一、栈的定义
栈是一种遵循后进先出原则的数据结构,它只允许在一端进行插入和删除操作,这一端通常被称为栈顶(Top)。
栈的应用场景非常广泛,从函数调用的内部实现到浏览器的前进后退按钮,栈都发挥着重要的作用。
今天,我们将一起探索如何在C语言中实现一个简单的栈。 在接下来的内容中,我们将首先定义栈的基本结构和操作,然后逐步编写代码来实现这些操作。我们将从创建一个空栈开始,然后实现向栈中添加元素(入栈,Push)、从栈中移除元素(出栈,Pop)、查看栈顶元素以及判断栈是否为空(Empty)等基本操作。
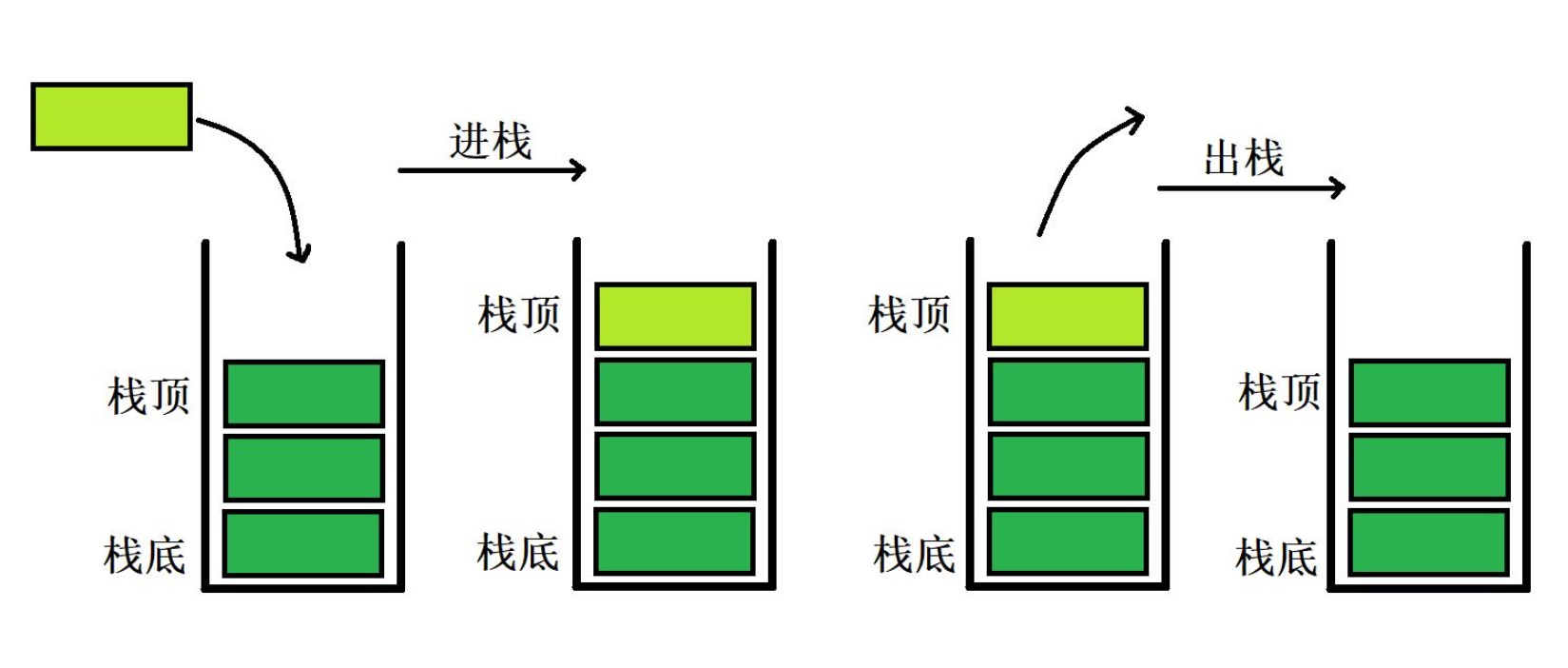
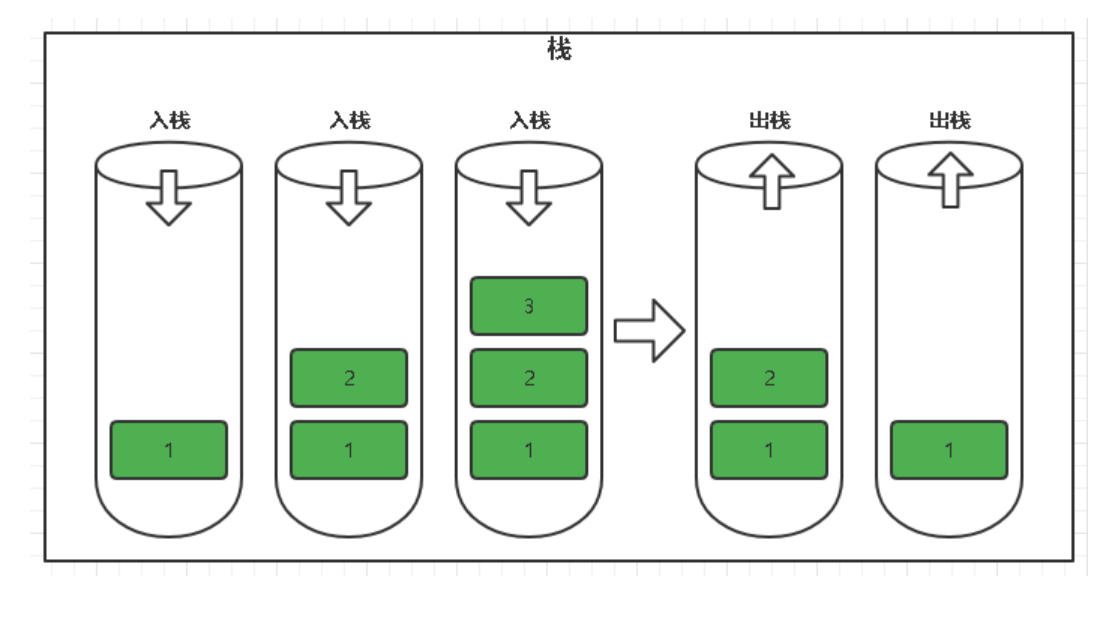
二、基本操作
// 支持动态增长的栈
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* _a;
int _top; // 栈顶
int _capacity;//容量
}Stack;
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* ps);
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data);
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps);
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps);
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps);
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps);
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps);三、实现栈
1.初始化栈
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack * ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->_a = NULL;
ps->_top = 0;
ps->_capacity = 0;
}2.入栈
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->_top == ps->_capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->_capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->_capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->_a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
ps->_a = tmp;
ps->_capacity = newcapacity;
}
ps->_a[ps->_top] = data;
ps->_top++;
}assert(ps);: 确保传入的栈指针ps不为空。
if (ps->_top == ps->_capacity): 判断栈顶指针_top是否等于栈的容量_capacity。如果是,说明栈已满,需要扩容。
ps->_a[ps->_top] = data;: 将数据data放入栈顶的位置(由_top指示)。
ps->_top++;: 栈顶指针递增,表示新元素已入栈 。ps->_a = tmp;: 如果realloc成功,更新栈的数据指针_a。
ps->_capacity = newcapacity;: 更新栈的容量_capacity。ps->_a[ps->_top] = data;: 将数据data放入栈顶的位置(由_top指示)。
ps->_top++;: 栈顶指针递增,表示新元素已入栈。
3.出栈
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->_top > 0);
ps->_top--;
}ps->_top--;: 将栈顶指针_top递减,表示栈顶元素已经被移除。
4.检测栈是否为空
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top == 0;
}return ps->_top == 0;: 这里检查栈顶指针 _top 是否等于 0。在栈的实现中,通常将 _top 初始化为 0,表示栈为空。当栈顶指针为 0 时,意味着没有元素在栈中,因此栈是空的。
5..获取栈顶元素
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->_top > 0);
return ps->_a[ps->_top - 1];
}return ps->_a[ps->_top - 1];: 这里通过数组下标访问栈顶的元素。因为栈是后入先出的数据结构,所以栈顶元素位于数组的 _top - 1 位置,因此,我们返回 ps->_a[ps->_top - 1] 来获取栈顶的元素。
6.获取元素个数
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top;
}7.销毁栈
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->_a);
ps->_a = NULL;
ps->_top = 0;
ps->_capacity = 0;
}free(ps->_a);: 使用 free 函数释放栈所使用的数组 _a 所占用的内存。
ps->_a = NULL;: 将栈的数组指针 _a 设置为 NULL,避免野指针问题,是一个好的编程习惯,可以确保在栈被销毁后,其成员不会被误用。
全部代码
void StackInit(Stack * ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->_a = NULL;
ps->_top = 0;
ps->_capacity = 0;
}
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->_top == ps->_capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->_capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->_capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->_a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
ps->_a = tmp;
ps->_capacity = newcapacity;
}
ps->_a[ps->_top] = data;
ps->_top++;
}
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->_top > 0);
ps->_top--;
}
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->_top > 0);
return ps->_a[ps->_top - 1];
}
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top;
}
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top == 0;
}
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->_a);
ps->_a = NULL;
ps->_top = 0;
ps->_capacity = 0;
}




















 503
503

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








