网上说的天花乱坠的,也不如直接看 Doug Lea 大佬源码的注释来的更加贴切些。

corePoolSize:the number of threads to keep in the pool, even if they are idle, unless {@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut} is set
核心线程数:线程池中保留的线程数,即使它们是空闲的,除非设置 allowCoreThreadTimeOut。
maximumPoolSize:the maximum number of threads to allow in the pool
最大线程数:线程池中允许的最大线程数
keepAliveTime:when the number of threads is greater than the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads will wait for new tasks before terminating.
线程空闲时间:如果经过 keepAliveTime 时间后,超过核心线程数的线程还没有接受到新的任务,那就回收。
unit:the time unit for the {@code keepAliveTime} argument
单位:keepAliveTime 的时间单位
workQueue:the queue to use for holding tasks before they are executed. This queue will hold only the {@code Runnable} tasks submitted by the {@code execute} method.
存放待执行任务的队列:当提交的任务数超过核心线程数后,再提交的任务就存放在这里。它仅仅用来存放被 execute 方法提交的 Runnable 任务。
threadFactory:the factory to use when the executor creates a new thread
线程工厂:执行程序创建新线程时使用的工厂。比如我们项目中自定义的线程工厂,排查问题的时候,根据线程工厂的名称就知道这个线程来自哪里,很快地定位出问题,
handler :the handler to use when execution is blocked because the thread bounds and queue capacities are reached
拒绝策略:当队列里面放满了任务、最大线程数的线程都在工作时,这时继续提交的任务线程池就处理不了,应该执行怎么样的拒绝策略。
二、线程池的实现原理
==========
本文描述线程池是 JDK 8 中提供的 ThreadPoolExecutor 类,那我们就从 ThreadPoolExecutor 类来看下它的 UML 依赖关系。
2.1 总体设计
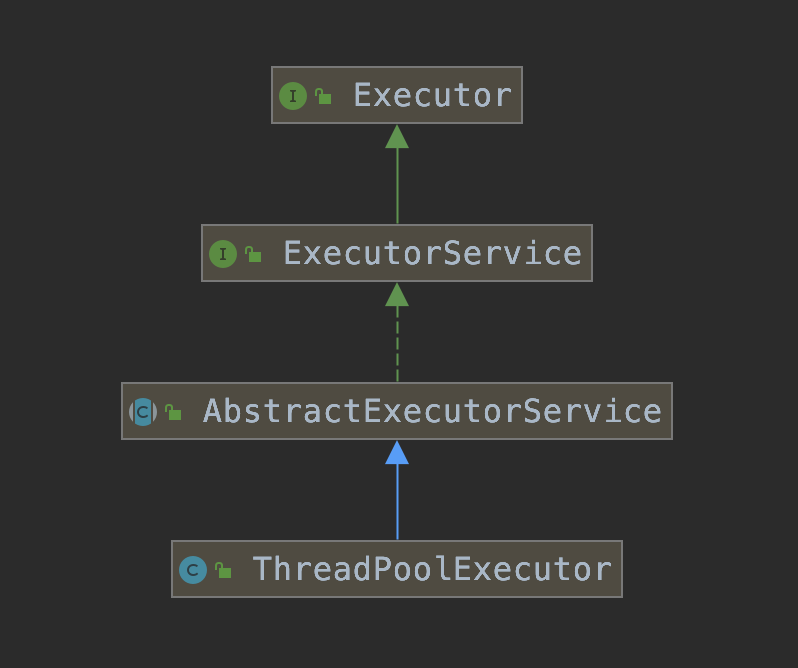
-
蓝色实线:继承关系
-
绿色虚线:接口实现关系
-
绿色实现:接口继承关系








 线程池在内部实际上构建了一个生产者消费者模型,将线程和任务两者解耦,并不直接关联,从而良好的缓冲任务,复用线程。
线程池在内部实际上构建了一个生产者消费者模型,将线程和任务两者解耦,并不直接关联,从而良好的缓冲任务,复用线程。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 1637
1637











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








