Sync包
sync包是go提供的用于并发控制的方法,类似于Java的JUC包。
(图片来自《go设计与实现》)
互斥锁 Mutex
Go 语言的 sync.Mutex 由两个字段 state 和 sema 组成。
state表示当前互斥锁的状态。sema是用于控制锁状态的信号量。
type Mutex struct {
state int32
sema uint32
}
go的互斥锁功能相对比较简单:
mutex 本身没有包含持有这把锁的 goroutine 的信息,因此
- 无法实现可重入锁。
- 可能锁会被其他goroutine释放。
常见的错误场景:
- Lock / UnLock 不是成对出现
- Copy 已使用的 Mutex(不可以复制)
原因:Mutex 是一个有状态的字段,在并发环境下,状态时时在变化。 - 重入
- 死锁
状态
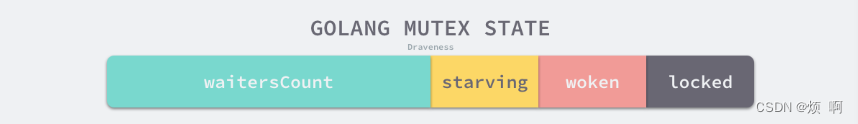
在默认情况下,互斥锁的所有状态位都是 0,int32 中的不同位分别表示了不同的状态:
mutexLocked— 表示互斥锁的锁定状态。mutexWoken— 表示从正常模式被从唤醒。mutexStarving— 当前的互斥锁进入饥饿状态。waitersCount— 当前互斥锁上等待的 Goroutine 个数。
const (
mutexLocked = 1 << iota // mutex is locked
mutexWoken
mutexStarving
mutexWaiterShift = iota
// Mutex fairness.
//
// Mutex can be in 2 modes of operations: normal and starvation.
// In normal mode waiters are queued in FIFO order, but a woken up waiter
// does not own the mutex and competes with new arriving goroutines over
// the ownership. New arriving goroutines have an advantage -- they are
// already running on CPU and there can be lots of them, so a woken up
// waiter has good chances of losing. In such case it is queued at front
// of the wait queue. If a waiter fails to acquire the mutex for more than 1ms,
// it switches mutex to the starvation mode.
//
// In starvation mode ownership of the mutex is directly handed off from
// the unlocking goroutine to the waiter at the front of the queue.
// New arriving goroutines don't try to acquire the mutex even if it appears
// to be unlocked, and don't try to spin. Instead they queue themselves at
// the tail of the wait queue.
//
// If a waiter receives ownership of the mutex and sees that either
// (1) it is the last waiter in the queue, or (2) it waited for less than 1 ms,
// it switches mutex back to normal operation mode.
//
// Normal mode has considerably better performance as a goroutine can acquire
// a mutex several times in a row even if there are blocked waiters.
// Starvation mode is important to prevent pathological cases of tail latency.
starvationThresholdNs = 1e6
)
sync.Mutex 有两种模式 — 正常模式和饥饿模式。
在正常模式下,锁的等待者会按照先进先出的顺序获取锁,但被唤醒的goroutine不拥有互斥锁,并与新到达的goroutine争夺所有权。
新来的goroutines有一个优势——它们已经在CPU上运行了,而且可能有很多,所以被唤醒的gorountine很有可能会失败。
为了减少这种情况的出现,一旦 Goroutine 超过 1ms 没有获取到锁,它就会将当前互斥锁切换饥饿模式,防止部分 Goroutine 饿死。
从性能上来看,如果我们能够把锁交给正在占用 CPU 时间片的 goroutine 的话,那就不需要做上下文的切换,在高并发的情况下,可能会有更好的性能。
饥饿模式是为了保证互斥锁的公平性。
在饥饿模式中,互斥锁会直接交给等待队列最前面的 Goroutine。新的 Goroutine 在该状态下不能获取锁、也不会进入自旋状态,它们只会在队列的末尾等待。如果一个 Goroutine 获得了互斥锁并且它在队列的末尾或者它等待的时间少于 1ms,那么当前的互斥锁就会切换回正常模式。
与饥饿模式相比,正常模式下的互斥锁能够提供更好地性能,饥饿模式的能避免 Goroutine 由于陷入等待无法获取锁而造成的高尾延时。





















 1328
1328











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








