目录
203. 移除链表元素
题目链接:
题目要求:
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
题目用例:
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6 输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [], val = 1 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7 输出:[]
实现思路:
1.创建一个虚拟头指针(dummy),值为0,并使它指向当前链表头指针(head)。这样即使头节点需要被删除,我们也能通过dummy来找到新的头节点。
2.创建一个当前指针(current)等于虚拟头指针。这样我们可以从链表的头部开始遍历,而不用担心丢失对链表的引用。
3.循环遍历从current.next,直到遍历到current.next==null时结束,在循环中寻找下一个值。
如果为是要被删除的val就让它指向下下个位置(current.next = current.next.next),
否则就进入下个位置(current = current.next)
4.遍历结束后,返回虚拟头指针的下一个节点(dummy.next),这就是新的头节点。
实现代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
//给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
//创建一个虚拟头指针,值为0
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
//创建一个虚拟头指针指向头指针
dummy.next = head;
// dummy指针用于遍历链表
ListNode current = dummy;
//进入while循环,判断下一个指针值不为空
while(current.next != null){
if(current.next.val == val){
current.next = current.next.next;
}
else {
current = current.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}测试代码:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [], val = 1
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
输出:[]*/
Solution solution = new Solution();
//示例1:
ListNode head1 = new ListNode(1);
head1.next = new ListNode(2);
head1.next.next = new ListNode(6);
head1.next.next.next = new ListNode(3);
head1.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(4);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(6);
int val1=6;
ListNode ListNode1 = solution.removeElements(head1, val1);
printListNode(ListNode1);
System.out.println("==============================");
//示例2:
ListNode head2 =null;
int val2=1;
ListNode ListNode2 = solution.removeElements(head2, val2);
printListNode(ListNode2);
System.out.println("=================================");
//示例3:
ListNode head3 = new ListNode(7);
head3.next = new ListNode(7);
head3.next.next = new ListNode(7);
head3.next.next.next = new ListNode(7);
int val3=7;
ListNode ListNode3 = solution.removeElements(head3, val3);
printListNode(ListNode3);
}
//辅助函数,打印链表
public static void printListNode (ListNode head){
ListNode current = head;
while(current != null){
System.out.print(current.val + " ");
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
707. 设计链表
题目链接:
题目要求:
你可以选择使用单链表或者双链表,设计并实现自己的链表。
单链表中的节点应该具备两个属性:val 和 next 。val 是当前节点的值,next 是指向下一个节点的指针/引用。
如果是双向链表,则还需要属性 prev 以指示链表中的上一个节点。假设链表中的所有节点下标从 0 开始。
题目用例:
示例:
输入 ["MyLinkedList", "addAtHead", "addAtTail", "addAtIndex", "get", "deleteAtIndex", "get"] [[], [1], [3], [1, 2], [1], [1], [1]] 输出 [null, null, null, null, 2, null, 3]
实现思路:
1.写起来文字太长建议去看视频帮你把链表操作学个通透!LeetCode:707.设计链表_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
实现代码:
class MyLinkedList {
private ListNode dummy;// 虚拟头节点
private int size; //创建链表大小
public MyLinkedList() {
dummy=new ListNode(0);// 创建一个虚拟头节点
dummy.next=null;// 虚拟头节点的next指针指向null,因为链表开始时是空的
size=0;
}
public int get(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
// 索引越界
return -1;
}
ListNode current = dummy.next; // 从虚拟头节点的下一个节点开始遍历
int tempIndex = 0;
// 遍历到目标索引
while (tempIndex < index) {
current = current.next;
tempIndex++;
}
// 返回目标节点的值
return current.val;
}
public void addAtHead(int val) {
// 创建一个新节点
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(val);
// dummy.next指向新节点,新节点的next指向原链表的头部
newNode.next = dummy.next;
dummy.next = newNode;
//链表大小+1
size++;
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(val);
ListNode current = dummy;
// 遍历到链表尾部
while (current.next != null) {
current = current.next;
}
// 将新节点添加到链表尾部
current.next = newNode;
size++;
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if (index < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引不能是负数");
}
if (index > size) { // 如果 index 大于链表长度,则不插入新节点
return;
}
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(val);
ListNode current = dummy;
int tempIndex = 0;
// 遍历链表,找到要插入位置的前一个节点
while (current.next != null && tempIndex < index) {
current = current.next;
tempIndex++;
}
// 如果 tempIndex 等于 index,说明找到了插入位置
newNode.next = current.next; // 将新节点的 next 指针指向当前节点的下一个节点
current.next = newNode; // 将当前节点的 next 指针指向新节点
size++; // 链表大小加1
}
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
System.out.println("索引越界");
return; // 索引无效,直接返回
}
ListNode current = dummy; // 使用current变量遍历链表,保持dummy不变
// 遍历链表直到找到要删除节点的前一个节点
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
// 删除节点
current.next = current.next.next;
size--; // 链表大小减1
System.out.println("节点已删除");
}
}
测试代码:
public class Test {
/*示例:
输入
["MyLinkedList", "addAtHead", "addAtTail", "addAtIndex", "get", "deleteAtIndex", "get"]
[[], [1], [3], [1, 2], [1], [1], [1]]
输出
[null, null, null, null, 2, null, 3]
解释
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.addAtHead(1);
myLinkedList.addAtTail(3);
myLinkedList.addAtIndex(1, 2); // 链表变为 1->2->3
myLinkedList.get(1); // 返回 2
myLinkedList.deleteAtIndex(1); // 现在,链表变为 1->3
myLinkedList.get(1); // 返回 3*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
//示例
MyLinkedList obj = new MyLinkedList();
obj.addAtHead(1);
obj.addAtTail(3);
obj.addAtIndex(1,2);
int param_1 = obj.get(1);
System.out.println(param_1);
obj.deleteAtIndex(1);
int param_2= obj.get(1);
System.out.println(param_2);
}
}
206. 反转链表
题目链接:
题目要求:
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
题目用例:
示例 1:
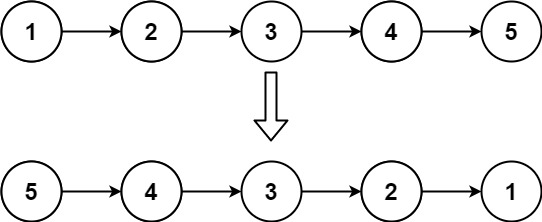
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:
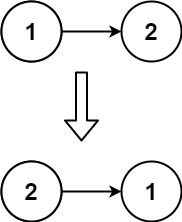
输入:head = [1,2] 输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]
实现思路:
1.定义当前节点(current)和前一个节点(prev)位置的指针
2.当节点不为null时开始循环,定义临时节点来存储当前下一个指向的节点信息
3.反转当前节点的next指针使它指向prev,并更新prev和current的值
4.返回prev节点,这就是反转链表的头结点
实现代码:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 定义之前节点位置,初始化为null
ListNode prev = null;
// 定义当前节点位置,初始化为头节点
ListNode current = head;
// 当当前节点不为null时循环
while (current != null) {
// 定义临时指针,保存下一个节点
ListNode temp = current.next;
// 反转当前节点的next指针
current.next = prev;
// 更新prev和current
prev = current;
current = temp;
}
// prev现在指向反转链表的头节点
return prev;
}
}测试代码:
public class Test {
/* 示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution=new Solution();
//示例1
ListNode head1 = new ListNode(1);
head1.next = new ListNode(2);
head1.next.next = new ListNode(3);
head1.next.next.next = new ListNode(4);
head1.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(5);
printList(solution.reverseList(head1));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("====================================================");
//示例二
ListNode head2 = new ListNode(1);
head2.next = new ListNode(2);
printList(solution.reverseList(head2));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("=====================================================");
//示例三
ListNode head3 = null;
printList(solution.reverseList(head3));
}
public static void printList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}





















 643
643

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








