1.队列的概念及结构
2.队列的实现
3.关于队列的例题
1.队列的概念及结构
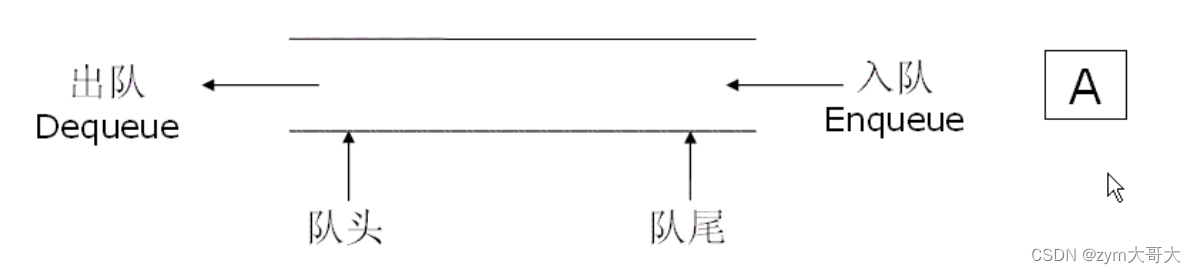
队列:只允许在一端进行数据操作,在另外一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出的特点,入队列是指进行插入操作的一端称为队尾,出队列是指进行删除操作的一端称为对头。
 队列的实际运用
队列的实际运用
在公平性方面上的运用,例如抽号机,就是运用了队列的相关知识,先抽号先进入队列,先排队一样。
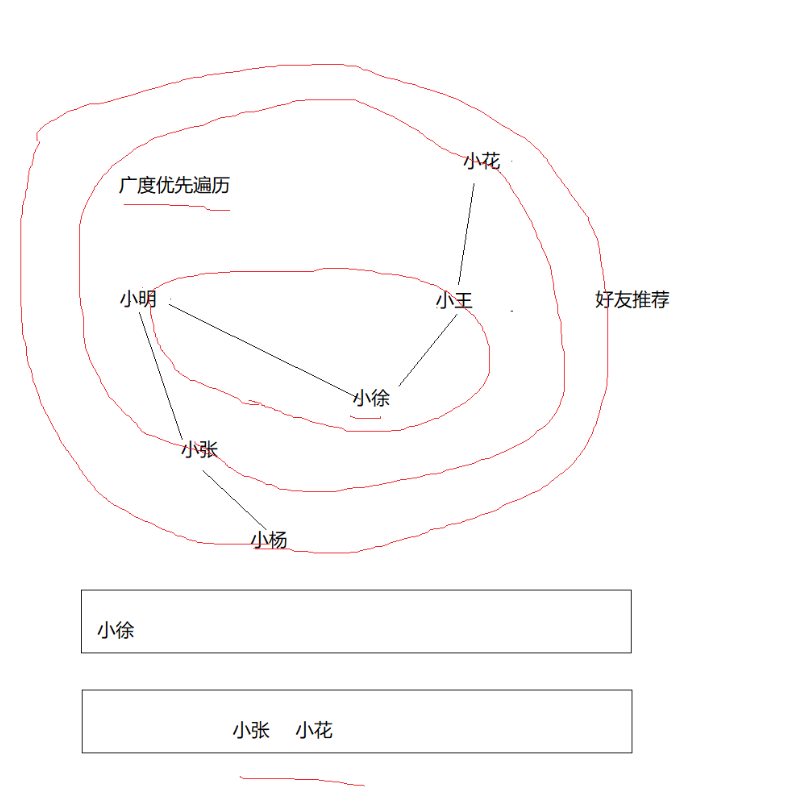
在广度优先遍历上也可以使用队列,在推荐好友时,会从你的好友的好友列表上给你推荐,在队列中是任何实现呢?
简单来说就是先把小徐入栈,然后把小徐出栈,同时把小徐的好友全部入栈,继续一样的步骤,每次出栈都会把出栈的好友入栈,广度的遍历相关的所有人。
2.队列的实现
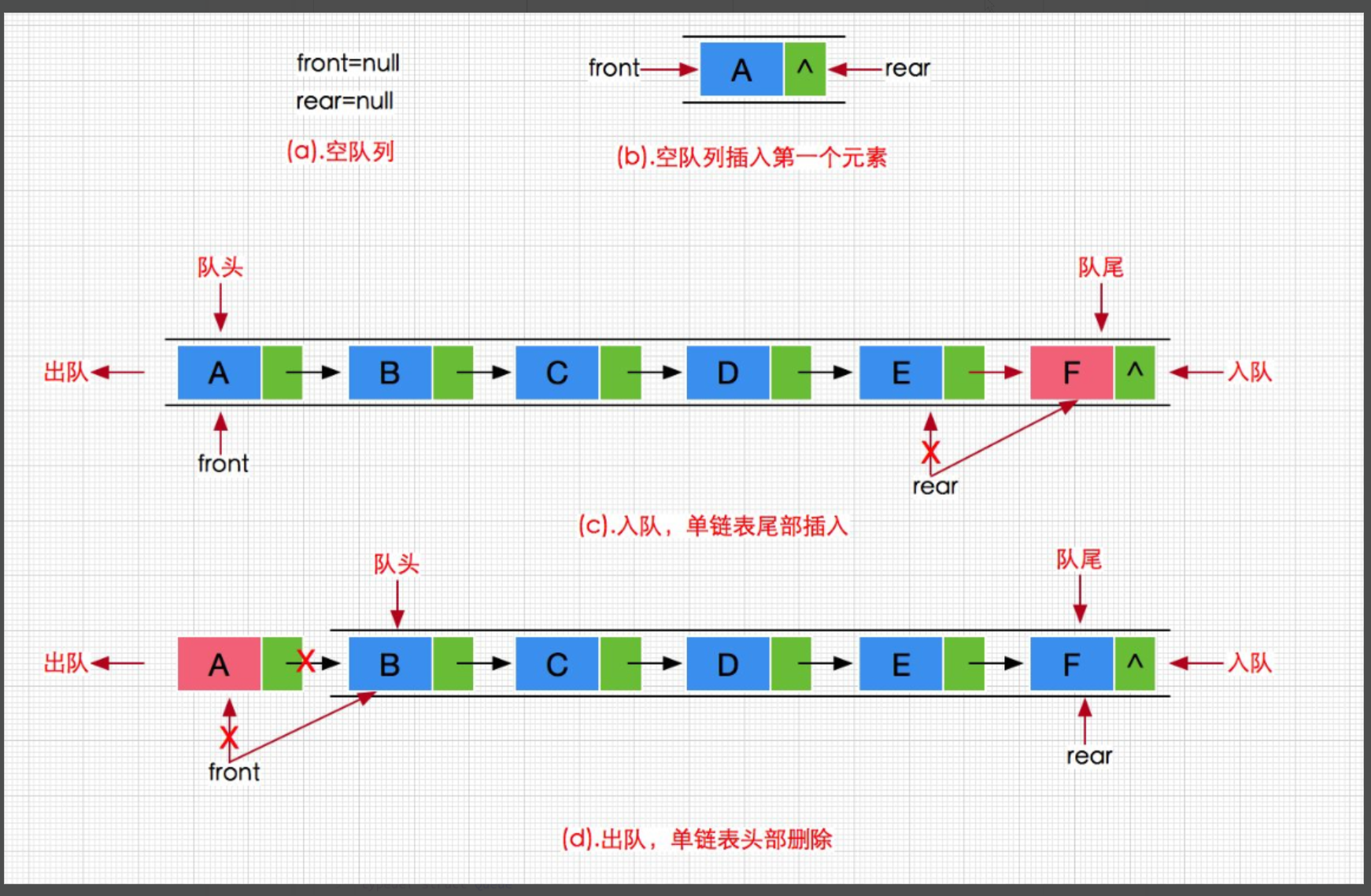
队列也可以使用数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率比较低(挪动数组的所有元素向前一步)。
代码实现:
test.c文件:
#include"queue.h"
int main()
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 3);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}queue.h文件:
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType val;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;//这里需要用到头指针和尾指针,因为队列的出队和入队的位置需要知道,
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;//设立这个结构体是为了在调用函数时可以减少参数以及需要用二级传参,只需要传Queue的一级指针和一个参数就行,是代码简介以及便利。
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
// 队尾插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
// 队头删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
// 取队头和队尾的数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);queue.c文件:
#include"queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
// 队尾插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
QNode* a = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (a == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail:");
return;
}
a->val = x;
a->next = NULL;//创建空间后把next置为NULL
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
pq->phead = pq->ptail = a;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next= a;
pq->ptail = a;//把尾指针的俩条线都放到最后一个空间上
}
pq->size++;
}
// 队头删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
if (pq->phead->next==NULL)//pq->phead==pq->ptail
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead=next;
}
pq->size--;
}
// 取队头和队尾的数
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->phead->val;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->ptail->val;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size == 0;
}
3.关于队列的例题
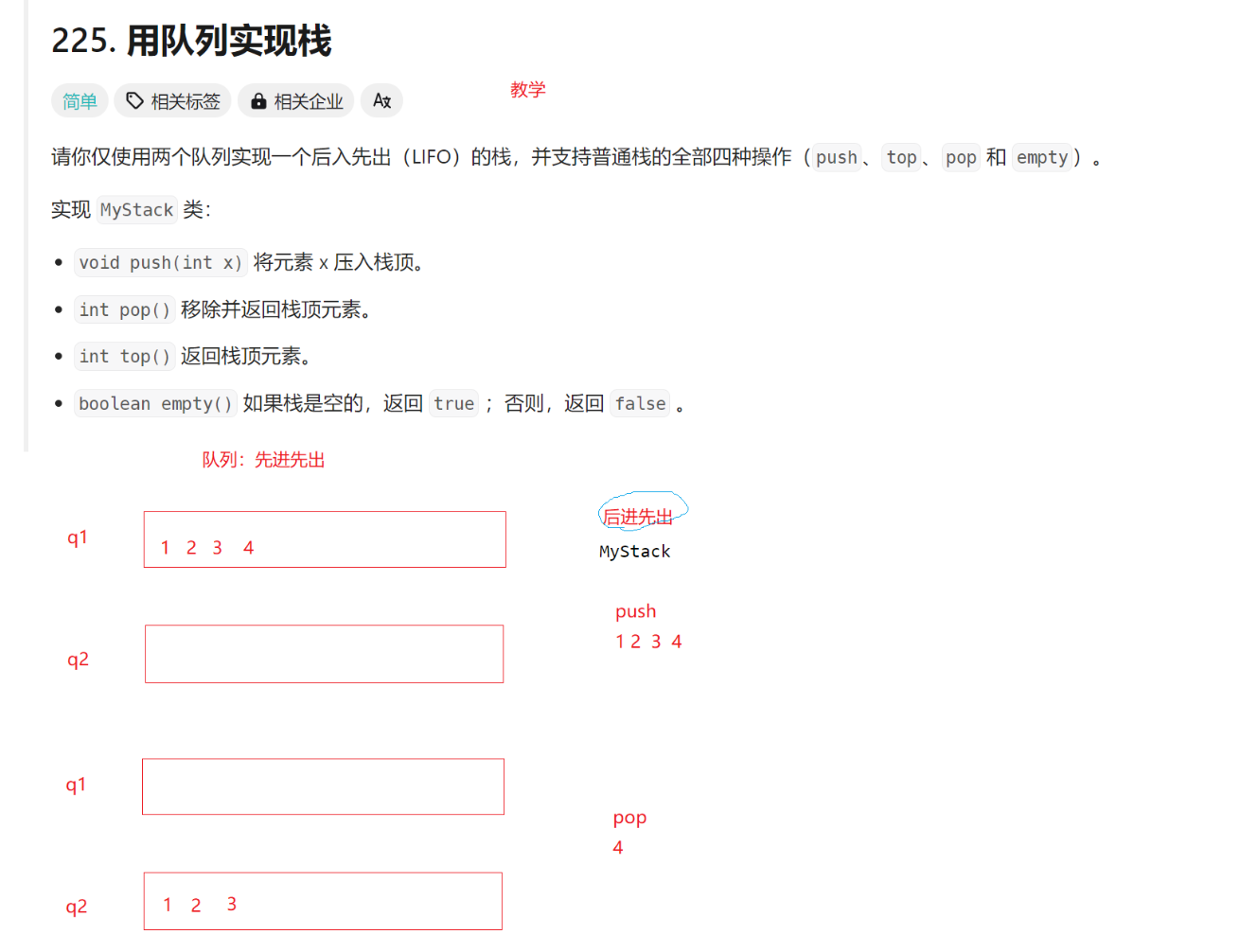
此题是用队列的知识来实现栈,(队列是先进先出,栈是后进先出)
这道题方法是创建俩个队列,进数据就全部进其中一个,实现移除栈顶元素时,就把除栈顶元素的其他元素移到另一个队列上,原来队列就只剩要被移除的元素(出列),返回栈顶元素就是把队列的最后一个元素返回,判断空时需要把俩个队列都判断,都为空时才为空。
代码实现:
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode {
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType val;
} QNode;
typedef struct Queue {
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
} Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
// 队尾插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
// 队头删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
// 取队头和队尾的数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
void QueueInit(Queue* pq) {
assert(pq);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq) {
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur) {
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
// 队尾插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x) {
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL) {
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->next = NULL;
newnode->val = x;
if (pq->ptail == NULL) {
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
} else {
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
// 队头删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq) {
assert(pq);
assert(pq->size != 0);
/*QNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
if (pq->phead == NULL)
pq->ptail = NULL;*/
// 一个节点
if (pq->phead->next == NULL) {
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
} else // 多个节点
{
QNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq) {
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
return pq->phead->val;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq) {
assert(pq);
assert(pq->ptail);
return pq->ptail->val;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq) {
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq) {
assert(pq);
return pq->size == 0;
}
typedef struct {
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* pst = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&(pst->q1));
QueueInit(&(pst->q2));
return pst;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
if (!QueueEmpty(&(obj->q1))) {
QueuePush(&(obj->q1), x);
} else {
QueuePush((&obj->q2), x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
Queue* empty = &(obj->q1);//假设法,随便假设其中一个为空,在通过判断来决定是否假设正确,错的话在互相交换
Queue* noempty = &(obj->q2);
if (!QueueEmpty(&(obj->q1))) {
empty = &(obj->q2);
noempty = &(obj->q1);
}
while (QueueSize(noempty) > 1) {
QueuePush(empty, QueueFront(noempty));
QueuePop(noempty);
}
int top = QueueFront(noempty);
QueuePop(noempty);
return top;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
if (!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)) {
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
} else {
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&(obj->q1)) && QueueEmpty(&(obj->q2));
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestroy(&(obj->q1));//因为队列是链表实现的,后面连着很多节点,不能直接用free调用函数来销毁
QueueDestroy(&(obj->q2));
free(obj);//free的功能是把指向的空间释放,但指针仍然存在,依旧指向原来的空间。
}




















 3485
3485

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








