做题链接
题目描述
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示Node.val的整数。random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从0到n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为null。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
示例 1:
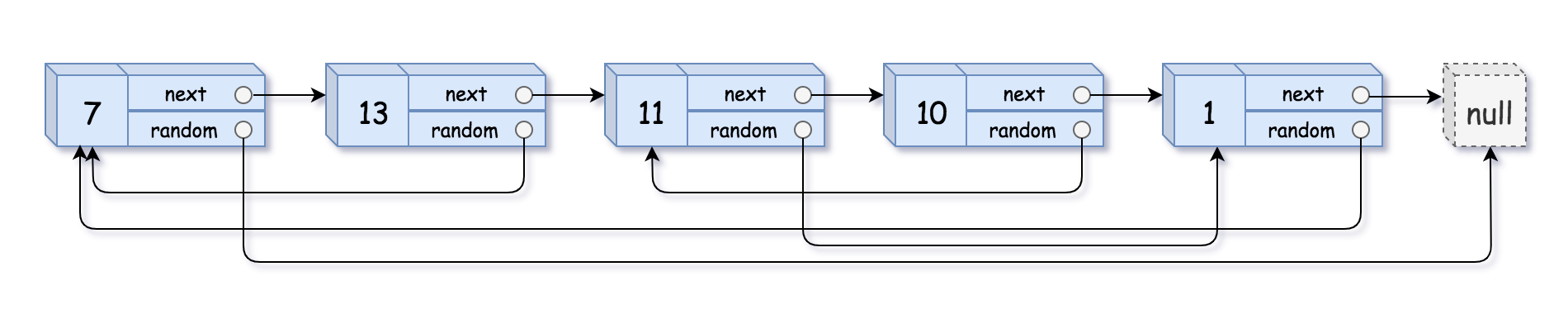
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]] 输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
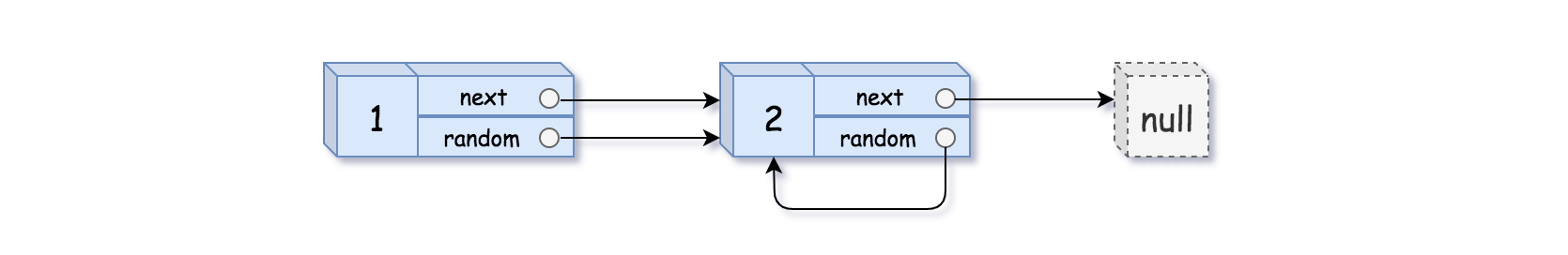
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]] 输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
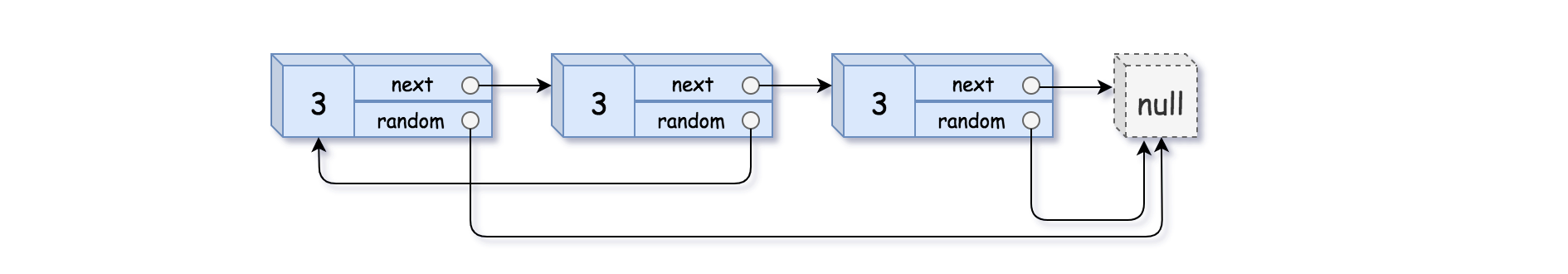
输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]] 输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
提示:
0 <= n <= 1000-104 <= Node.val <= 104Node.random为null或指向链表中的节点。
解题思路
此题难点在于random指针的控制。
1.第一步,遍历原链表, 在原节点(cur)后插入该节点的拷贝节点(copy)。这样,我们可以在遍历原链表时通过该节点的next指针找到它的拷贝节点(copy = cur->next)。
2.第二步,遍历插入拷贝节点后的链表,控制random。
当原节点的random指向NULL(cur->random = NULL),我们让拷贝节点的random指向NULL即可(copy->random = NULL);
当原节点的random指向原链表中的任意节点,我们可以通过原节点的random找到它指向的原链表中的某一个节点,在通过该节点的next指针找到它的拷贝节点,就能把原节点的拷贝节点与该节点的拷贝节点连接(copy->random = cur->random->next)。
3.第三步,再次遍历插入拷贝节点后的链表,把拷贝节点插入到新链表中。
解题代码
/**
* Definition for a Node.
* struct Node {
* int val;
* struct Node *next;
* struct Node *random;
* };
*/
typedef struct Node Node;
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
//空链表无须拷贝,直接返回
if(head == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
//第一步
Node* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
Node* copy = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(copy == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(1);
}
copy->val = cur->val;
//拷贝节点插入到原节点之后
copy->next = cur->next;
cur->next = copy;
cur = copy->next;
}
//第二步,控制random
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
Node* copy = cur->next;
if(cur->random == NULL)
{
copy->random = NULL;
}
else
{
copy->random = cur->random->next;
}
cur = copy->next;
}
//第三步,把拷贝节点插入到新链表中
Node* newhead,*newtail;
newhead = newtail = NULL;
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
Node* copy = cur->next;
if(newhead == NULL)
{
newhead = newtail = copy;
}
else
{
newtail->next = copy;
newtail = newtail->next;
}
cur->next = copy->next;//恢复原链表
cur = copy->next;
}
return newhead;
}以上仅提供了解题的一种思路。感谢各位读者的支持!





















 793
793











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








