代码随想录算法训练营第十八天:二叉树的层序遍历(中间放假)

102.二叉树的层序遍历
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。

#思路
我们之前讲过了三篇关于二叉树的深度优先遍历的文章:
接下来我们再来介绍二叉树的另一种遍历方式:层序遍历。
层序遍历一个二叉树。就是从左到右一层一层的去遍历二叉树。这种遍历的方式和我们之前讲过的都不太一样。
需要借用一个辅助数据结构即队列来实现,队列先进先出,符合一层一层遍历的逻辑,而用栈先进后出适合模拟深度优先遍历也就是递归的逻辑。
而这种层序遍历方式就是图论中的广度优先遍历,只不过我们应用在二叉树上。
使用队列实现二叉树广度优先遍历,动画如下:
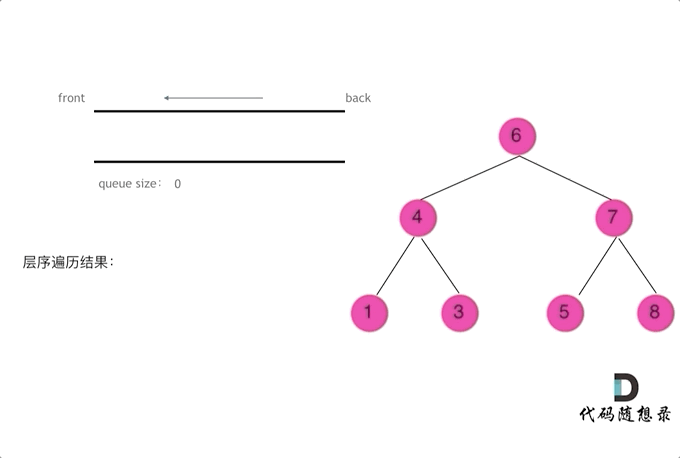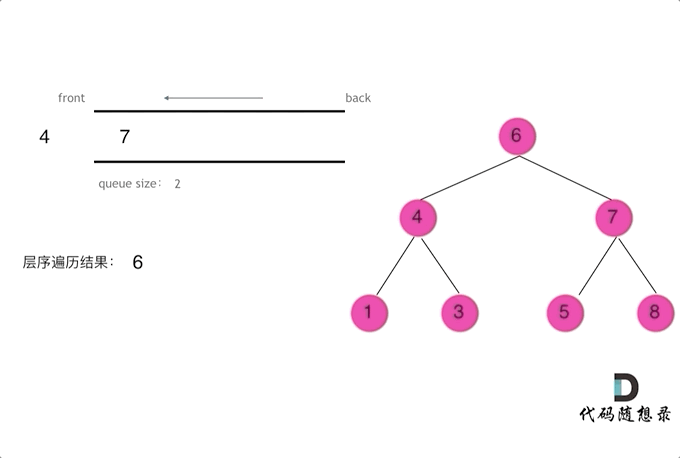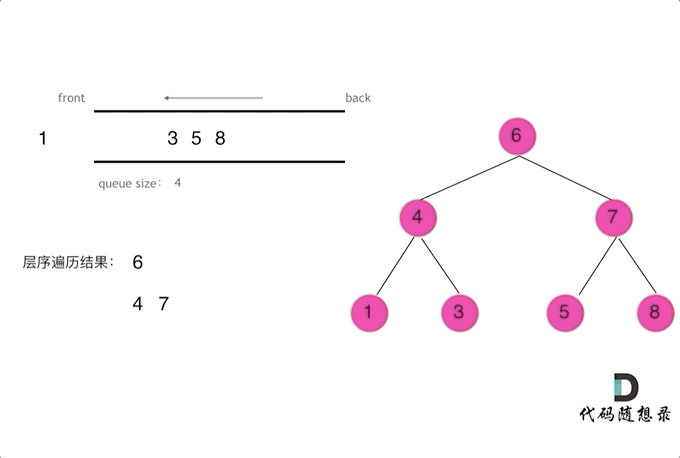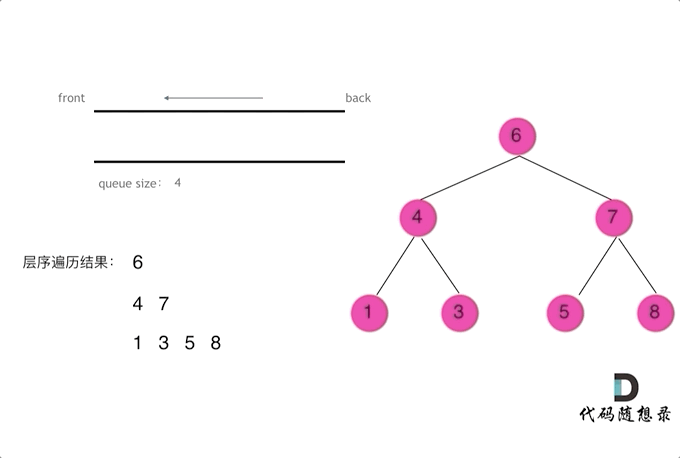
这样就实现了层序从左到右遍历二叉树。
代码如下:这份代码也可以作为二叉树层序遍历的模板,打十个就靠它了。
c++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
vector<vector<int>> result;
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
vector<int> vec;
// 这里一定要使用固定大小size,不要使用que.size(),因为que.size是不断变化的
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
vec.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
result.push_back(vec);
}
return result;
}
};
# 递归法
class Solution {
public:
void order(TreeNode* cur, vector<vector<int>>& result, int depth)
{
if (cur == nullptr) return;
if (result.size() == depth) result.push_back(vector<int>());
result[depth].push_back(cur->val);
order(cur->left, result, depth + 1);
order(cur->right, result, depth + 1);
}
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
int depth = 0;
order(root, result, depth);
return result;
}
};
107.二叉树的层次遍历 II
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值自底向上的层次遍历。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)

思路
相对于102.二叉树的层序遍历,就是最后把result数组反转一下就可以了。
C++代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
vector<vector<int>> result;
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
vector<int> vec;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
vec.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
result.push_back(vec);
}
reverse(result.begin(), result.end()); // 在这里反转一下数组即可
return result;
}
};
199.二叉树的右视图
给定一棵二叉树,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。

#思路
层序遍历的时候,判断是否遍历到单层的最后面的元素,如果是,就放进result数组中,随后返回result就可以了。
C++代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
vector <int> ans;
void dfs(TreeNode *node ,int depth){
if (node == nullptr)return ;
if (depth == ans.size())
ans.push_back(node->val);
dfs(node->right,depth + 1);
dfs(node->left,depth+1);
}
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root,0);
return ans;
}
};
637.二叉树的层平均值
给定一个非空二叉树, 返回一个由每层节点平均值组成的数组。

#思路
本题就是层序遍历的时候把一层求个总和在取一个均值。
C++代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if(root != NULL) que.push(root) ;
vector<double> result;
while(!que.empty()){
int size = que.size();
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0;i< size;i++){
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
sum += node->val;
if(node->left)que.push(node->left);
if(node->right)que.push(node->right);
}
result.push_back(sum/size);
}
return result;
}
};
429.N叉树的层序遍历
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的层序遍历。 (即从左到右,逐层遍历)。
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
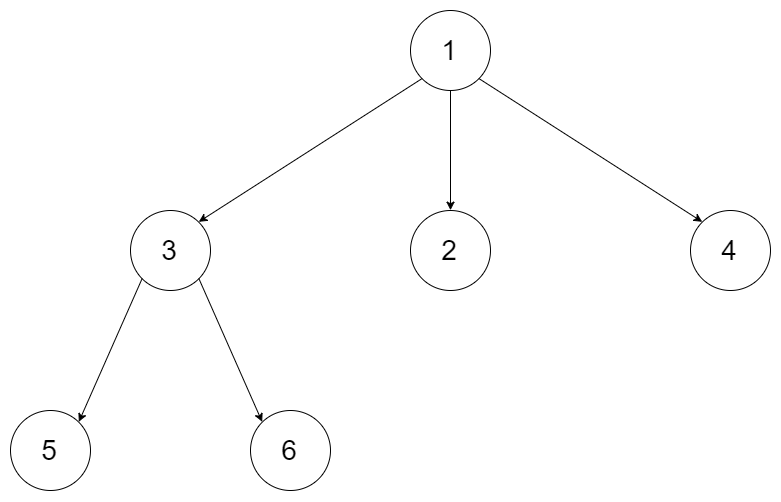
返回其层序遍历:
[ [1], [3,2,4], [5,6] ]
#思路
这道题依旧是模板题,只不过一个节点有多个孩子了
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
if(!root){
return {};
}
vector<vector<int>> ans;
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
int cnt = q.size();
vector<int> level;
for(int i = 0;i<cnt;++i){
Node* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
level.push_back(cur->val);
for(Node* child:cur->children){
q.push(child);
}
}
ans.push_back(move(level));
}
return ans;
}
};
515.在每个树行中找最大值
您需要在二叉树的每一行中找到最大的值。
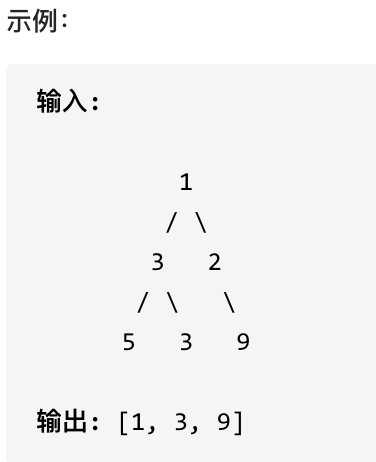
#思路
层序遍历,取每一层的最大值
C++代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> largestValues(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
vector<int> result;
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
int maxValue = INT_MIN; // 取每一层的最大值
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
maxValue = node->val > maxValue ? node->val : maxValue;
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
result.push_back(maxValue); // 把最大值放进数组
}
return result;
}
};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> largestValues(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ans;
auto dfs = [&](auto && dfs,auto&& r,int d){
if(!r) return;
if(ans.size () == d)ans.emplace_back(r->val);
else ans[d] = max(ans[d],r->val);
dfs(dfs,r->left,d+1);
dfs(dfs,r->right,d+1);
};
dfs(dfs,root,0);
return ans;
}
};
116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
给定一个完美二叉树,其所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点。二叉树定义如下:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
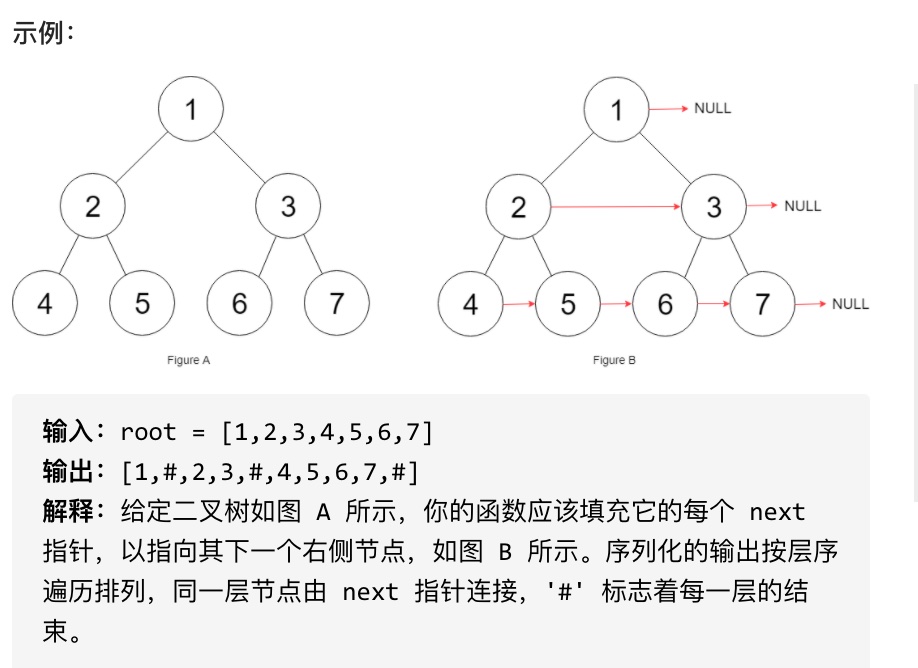
#思路
本题依然是层序遍历,只不过在单层遍历的时候记录一下本层的头部节点,然后在遍历的时候让前一个节点指向本节点就可以了
C++代码:
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
// vector<int> vec;
Node* nodePre;
Node* node;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
nodePre = que.front(); // 取出一层的头结点
que.pop();
node = nodePre;
} else {
node = que.front();
que.pop();
nodePre->next = node; // 本层前一个节点next指向本节点
nodePre = nodePre->next;
}
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
nodePre->next = NULL; // 本层最后一个节点指向NULL
}
return root;
}
};
迭代解法二
题目要求是常量的辅助空间,所以第一种解法并不符合要求,下面来看下 O(1)O(1) O ( 1 ) 空间复杂度的实现细节。
注意,题目说的二叉树是一棵完美二叉树,即每一层的节点都是满的。
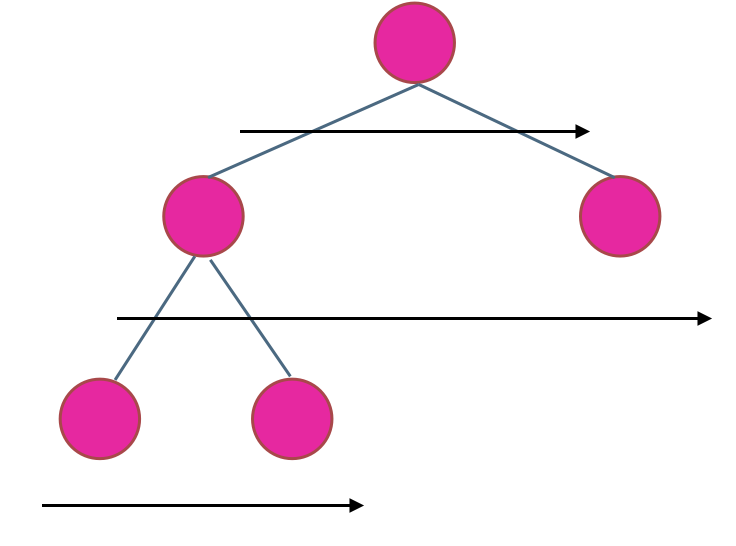
仔细看下完成后的串联树,其连接的方式有两种:
第一种 是这两个串联的节点都有一个共同的父节点,通过父节点就可以将这两个子节点串联起来
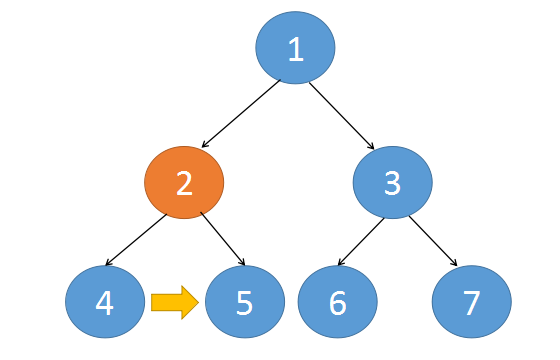
{:align=center}
第二种 是这两个串联的节点的父节点不同,对于这种情况,如果我们能将这一层的上一层串联好。那么可以通过父节点的next找到邻居,完成串联。
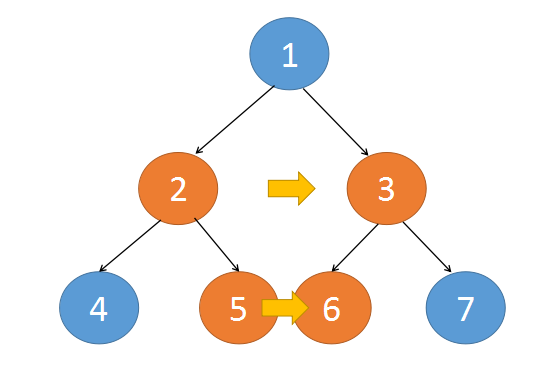
{:align=center}
即
root.right.next => root.next.left
这里我们需要保证 root.next 不为空就可以了。
也就是说当我们要串联第 i 层节点时,需要先完成第 i-1 层的节点串联
第一层最多只有一个节点,不需要串联
第二层最多只有两个节点,借助根节点就可以完成串联了
第三层串联时,上一层已经串联完了,所以第三层可以完成串联
同理,可以完成第四层,第五层,第N层的串联
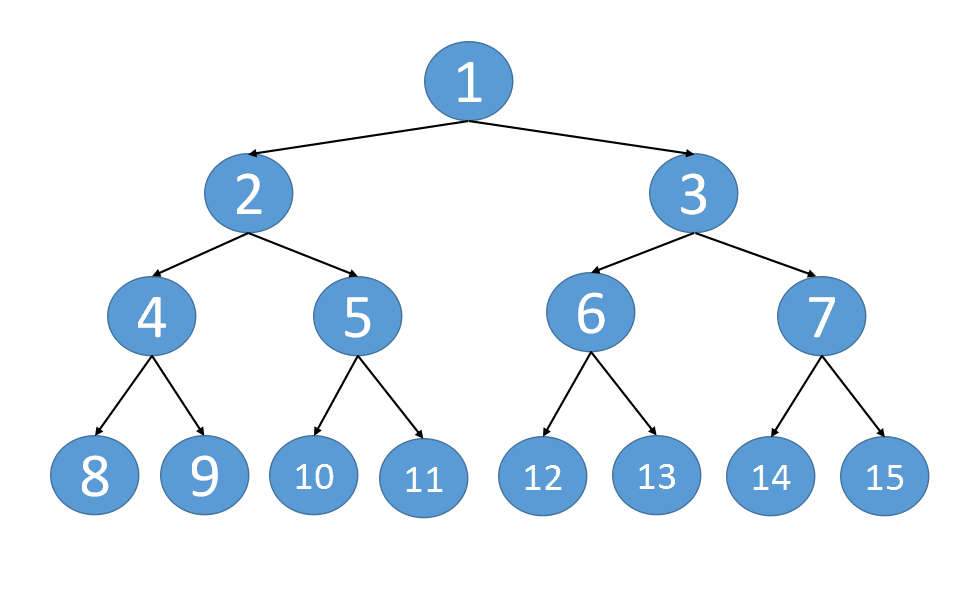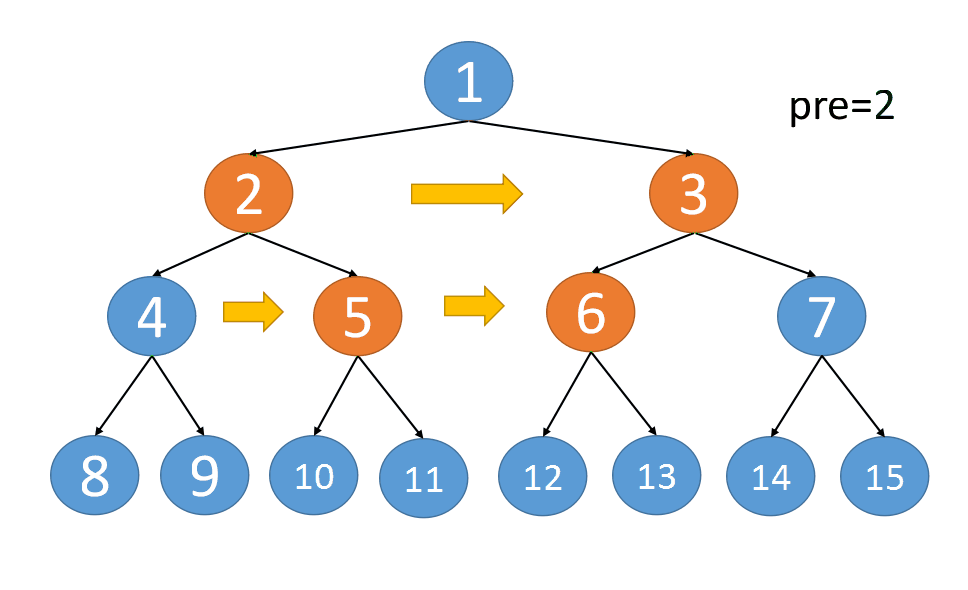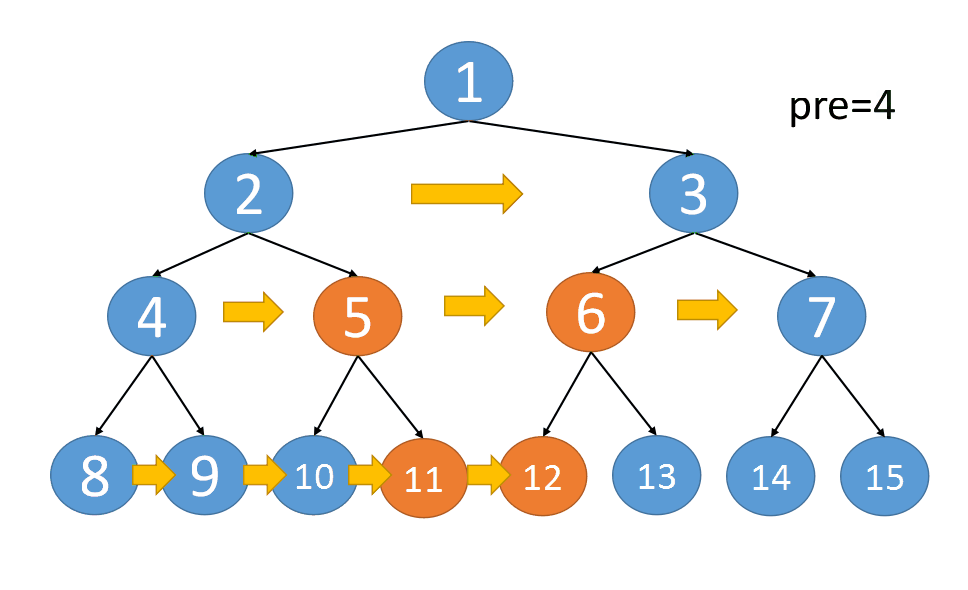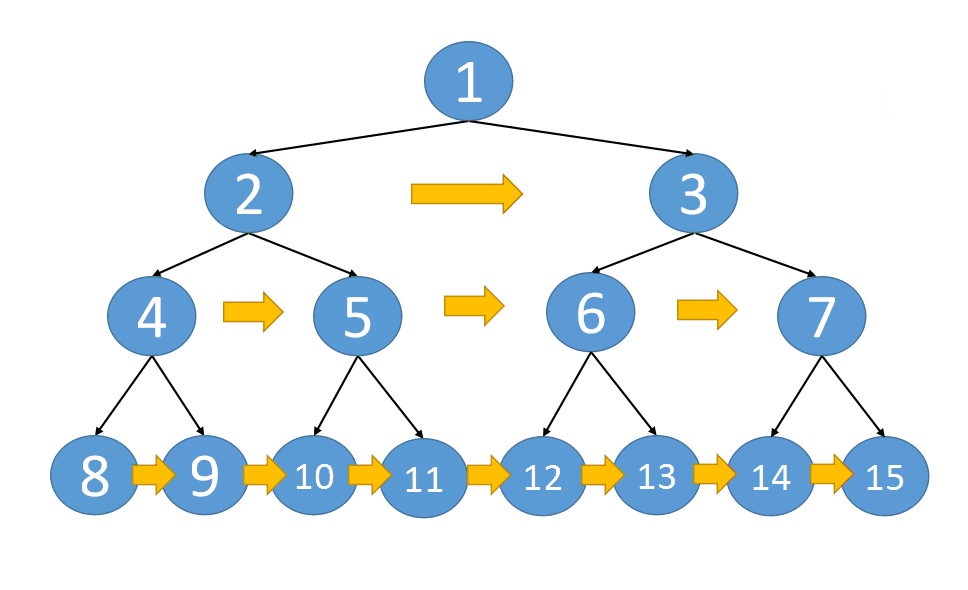
{:align=center}
时间复杂度:O(n)O(n) O ( n )
空间复杂度:O(1)O(1) O ( 1 )
leftmost = root
while (leftmost.left != null) {
head = leftmost
while (head.next != null) {
1) Establish Connection 1
2) Establish Connection 2 using next pointers
head = head.next
}
leftmost = leftmost.left
}
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return root;
}
// 从根节点开始
Node* leftmost = root;
while (leftmost->left != nullptr) {
// 遍历这一层节点组织成的链表,为下一层的节点更新 next 指针
Node* head = leftmost;
while (head != nullptr) {
// CONNECTION 1
head->left->next = head->right;
// CONNECTION 2
if (head->next != nullptr) {
head->right->next = head->next->left;
}
// 指针向后移动
head = head->next;
}
// 去下一层的最左的节点
leftmost = leftmost->left;
}
return root;
}
};
117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
#思路
这道题目说是二叉树,但116题目说是完整二叉树,其实没有任何差别,一样的代码一样的逻辑一样的味道
C++代码:
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
vector<int> vec;
Node* nodePre;
Node* node;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
nodePre = que.front(); // 取出一层的头结点
que.pop();
node = nodePre;
} else {
node = que.front();
que.pop();
nodePre->next = node; // 本层前一个节点next指向本节点
nodePre = nodePre->next;
}
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
nodePre->next = NULL; // 本层最后一个节点指向NULL
}
return root;
}
};
方法二:使用已建立的 next\text{next} next 指针
思路与算法
因为必须处理树上的所有节点,所以无法降低时间复杂度,但是可以尝试降低空间复杂度。
在方法一中,因为对树的结构一无所知,所以使用队列保证有序访问同一层的所有节点,并建立它们之间的连接。然而不难发现:一旦在某层的节点之间建立了 next\text{next} next 指针,那这层节点实际上形成了一个链表。因此,如果先去建立某一层的 next\text{next} next 指针,再去遍历这一层,就无需再使用队列了。
基于该想法,提出降低空间复杂度的思路:如果第 iii 层节点之间已经建立 next\text{next} next 指针,就可以通过 next\text{next} next 指针访问该层的所有节点,同时对于每个第 iii 层的节点,我们又可以通过它的 left\rm leftleft 和 right\rm rightright 指针知道其第 i+1i+1i + 1 层的孩子节点是什么,所以遍历过程中就能够按顺序为第 i+1i + 1i + 1 层节点建立 next\text{next} next 指针。
具体来说:
- 从根节点开始。因为第 000 层只有一个节点,不需要处理。可以在上一层为下一层建立 next\text{next} next 指针。该方法最重要的一点是:位于第 xxx 层时为第 x+1x + 1x + 1 层建立 next\text{next} next 指针。一旦完成这些连接操作,移至第 x+1x + 1x + 1 层为第 x+2x + 2x + 2 层建立 next\text{next} next 指针。
- 当遍历到某层节点时,该层节点的 next\text{next} next 指针已经建立。这样就不需要队列从而节省空间。每次只要知道下一层的最左边的节点,就可以从该节点开始,像遍历链表一样遍历该层的所有节点。
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node* next;
Node() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}
Node(int _val) : val(_val), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}
Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right, Node* _next)
: val(_val), left(_left), right(_right), next(_next) {}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
void handle(Node* &last,Node* &p,Node* &nextStart){
if(last){
last->next = p;
}
if(!nextStart){
nextStart = p;
}
last = p;
}
Node* connect(Node* root) {
if(!root){
return nullptr;
}
Node* start = root;
while(start){
Node* last = nullptr,*nextStart = nullptr;
for(Node *p = start;p!=nullptr;p = p->next){
if(p->left){
handle(last,p->left,nextStart);
}
if(p->right){
handle(last,p->right,nextStart);
}
}
start = nextStart;
}
return root;
}
};
104.二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],

返回它的最大深度 3 。
#思路
使用迭代法的话,使用层序遍历是最为合适的,因为最大的深度就是二叉树的层数,和层序遍历的方式极其吻合。
在二叉树中,一层一层的来遍历二叉树,记录一下遍历的层数就是二叉树的深度,如图所示:
所以这道题的迭代法就是一道模板题,可以使用二叉树层序遍历的模板来解决的。
C++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int depth = 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
depth++; // 记录深度
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return depth;
}
};
111.二叉树的最小深度
#思路
相对于 104.二叉树的最大深度 ,本题还也可以使用层序遍历的方式来解决,思路是一样的。
需要注意的是,只有当左右孩子都为空的时候,才说明遍历的最低点了。如果其中一个孩子为空则不是最低点
代码如下:(详细注释)
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int depth = 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
depth++; // 记录最小深度
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
if (!node->left && !node->right) { // 当左右孩子都为空的时候,说明是最低点的一层了,退出
return depth;
}
}
}
return depth;
}
};
总结
二叉树的层序遍历,就是图论中的广度优先搜索在二叉树中的应用,需要借助队列来实现(此时又发现队列的一个应用了)。
来吧,一口气打十个:
- 102.二叉树的层序遍历(opens new window)
- 107.二叉树的层次遍历II(opens new window)
- 199.二叉树的右视图(opens new window)
- 637.二叉树的层平均值(opens new window)
- 429.N叉树的层序遍历(opens new window)
- 515.在每个树行中找最大值(opens new window)
- 116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针(opens new window)
- 117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II(opens new window)
- 104.二叉树的最大深度(opens new window)
- 111.二叉树的最小深度(opens new window)
致敬叶师傅!
























 973
973











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








