我们之前学习过MySQL中的事务操作,Spring也对事务进行了实现。
1. Spring 中事务的实现
Spring 中的事务操作分为两类:
- 编程式事务(手动写代码操作事务)
- 声明式事务(利用注解自动开启和提交事务)
学习事务之前我们先准备数据和数据的访问代码
需求:用户注册,注册时在日志表中插入一条操作记录
数据准备:
-- 创建数据库
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS trans_test;
CREATE DATABASE trans_test DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4;
-- ⽤⼾表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS user_info;
CREATE TABLE user_info (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_name` VARCHAR (128) NOT NULL,
`password` VARCHAR (128) NOT NULL,
`create_time` DATETIME DEFAULT now(),
`update_time` DATETIME DEFAULT now() ON UPDATE now(),
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE = INNODB DEFAULT CHARACTER
SET = utf8mb4 COMMENT = '⽤⼾表';
-- 操作⽇志表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS log_info;
CREATE TABLE log_info (
`id` INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
`user_name` VARCHAR ( 128 ) NOT NULL,
`op` VARCHAR ( 256 ) NOT NULL,
`create_time` DATETIME DEFAULT now(),
`update_time` DATETIME DEFAULT now() ON UPDATE now()
) DEFAULT charset 'utf8mb4';代码准备:
创建项目并引入 Spring Web , Mybatis, mysql 等依赖 ,
配置文件:
spring:
application:
name: J20240422-SpringTrans
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/trans_test?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
mybatis:
configuration: # 配置打印 MyBatis⽇志
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true #配置驼峰⾃动转换实体类:
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
public class LogInfo {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String op;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
}import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
public class UserInfo {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
}mapper:
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
@Insert("insert into user_info (`user_name`, `password`) values (#{userName}, #{password})")
Integer registry(String userName, String password);
}import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface LogMapper {
@Insert("insert into log_info (user_name, op) values (#{userName}, #{op})")
Integer insertLog(String userName, String op);
}service:
import com.example.j20240422springtrans.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
public Integer registry(String userName, String password) {
return userMapper.registry(userName, password);
}
}import com.example.j20240422springtrans.mapper.LogMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class LogService {
@Autowired
LogMapper logMapper;
public Integer insertLog(String userName, String op) {
return logMapper.insertLog(userName, op);
}
}controller:
import com.example.j20240422springtrans.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/registry")
public Boolean registry(String userName, String password) {
if(!StringUtils.hasLength(userName) || !StringUtils.hasLength(password)) {
return false;
}
userService.registry(userName, password);
return true;
}
}2 Spring 编程式事务
Spring 手动操作事务和MySQL 操作事务类似,有三个操作:
- 开启事务
- 提交事务
- 回滚事务
SpringBoot 内置了两个对象:
- DataSourceTransactionManager 事务管理器,用来开启事务,提交或回滚事务。
- TransactionDefinition 是事务的属性,在获取事务时需要将TransactionDefinition 传递进去获得一个事务 TransactionStatus 记录当前事务的状态。
import com.example.j20240422springtrans.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionDefinition;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionStatus;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager;
@Autowired
private TransactionDefinition transactionDefinition;
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/registry")
public Boolean registry(String userName, String password) {
if(!StringUtils.hasLength(userName) || !StringUtils.hasLength(password)) {
return false;
}
//开启事务
TransactionStatus transactionStatus = dataSourceTransactionManager.getTransaction(transactionDefinition);
userService.registry(userName, password);
//回滚事务
//dataSourceTransactionManager.rollback(transactionStatus);
//提交事务
dataSourceTransactionManager.commit(transactionStatus);
return true;
}
}使用浏览器访问:127.0.0.1:8080/user/registry?userName=xiaogang&password=123456
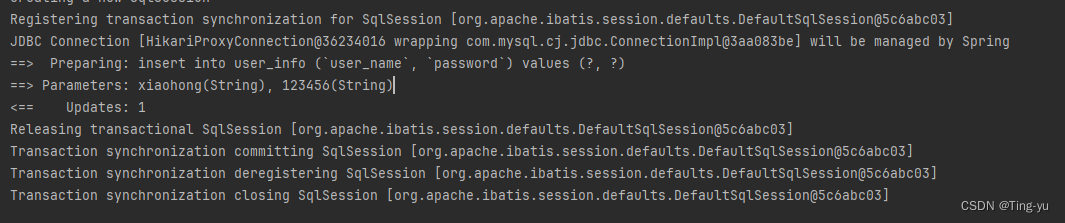
可以看到事务提交,数据库中也能查到信息:

我们把回滚事务的代码取消注释再次运行:
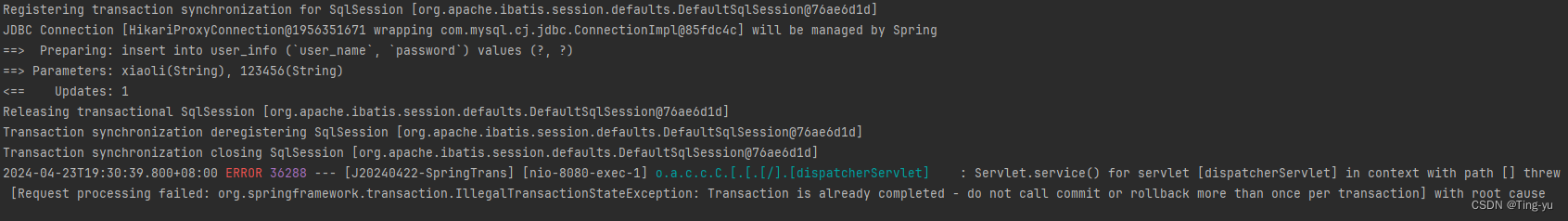
可以看到 mybatis的日志显示插入成功了,但是我们的事务日志显示回滚了,并且数据库中并没有对应的值:

我们再次注释掉回滚事务的代码,再次插入一条数据:
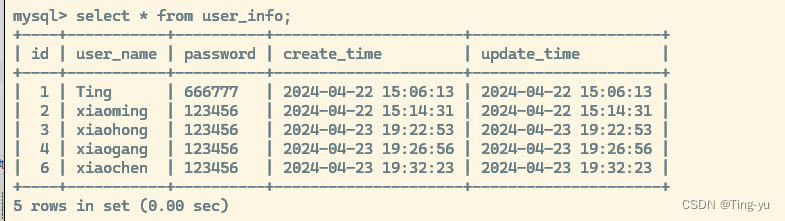
我们发现缺少了id为5的主键,说明事务的回滚相当于把我们插入的数据删除了。
解释:
- 开启事务,相当于储存了当前事务的一个状态,而回滚事务相当于通过储存的事务状态来恢复为之前的事务。
3. Spring 声明式事务
声明式事务的实现很简单:
1. 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
</dependency>
2. 在需要事务的方法上添加 @Transactional 注解
import com.example.j20240422springtrans.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/trans")
public class TransController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Transactional
@RequestMapping("/registry")
public Boolean registry(String userName, String password) {
if(!StringUtils.hasLength(userName) || !StringUtils.hasLength(password)) {
return false;
}
userService.registry(userName, password);
return true;
}
}当运行到该方法时,会自动开始事务,并在结束时提交事务。
@Transactional 可用用来修饰类和方法:
- 修饰方法时:只有修饰public 方法时才生效
- 修饰类时:相当于修饰类中的所有 public 方法
- 在方法执行过程中,如果出现异常且异常未被捕获就进行事务回滚操作,也可以手动回滚
回滚演示:
1. 出现未捕获异常
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/trans")
public class TransController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Transactional
@RequestMapping("/registry")
public Boolean registry(String userName, String password) {
if(!StringUtils.hasLength(userName) || !StringUtils.hasLength(password)) {
return false;
}
userService.registry(userName, password);
int a = 10 / 0;
return true;
}
}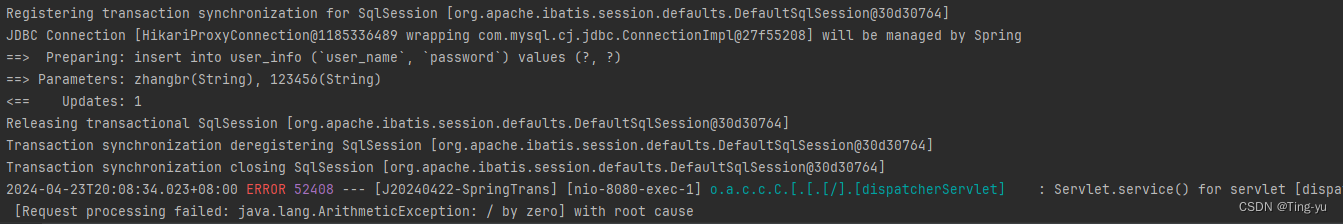
事务未被提交,数据库中也没有对应的值: 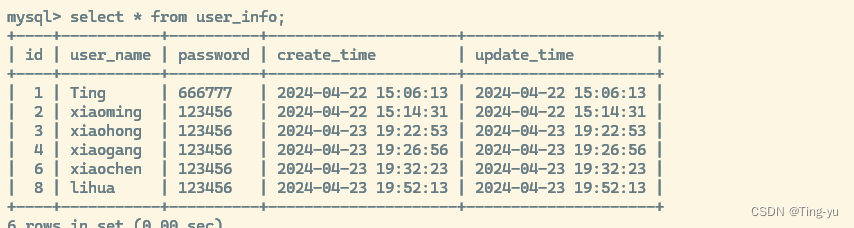
2. 手动回滚
使用 TransactionalAspectSupport.currentTransactionStatus() 获取当前的事务,使用 setRollbackOnly 设置 setRollbackOnly
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/trans")
public class TransController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Transactional
@RequestMapping("/registry")
public Boolean registry(String userName, String password) {
if(!StringUtils.hasLength(userName) || !StringUtils.hasLength(password)) {
return false;
}
userService.registry(userName, password);
//手动回滚
TransactionAspectSupport.currentTransactionStatus().setRollbackOnly();
return true;
}
}






 本文详细介绍了Spring框架中事务的两种实现方式:编程式事务(手动控制)和声明式事务(使用注解自动管理)。通过实际操作演示了如何在SpringBoot项目中使用DataSourceTransactionManager和@Transactional注解进行事务处理,以及异常处理中的回滚机制。
本文详细介绍了Spring框架中事务的两种实现方式:编程式事务(手动控制)和声明式事务(使用注解自动管理)。通过实际操作演示了如何在SpringBoot项目中使用DataSourceTransactionManager和@Transactional注解进行事务处理,以及异常处理中的回滚机制。















 988
988

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










