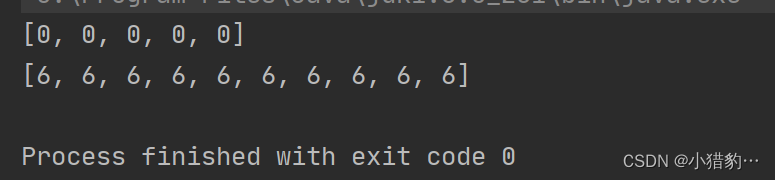
public class Null {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[]e ={1,2,3,4,5};
Arrays.fill(e,0);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(e));
int[]f = new int[10];
Arrays.fill(f,6);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(f));
}
}
4. sort( )方法
• 排序,且可通过索引局部排序
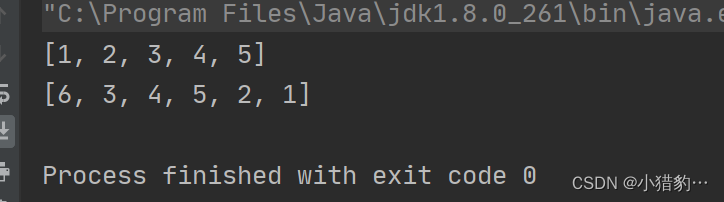
public class Null {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//全部排序
int[] a = {5,4,3,2,1};
Arrays.sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
//通过索引指定区间排序,tolndex索引对应的值不参与排序
int[] b ={6,5,4,3,2,1};
Arrays.sort(b,1,4); //对数组b索引1~4元素排序,所有4不参与
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b));
}
}
5. binarySearch( )方法
• 二分查找,查找前需要先排序
public class Null {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] b ={5,4,6,8,2,1,7};
Arrays.sort(b); //排序后 b={1,2,4,5,6,7,8}
int index =Arrays.binarySearch(b,6); //需要找6
System.out.println(index); //输出索引,排序后6对应的索引为4
}
}
6. toString( )方法
• 将数组中的元素内容拼接成一个字符串输出
public class Null {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a={1,2,3,4};
System.out.println(a); //输出数组首元素地址,不是数组的元素内容
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));;//通过toString()输出元素内容
}
} 
String类
1. 获取功能的常用方法
• int length( ) 获取字符串长度
• char charAt( ) 获取指定位置上的字符
• int indexOf( ) 获取字符首次出现的位置,也可以从指定位置开始查找
• lastIndexOf( ) 从后往前找
• String substring( ) 从指定位置开始截取一个字符串副本
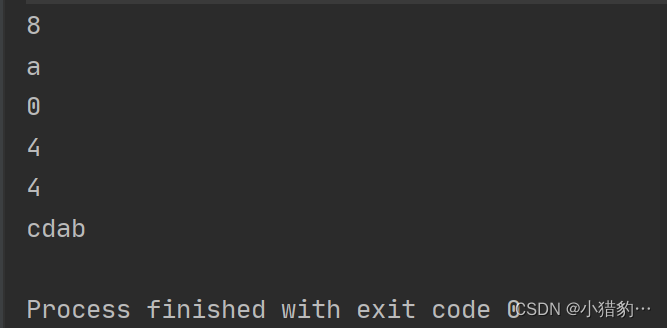
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取功能
String s1 = "abcdabcd";
//int length() 获取字符串长度
System.out.println(s1.length()); // 8
//char charAt() 获取指定位置上的字符
System.out.println(s1.charAt(4)); //索引4对应的字符 a
//int indexOf() 获取字符首次出现的位置
System.out.println(s1.indexOf("a")); //注意是首次出现的位置
//int indexOf(str: ,fromindex: ) 从指定位置开始查找
System.out.println(s1.indexOf("a",4));
//lastIndexOf() 从后往前找
System.out.println(s1.lastIndexOf("a"));
//String substring() 从指定位置开始截取一个字符串副本
String s2=s1.substring(2,6); //截取索引2~6的字符串(不包含索引6对应的字符)
System.out.println(s2); // 2 <= res < 6
}
2. 转换功能的常用方法
• String toUpperCase( ) 将字符串内容全部转换为大写
• String toLowerCase( ) 将字符串内容全部转换为小写
• String concat(String str) 拼接指定字符串内容到原字符串末尾
• String [ ] split(分割符) 通过分割符将字符串分割并以数组形式返回
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1="WoShiChinese";
System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase()); //转大写
System.out.println(s1.toLowerCase()); //转小写
String s2 ="我爱中国";
System.out.println(s2.concat(s1)); //拼接s1字符串内容到s2字符串末尾
//String[] split(分割符)
String s3 = "张三:中国人;"+"Tom:英国人;"+"梅西:阿根廷人;";
String[] strings = s3.split(";"); //通过" ; "来截取s3字符串
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strings));
}

3. 替换功能的常用方法
• String replace(char old,char new) 单个字符替换
• String replace(String old,String new) 整个字符串替换
• replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) 替换字符串中所有数字
• replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement) 替换字符串中第一个数字
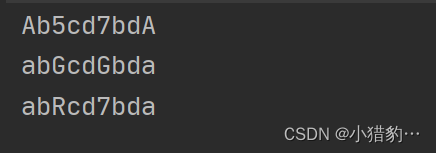
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = " ab5cd7bda";
//用"A"替换字符串中所有的"a"
System.out.println(s1.replace("a","A"));
//用"G"替换字符串中所有数字 \\d表示所有字符串中所有的数字
System.out.println(s1.replaceAll("\\d","G"));
//用"R"替换字符串中第一个数字
System.out.println(s1.replaceFirst("\\d","R"));
}
4. 去除字符串两端空格
• String trim( ) 去除字符串两端空格(字符串中间的空格不能去除)
public static void main(String[] args) {
//String trim() 去除字符串两端空格
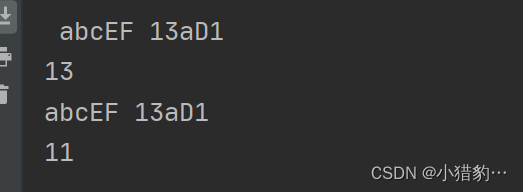
String s2 =" abcEF 13aD1 ";
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s2.length()); //原字符串长度
System.out.println(s2.trim());//去除两端空格,字符串中间的空格不能去除
System.out.println(s2.trim().length()); //去除空格后字符串的长度
}StringBuffer类
注意:
- String可以直接创建字符串对象,而StringBuffer不能,需要新创建一个字符串对象。
String s1 = "abc";
StringBuffer s2 = new StringBuffer("abc");添加功能
○ public StringBuffer append(String str) 在原字符串末尾添加字符串
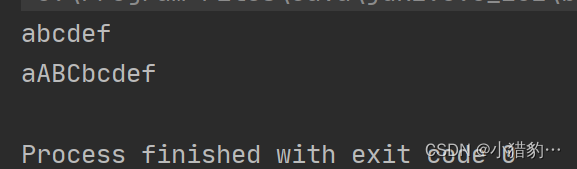
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer s1 = new StringBuffer("abc");
s1.append("def"); // 不能使用+=
System.out.println(s1);
}输出:abcdef
○ public StringBuffer insert(int offset,String str) 向指定位置插入字符串
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer s1 = new StringBuffer("abc");
//向字符串s1末尾添加"def"
s1.append("def"); // 不能使用+=
System.out.println(s1);
//向指定位置插入字符串
s1.insert(1,"ABC"); //向索引为1的位置插入字符串"ABC"
System.out.println(s1);
}输出:aABCbcdef
删除功能
○ public StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index) 删除单个字符
○ public StringBuffer delete(int start,int end) 删除指定区间的元素,不包含结尾
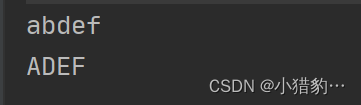
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer s1 = new StringBuffer("abcdef");
s1.deleteCharAt(2); //删除索引为2的字符
System.out.println(s1);
//删除指定区间的元素,不包含结尾
StringBuffer s2 = new StringBuffer("ABCDEF");
s2.delete(1,3);
System.out.println(s2);
}
替换功能
○ public StringBuffer replace(int start,int end,String str)
StringBuffer s1 = new StringBuffer("abcdef");
s1.replace(0,3,"ABC");
System.out.println(s1);输出:ABCdef
反转功能
○ public StringBuffer reverse( )
StringBuffer s1 = new StringBuffer("abcdef");
s1.reverse(); //反转
System.out.println(s1);输出:fedcba
截取功能
○ 从StringBuffer中截取一个副本,返回给一个新的String对象,StringBuffer对象不变
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer s1 = new StringBuffer("abcdef");
//从StringBuffer中截取一个副本,返回给一个新的String对象,StringBuffer对象不变
String s2=s1.substring(1,4);
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
} 
StringBuffer和String的区别
- String修饰的字符串是一个值不能改变的字符串,用String声明的字符串对象值一旦给定就不能改变了,每次拼接都会创建新的字符串对象,耗时且占用空间。
- StringBuffer是内容可以改变的字符串,值可以改变且不需要创建新对象,在多任务执行时是安全的,适合单线程。
Math类
○ 可以直接调用
介绍:
java.lang.Math 提供了一系列静态方法用于科学计算;其方法的参数和返回值类型一般为double型.
常用方法有:
○ abs 绝对值
○ sqrt 平方根
○ pow(double a, double b) a的b次幂
○ max(double a, double b) min(double a, double b) 比较两数的大小
○ random( ) 返回 0.0 到 1.0 的随机数
○ long round(double a) double型的数据a转换为long型(四舍五入)
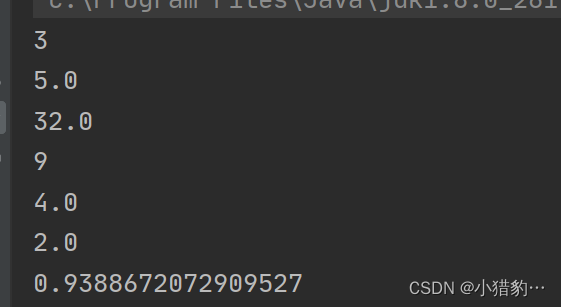
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Math类
System.out.println(Math.abs(-3)); //绝对值
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(25)); //平方根
System.out.println(Math.pow(2,5)); //次方
System.out.println(Math.round(9.35));//四舍五入
System.out.println(Math.floor(4.9)); //向下舍去
System.out.println(Math.ceil(1.1)); //向上补加
System.out.println(Math.random()); //0~1随机生成 (不等于1)
}
Random类
○ 不能直接调用,使用Random类之前需要创建新的对象。
○ 介绍:此类用于产生随机数
○ 常用方法有:
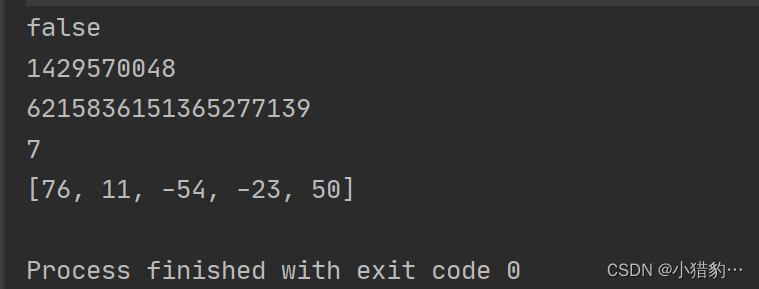
import java.util.Random;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
System.out.println(random.nextBoolean()); //true 或 false
System.out.println(random.nextInt());//在int的取值范围内随机返回一个整数
System.out.println(random.nextLong());
System.out.println(random.nextInt(35)+1); //在给定范围内随机获取一个数 0=<res<给定数
byte[] bytes = new byte[5];
random.nextBytes(bytes); //随机取出数组长度个byte类型的随机数
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
}
Date类
○ 不能直接调用,使用Date类之前需要创建新的对象。
1. 获取程序运行时刻的时间
Date date = new Date();//获取程序运行时刻的时间
System.out.println(date);2. 获取自1970 1.1 0:0:0 到程序运行时刻的毫秒值
Date date = new Date();
//获取的是自1970 1.1 0:0:0 到程序运行时刻的毫秒值
System.out.println(date.getTime());3. 测试效率
//测试效率
Date date1 = new Date();
System.out.println(date1.getTime()-date.getTime());测试效率
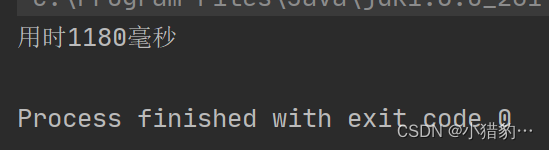
○ 测试String字符串和StringBuffer字符串循环拼接10万次,程序运行耗时。
○ 测试String字符串拼接速度.
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取程序运行时刻的时间
Date date = new Date();
// System.out.println(date.getTime());
String s1 = "w";
// StringBuffer s2 = new StringBuffer("w");
String s3 = "";
// StringBuffer s4 =new StringBuffer("");
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
s3 = s3.concat(s1);
}
//获取下一个程序运行时刻的时间,即上一个程序运行结束时刻的时间
Date date1 = new Date();
// System.out.println(date1.getTime());
System.out.println("用时"+(date1.getTime()-date.getTime())+"毫秒");//最终运行时间
}
○ 测试StringBuffer字符串拼接速度。
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取程序运行时刻的时间
Date date = new Date();
// System.out.println(date.getTime());
//String s1 = "w";
StringBuffer s2 = new StringBuffer("w");
//String s3 = "";
StringBuffer s4 =new StringBuffer("");
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
s4 = s4.append(s2);
}
//获取下一个程序运行时刻的时间,即上一个程序运行结束时刻的时间
Date date1 = new Date();
// System.out.println(date1.getTime());
System.out.println("用时"+(date1.getTime()-date.getTime())+"毫秒");//最终运行时间
}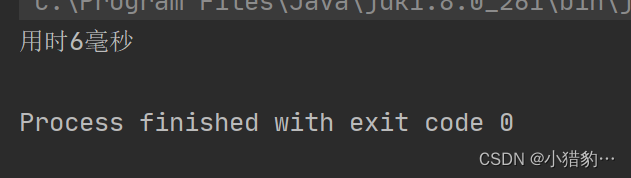
- 在前文中我们了解了二者的区别,通过这次测试我们也验证了之前的结论:用String声明的字符串对象值一旦给定就不能改变了,每次拼接都会创建新的字符串对象,耗时且占用空间;而StringBuffer是内容可以改变的字符串,值改变的同时不需要创建新对象,所有拼接起来速度更快。





















 199
199











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








