目录
1.栈
1.1栈的概念及结构
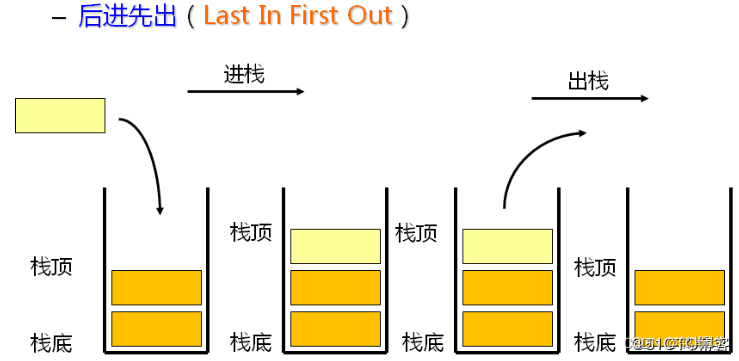
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。
进行数据插入和删除操作的一端
称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。
栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出
LIFO
(
Last In First Out
)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈
/
压栈
/
入栈,
入数据在栈顶
。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。
出数据也在栈顶
。
1.2栈的实现
栈的实现一般可以使用
数组或者链表实现
,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小。
这里实现栈用到了两个文件Stack.h和Stack.c
Stack.h中进行栈的定义和函数的定义和头文件的声明
Stack.h文件的内容:
头文件的声明
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <assert.h>
定义栈的结构体(以int为例)
typedef int StDateType;
//方便以后更改栈的数据类型
typedef struct Stack
{
StDateType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}stack;栈函数的定义
//初始化栈
void STInit(stack* pst);
//栈的销毁
void STDestroy(stack* pst);
//入栈
void STPush(stack* pst,StDateType x);
//出栈
void STPop(stack* pst);
//判空
bool STEmpty(stack* pst);
//栈的长度
int STSize(stack* pst);
//打印栈顶
StDateType STTop(stack* pst);Stack.c中进行栈函数的实现
Stack.c文件内容:
#include "Stack.h"
//初始化栈
void STInit(stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = pst->top = 0;
}
//栈的销毁
void STDestroy(stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = pst->top = 0;
}
//入栈
void STPush(stack* pst,StDateType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
//capacity为空时newcapacity为4,不为空时扩大为原来的二倍
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * pst->capacity;
StDateType* temp = (StDateType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(StDateType) * newcapacity);
//当capacity为0,a==NULL时,注意realloc当传递的指针为空时,作用相当于malloc
if (temp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc failed");
return;
}
pst->a = temp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
//出栈
void STPop(stack* pst)
{
//pst不能孔 栈也不能为空
assert(pst&&pst->top);
pst->top--;
}
//判空
bool STEmpty(stack* pst)
{
return pst->top == 0;
}
//栈的长度
int STSize(stack* pst)
{
return pst->top;
}
//打印栈顶
StDateType STTop(stack* pst)
{
//pst不能孔 栈也不能为空
assert(pst && pst->top);
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}特别注意:
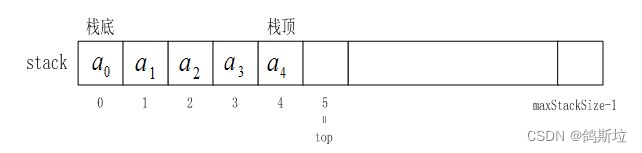
在这里我们要注意一下栈top的值,我们在初始化时top=capacity=0,我这里top指向的是栈的元素的下一个位置。
还有另外一种初始化方法,top=-1,capacity=0.这样top指向的就是栈顶元素。
但是这两种方法确定后,后面的函数实现也会随之改变,需要格外注意,不同人有不同的实现栈的方法,只要能够实现都是可以的。
我们实现了栈,下面我们来看一道力扣上面的题目运用一下!
2.栈的运用——(有效的括号)
题目链接
题目

考虑到括号之间的前后匹配,靠后的左空号先与右括号匹配可以想到 “后进先出” 创建栈遇到左括号压栈,遇到右括号判断是否配对,若配对则出栈,
前面我们实现了栈,在解题时直接复制函数的实现下面是问题的答案:
typedef char StDateType;
typedef struct Stack {
StDateType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
} stack;
// 初始化栈
void STInit(stack* pst) {
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = pst->top = 0;
}
// 栈的销毁
void STDestroy(stack* pst) {
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = pst->top = 0;
}
// 入栈
void STPush(stack* pst, StDateType x) {
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == pst->capacity) {
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * pst->capacity;
StDateType* temp =
(StDateType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(StDateType) * newcapacity);
if (temp == NULL) {
perror("realloc failed");
return;
}
pst->a = temp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
// 出栈
void STPop(stack* pst) {
assert(pst && pst->top);
pst->top--;
}
// 判空
bool STEmpty(stack* pst) { return pst->top == 0; }
// 栈的长度
int STSize(stack* pst) { return pst->top; }
// 栈定
StDateType STTop(stack* pst) {
assert(pst && pst->top);
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
bool isValid(char* s) {
stack st;
STInit(&st);
while (*s) {
//左括号就压栈
if (*s == '(' || *s == '{' || *s == '[') {
STPush(&st, *s);
}
//右括号就匹配出栈
else
{
//出栈但栈为空说明有问题,返回false
if (STEmpty(&st)) {
//防止内存泄露
STDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
char temp = STTop(&st);
//出栈
STPop(&st);
//遇到不匹配的括号返回false
if ((temp == '(' && *s != ')') || (temp == '[' && *s != ']') ||
(temp == '{' && *s != '}'))
{
//防止内存泄露
STDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
}
s++;
}
bool ret = STEmpty(&st);
//防止内存泄露
STDestroy(&st);
return ret;
}在这道题中我们也可以很好的体会到typedef char StDateType的好处,该一出而动全身很是好用。
感谢观看,欢迎评论区讨论





















 2810
2810











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








