文章目录
Ⅰ.string的用法
1.string 对象的创建(构造)
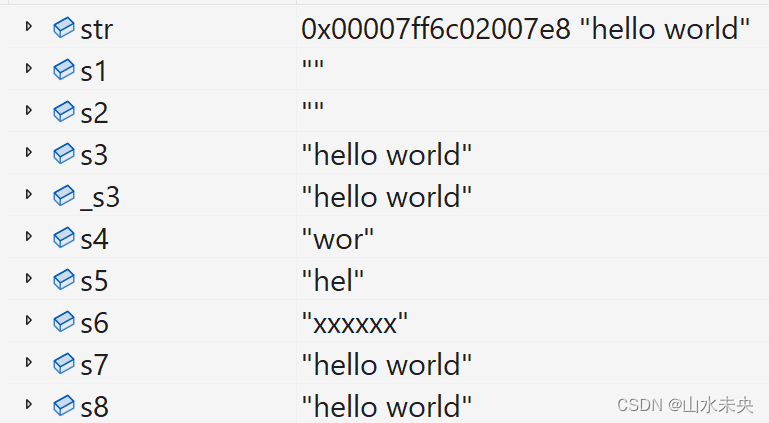
//创建
void test_string1()
{
// 空串
string s1;
//拷贝构造
string s2(s1);
//字符串常量构造
const char* str = "hello world";
string s3(str);
string _s3("hello world");
//从s3的下标为6的位置连续的三个字符
string s4(s3, 6, 3);
// 字符串str的前三个字符
string s5(str, 3);
// 6个x
string s6(6, 'x');
// 迭代器区间
string s7(s3.begin(), s3.end());
//了解即可
string s8 = { "hello world" };
}
2.string的销毁(析构)
声明周期结束时,编译器自动调用
3.string的遍历
第一种:下标方括号访问
void test_string2()
{
string s("hello world");
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
cout << s[i];
}
}
第二种:迭代器区间
void test_string2()
{
string s("hello world");
string::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it;
it++;
}
}
第三种:范围for
void test_string2()
{
string s("hello world");
for (char ch : s)
{
cout << ch;
}
}
4. string的增
第一种:在位追加一个字符
void test_string3()
{
string s("hello");
s.push_back('a');
s.push_back('b');
s.push_back('c');
}
void test_string3()
{
string s("hello");
s += 'a';
s += 'a';
s += 'a';
}
第二种:在尾追加一个字符串
void test_string3()
{
string s("hello ");
s.append("world");
}
void test_string3()
{
string s("hello ");
s += "abcde";
}
第三种:在任意位置插入一个或者多个字符
void test_string3()
{
string s0("xxx");
string s("hello world");
// 从下标为6的地方开始插入一个string
s.insert(6, s0);
cout << s;// hello xxxworld
}
void test_string3()
{
string s0("xxxyyy");
string s("hello world");
// 在s下标为0的位置,插入一个s0的字串(从下标为3开始的连续的三个字符)
s.insert(0, s0, 3, 3);
cout << s;//xxxhello wrold
}
void test_string3()
{
string s("hello world");
string::iterator it = s.begin();
s.insert(it + 6, 3, 'x');
cout << s;// hello xxxworld
}
5.string的删
void test_string4()
{
string s("hello wrold");
//从下标为6的位置开始,删除一个字符
s.erase(6, 1);
cout << s;//hello rold
}
void test_string4()
{
string s("hello wrold");
string::iterator it = s.begin();
s.erase(it + 6);
cout << s;//hello rold
}
void test_string4()
{
string s("hello wrold");
string::iterator it = s.begin();
s.erase(it,it+s.size());
cout << s; //空串
}
6.string的查
| 函数名称 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|
| find(c,pos) | 从下标为pos的位置开始,向后查到第一个字符为c,找到就返回其下标 |
| rfind(c,pos) | 从下标为pos的位置开始,向前查找第一个字符为c,找到就返回其下标 |
void test_string5()
{
string s("hello world");
size_t pos1 = s.find('l', 0);
if (pos1 != s.npos) cout << pos1 << endl; // 2
size_t pos2 = s.rfind('l', 11);
if (pos2 != s.npos) cout << pos2 << endl; // 9
}
7.string的改
| 函数名称 | 功能介绍 |
|---|---|
| replace(pos,n,s) | 从pos位置开始替换n个字符为s串 |
void test_string6()
{
string s("hello abc");
s.replace(6, 3, "wrold"); //hello world
}
Ⅱ.string的底层原理
class string
{
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
public:
// 可加可不加,因为并没有使用私有的成员变量
//friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s);
//friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s);
iterator begin()
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _str;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _str + _size;
}
string(const char* str = "")
:_size(strlen(str))
{
_capacity = _size;
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
string(const string& s)
{
string tmp(s.c_str());
swap(tmp);
}
string& operator=(string tmp)
{
swap(tmp);
return *this;
}
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = _capacity = 0;
}
char& operator[](size_t pos)
{
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
const char& operator[](size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n + 1];
strcpy(tmp, _str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = n;
}
}
void resize(size_t n, char ch = '\0')
{
if (n <= _size)
{
_str[n] = '\0';
_size = n;
}
else
{
reserve(n);
for (size_t i = _size; i < n; i++)
{
_str[i] = ch;
}
_str[n] = '\0';
_size = n;
}
}
void push_back(char ch)
{
/*if (_size == _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity);
}
_str[_size++] = ch;
_str[_size] = 0;*/
insert(_size, ch);
}
void append(const char* str)
{
/*size_t len = strlen(str);
if (len + _size > _capacity)
{
reserve(len + _size);
}
strcpy(_str + _size, str);
_size += len;*/
insert(_size, str);
}
string& operator+=(char ch)
{
push_back(ch);
return *this;
}
string& operator+=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}
void clear()
{
_str[0] = '\0';
_size = 0;
}
void swap(string& s)
{
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
const char* c_str() const
{
return _str;
}
size_t size() const
{
return _size;
}
size_t capacity() const
{
return _capacity;
}
bool empty()
{
return _size == 0;
}
void insert(size_t pos, char ch)
{
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= _size);
if (_size == _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity);
}
size_t end = _size + 1;
while (end > pos)
{
_str[end] = _str[end - 1];
end--;
}
_str[pos] = ch;
_size++;
}
void insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= _size);
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (len + _size > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
size_t end = _size + len;
while (end > pos + len - 1)
{
_str[end] = _str[end - len];
end--;
}
strncpy(_str + pos, str, len);
_size += len;
}
void erase(size_t pos, size_t len = npos)
{
if (len >= _size - pos || len == npos)
{
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;
}
else
{
strcpy(_str + pos, _str + pos + len);
_size -= len;
}
}
size_t find(char ch,size_t pos = 0) const
{
for (int i = 0; i < _size; i++)
{
if (_str[i] == ch); return i;
}
return npos;
}
size_t find(const char* str,size_t pos = 0) const
{
char* p = strstr(_str+pos, str);
if (p) return p - _str;
else return npos;
}
string substr(size_t pos, size_t len = npos)
{
string sub;
if (len == npos || len >= _size - pos)
{
for(int i = pos;i<_size;i++)
sub += _str[i];
}
else
{
for (int i = pos; i < pos + len; i++)
sub += _str[i];
}
return sub;
}
private:
char* _str = nullptr;
size_t _size = 0;
size_t _capacity = 0;
static const int npos;
};
bool operator==(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return strcmp(s1.c_str(), s2.c_str()) == 0;
}
bool operator!=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return !(s1 == s2);
}
bool operator<(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return strcmp(s1.c_str(), s2.c_str()) < 0;
}
bool operator<=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return s1 < s2 || s1 == s2;
}
bool operator>(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return !(s1 <= s2);
}
bool operator>=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return !(s1 < s2);
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s)
{
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e;
}
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s)
{
s.clear();
char buff[128];
char ch;
ch = cin.get();
int i = 0;
while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n')
{
buff[i++] = ch;
if (i == 127)
{
buff[127] = '\0';
s += buff;
i = 0;
}
ch = cin.get();
}
if (i)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
}
return in;
}
istream& getline(istream& in, string& s)
{
s.clear();
char buff[128];
char ch;
ch = cin.get();
int i = 0;
while (ch != '\n')
{
buff[i++] = ch;
if (i == 127)
{
buff[127] = '\0';
s += buff;
i = 0;
}
ch = cin.get();
}
if (i)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
}
return in;
}
const int string::npos = -1;






















 4879
4879

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








