目录
1.1要使用clone()拷贝某个对象,首先要在此对象所属的类中实现Cloneable接口。
1.调用方式
首先说明,调用clone()方法会涉及“异常”的知识点,我面先忽视掉在本文章,后序会将的
1.1要使用clone()拷贝某个对象,首先要在此对象所属的类中实现Cloneable接口。
class Student implements Cloneable {}原因:实现Cloneable接口是为了告诉JAVA运行环境,该类支持克隆方法,让clone()能够安全的调用。
如果不实现此接口,编译器会抛CloneNotSupportedException异常
因此虽然clone()方法是属于Object类的成员方法,但我们会发现如果不实现Cloneable接口,使用clone()方法是会报错的。
1.2在类中重写clone()方法
在重写方法中返回super.clone()即可。其实就是调用父类(Object类)的clone()方法。
@Override
protect Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {//要把protect改成public
return super.clone();
}想要理解上述代码,这些关键点我们需要知道:
Object类是所有类的父类
而Object类在java.lang这个包底下
protect权限在不同的包里,只有子类能够访问
所以现在的clone()方法还不能用,需要把protect权限改成public
这样才能在有main方法的Test类(不同包的非子类)中,调用clone()方法。【当然,其实还不能调用clone()方法,因为我们刚才说了,忽视掉异常的知识点】
1.3解决异常
当我们想去 调用clone()方法,克隆一个学生的信息:
package demo2;
//Object在 java.lang这个包底下
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA
* Description:
* User:34398
* Date:2024-03-21
* Time:16:31
*/
class Money {
int price;
public Money(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
class Student extends Money implements Cloneable {
int age;
String name;
public Student(int age, int price, String name) {
super(price);
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {//要把protect改成public
return super.clone();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"price=" + price +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student1 = new Student(10, 12, "海");
Student student2 = student1.clone();
System.out.println(student1);
System.out.println(student2);
}
}
编译器报错
![]()
对和不实现Cloneable接口的提示一样
那如何解决呢?
我们现在还没有学习异常,直接说方法:
把重写clone()方法自动生成的
throws CloneNotSupportedException
拷贝放到main方法的末尾

这样就解决类异常的警报
——————————————————————————————————————————
那这样就可以调用clone()方法了吗?
en~~~
其实还不行…………
快了,还差最后一步!
当我们更改好了throws CloneNotSupportedException的方法
再次执行程序回报这样一个错误:

细心的大佬们一定回想起,重写的clone()方法返回的是Object类型
对这就是问题所在

Student 类和Object类并不兼容,并且是向下转型
因此需要强转
更改后再次运行,终于
package demo2;
//Object在 java.lang这个包底下
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA
* Description:
* User:34398
* Date:2024-03-21
* Time:16:31
*/
class Money {
int price;
public Money(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
class Student extends Money implements Cloneable {
int age;
String name;
public Student(int age, int price, String name) {
super(price);
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {//要把protect改成public
return super.clone();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"price=" + price +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {//要把throws CloneNotSupportedException,放到后面,牵扯到异常先不管
Student student1 = new Student(10, 12, "海");
Student student2 = (Student) student1.clone();
System.out.println(student1);
System.out.println(student2);
}
}
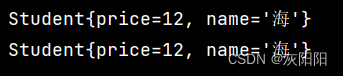
成功了。
1.4调用方法总结
1要在类中实现Cloneable接口(异常的知识)
2重写clone()方法,把throws CloneNotSupportedException放在main方法后面(异常的知识可以先后续学了在了解)
3.强制类型转换成要克隆的对象的类型(因为clone返回Object类型)
4.克隆方法是浅拷贝(接下来介绍)
2.clone()方法属于浅拷贝
想要理解浅拷贝 我们来看看这样一段代码
package demo1;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA
* Description:
* User:34398
* Date:2024-03-21
* Time:18:01
*/
class Money {
int price;
public Money(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Money{" +
"price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
class Student implements Cloneable {
String name;
Money money;
public Student(int price, String name) {
this.money = new Money(price);
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\''
+"资产="+money.price+
'}';
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Student student1 = new Student(12, "海");
Student student2 = (Student) student1.clone();
student1.money.price=2;
System.out.println(student1);
System.out.println(student2);
}
}
输出结果:

为什么》?
这其实就是浅拷贝了。
clone()方法使用只是把
student1里的成员变量money的引用拷贝给了student2
相当于student1.money和student2.money指向的是同一块内存
所以stu1和stu2的资产(price)都会被改变。
那么如何克隆一个不会被stu1影响的stu2呢?
2.1深拷贝
其实把上面抛出的问题解决,就是深拷贝了。
解决方法:
我们只需要在Money这个类中在使用clone()即可,同时对Student类中的clone()做一个小小的修改
package demo1;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA
* Description:
* User:34398
* Date:2024-03-21
* Time:18:01
*/
class Money implements Cloneable{//实现Cloneable
int price;
public Money(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Money{" +
"price=" + price +
'}';
}
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {//重写clone方法
return super.clone();
}
}
class Student implements Cloneable {
String name;
Money money;
public Student(int price, String name) {
this.money = new Money(price);
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
//下面是关键的两行代码
Student tmp = (Student) super.clone();
tmp.money = (Money) this.money.clone();
return tmp;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\''
+ "资产=" + money.price +
'}';
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Student student1 = new Student(12, "海");
Student student2 = (Student) student1.clone();
student1.money.price = 2;
System.out.println(student1);
System.out.println(student2);
}
}
运行结果:

这时候就不会一改全改了。








 本文详细介绍了如何在Java中使用`clone()`方法进行对象复制,包括实现`Cloneable`接口、重写`clone()`方法处理异常、浅拷贝与深拷贝的区别以及如何实现深拷贝。
本文详细介绍了如何在Java中使用`clone()`方法进行对象复制,包括实现`Cloneable`接口、重写`clone()`方法处理异常、浅拷贝与深拷贝的区别以及如何实现深拷贝。
















 165
165

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








