求高度(下往上数):一般后序遍历
求深度(上往下数):一般前序遍历
但求最大深度其实就是求根结点的高度,再加上前序遍历代码更繁琐,所以使用后序遍历。
104.二叉树的最大深度
题目内容:给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
示例 1:
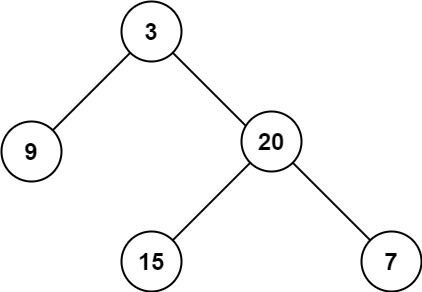
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:3
我的代码(迭代法):
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if(root) que.push(root);
int cnt = 0;
while(!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
while(size--) {
TreeNode* temp = que.front();
que.pop();
if(temp -> left) {
que.push(temp -> left);
}
if(temp -> right) {
que.push(temp -> right);
}
}
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
};反思:这道题使用二叉树的层序遍历,二叉树的最大深度其实就是二叉树的层数,所以直接套用层序遍历模板即可。
递归法:
class solution {
public:
int getdepth(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) return 0;
int leftdepth = getdepth(node->left); // 左
int rightdepth = getdepth(node->right); // 右
int depth = 1 + max(leftdepth, rightdepth); // 中
return depth;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getdepth(root);
}
};思路:递归法就是从下往上数,遇到叶子结点(高度为0),返回高度0;之后每层遍历都把高度+1,返回该结果给父节点。
111.二叉树的最小深度
题目内容:给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
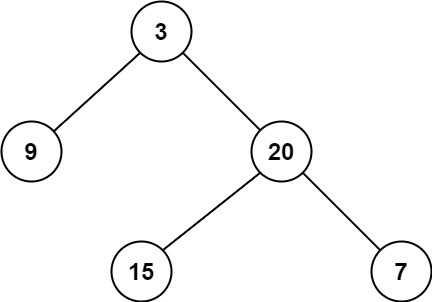
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:2
注意:只有遍历到叶子结点才能计算深度
本题迭代法其实和上一题差不多,因为循环轮数越多就代表深度越大,所以只要一遍历到叶子结点就可以算出最小深度。
我的代码(迭代法):
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
int result = 0;
while(!que.empty()) {
result++;
int size = que.size();
while(size--) {
TreeNode* temp = que.front();
que.pop();
if(temp -> left) que.push(temp -> left);
if(temp -> right) que.push(temp -> right);
if((temp -> left == nullptr) && (temp -> right == nullptr)) return result;
}
}
return result;
}
};递归法:
class Solution {
public:
int getDepth(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) return 0;
int leftDepth = getDepth(node->left); // 左
int rightDepth = getDepth(node->right); // 右
// 中
// 当一个左子树为空,右不为空,这时并不是最低点
if (node->left == NULL && node->right != NULL) {
return 1 + rightDepth;
}
// 当一个右子树为空,左不为空,这时并不是最低点
if (node->left != NULL && node->right == NULL) {
return 1 + leftDepth;
}
int result = 1 + min(leftDepth, rightDepth);
return result;
}
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getDepth(root);
}
};注意:递归法要注意踩坑,当左右子树只有一个空时还不算遍历到了叶子结点,并且要继续往有子树的方向继续遍历下去,所以中间加了两个判断条件,别的地方思路与上题递归法一致。
222.完全二叉树的结点个数
题目内容:给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
我的代码(迭代法):
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
int result = 0;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
result += size;
while(size--) {
TreeNode* temp = que.front();
que.pop();
if(temp -> left) que.push(temp -> left);
if(temp -> right) que.push(temp -> right);
}
}
return result;
}
};还是迭代法好啊。。。一个模板可以套这么多题目,递归法实在抽象理解起来对我来说有点困难了。。。





















 239
239

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








