1.Set
1.1Set概述
Set继承自Collecyion接口,没有特殊的方法。
1.2Set集合的特点
1.不包含重复元素
2.不维护元素的次序的集合
3.Set没有索引,不能通过索引访问元素
4.只能通过元素本身
1.3Set只是一个接口,不可单独实现
Set接口可通过其子类,Hashset来实现
2.HashSet
2.1Hashset概述
1.用来实现Set接口
2.底层数据结构为HasMap哈希表
3.对集合迭代顺序不做保证
4.线程不安全
5.允许一个null元素
6.HashSet 中的元素没有固定的顺序,元素的存储和检索顺序是不确定的
2.2HashSet常用API
1.add
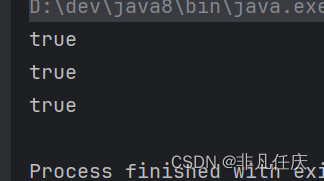
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> s =new HashSet<Integer>();
System.out.println(s.add(1));
System.out.println(s.add(2));
System.out.println(s.add(3));
}-
在执行add方法后,会返回一个boolean值
-
如果添加成功,返回true,否则返回false
2.remove
添加成功后可以通过remove删除元素
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> s =new HashSet<Integer>();
System.out.println(s.add(1));
System.out.println(s.add(2));
System.out.println(s.add(3));
s.remove(1);
System.out.println(s);
}
3.contains
判断HashSet中是否包含该元素
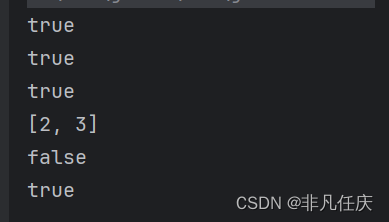
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> s =new HashSet<Integer>();
System.out.println(s.add(1));
System.out.println(s.add(2));
System.out.println(s.add(3));
s.remove(1);
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println(s.contains(1));
System.out.println(s.contains(2));
}
4.iterator
HashSet返回一个迭代器,可以遍历所有元素
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> s =new HashSet<Integer>();
System.out.println(s.add(1));
System.out.println(s.add(2));
System.out.println(s.add(3));
System.out.println(s.add(4));
System.out.println(s.add(5));
System.out.println(s.add(6));
Iterator<Integer> it =s.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
5.clear
清空所有元素
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> s =new HashSet<Integer>();
System.out.println(s.add(1));
System.out.println(s.add(2));
System.out.println(s.add(3));
System.out.println(s.add(4));
System.out.println(s.add(5));
System.out.println(s.add(6));
s.clear();
System.out.println(s);
}

3.Map
Map是一个接口,我们不能直接创建对象,可以通过多态的形式创建对象,Map中有两个
参数,一个是K表示键,一个是V表示值,且一个键有且对应一个值,Map中不能包含重复的
键,若是有重复的键添加,则会以最后一次的键为准,而其他的键会被覆盖。
具体实现常用的一般有两种,一是HashMap,另一个是TreeMap,今天我们只讲HashMap
4.HashMap
4.1HashMap概述
HashMap中的每个元素都包含一个键对象和一个值对象。键对象必须是唯一的,值对象可以重复。HashMap内部使用哈希表来存储数据,通过哈希算法将键映射到具体的位置,从而实现快速的查找和插入操作。
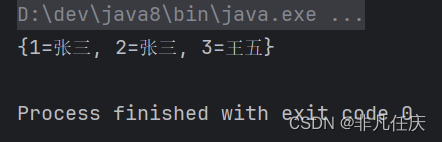
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("1", "张三");
map.put("2", "张三");
map.put("3", "李四");
map.put("3", "王五");//键重复,会覆盖上一个,留下最新的
System.out.println(map);//{2003=王五, 2002=张三, 2001=张三}
}
4.2HashMap常用API
1.put
向HashMap中添加元素
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("1", "张三");
map.put("2", "张三");
map.put("3", "李四");
map.put("3", "王五");//键重复,会覆盖上一个,留下最新的
System.out.println(map);//{2003=王五, 2002=张三, 2001=张三}
}
2.get
根据键获取对应位置的值
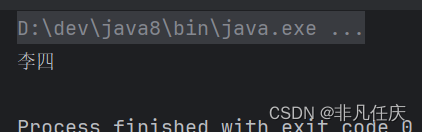
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("1", "张三");
map.put("2", "张三");
map.put("3", "李四");
System.out.println(map.get("3"));
}
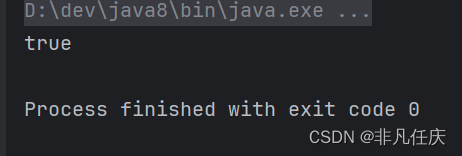
3.containsValue
判断HashMap中是否包含指定的值。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("1", "张三");
map.put("2", "张三");
map.put("3", "李四");
System.out.println(map.containsValue("李四"));
}
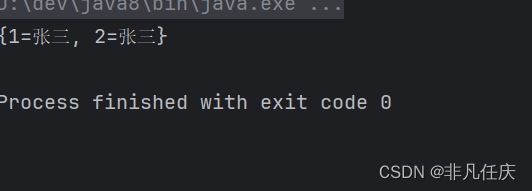
4.remove
根据键删除对应值
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("1", "张三");
map.put("2", "张三");
map.put("3", "李四");
map.remove("3");
System.out.println(map);
}
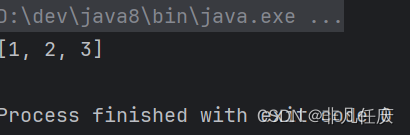
5.keySet
获取HashMap中所有的键,返回一个Set集合。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("1", "张三");
map.put("2", "张三");
map.put("3", "李四");
Set s =map.keySet();
System.out.println(s);
}
6.values
获取HashMap中所有的值,返回一个Collection集合。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("1", "张三");
map.put("2", "张三");
map.put("3", "李四");
Collection s =map.values();
System.out.println(s);
}
5.Stack
5.1Stack概述
一种线性数据结构,具有“先进后出”(Last In First Out,LIFO)的特性。栈可以看作是一种限制性的线性表,只允许在一端进行插入和删除操作,这一端称为栈顶。栈的另一端称为栈底,元素只能从栈顶进出。
栈常用的操作包括:
- push():向栈顶压入一个元素;
- pop():从栈顶弹出一个元素;
- peek():查看栈顶元素但不删除;
- isEmpty():判断栈是否为空;
- size():获取栈中元素的个数;
- clear():清空栈中的所有元素。






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








