List personListNew = personList.stream().map(person -> {
Person personNew = new Person(person.getName(), 0, 0, null, null);
personNew.setSalary(person.getSalary() + 10000);
return personNew;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(“一次改动前:” + personList.get(0).getName() + “–>” + personList.get(0).getSalary());
System.out.println(“一次改动后:” + personListNew.get(0).getName() + “–>” + personListNew.get(0).getSalary());
// 改变原来员工集合的方式
List personListNew2 = personList.stream().map(person -> {
person.setSalary(person.getSalary() + 10000);
return person;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(“二次改动前:” + personList.get(0).getName() + “–>” + personListNew.get(0).getSalary());
System.out.println(“二次改动后:” + personListNew2.get(0).getName() + “–>” + personListNew.get(0).getSalary());
}
}
一次改动前:Tom–>8900 一次改动后:Tom–>18900 二次改动前:Tom–>18900 二次改动后:Tom–>18900
案例三:将两个字符数组合并成一个新的字符数组。
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = Arrays.asList(“m,k,l,a”, “1,3,5,7”);
List listNew = list.stream().flatMap(s -> {
// 将每个元素转换成一个stream
String[] split = s.split(“,”);
Stream s2 = Arrays.stream(split);
return s2;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(“处理前的集合:” + list);
System.out.println(“处理后的集合:” + listNew);
}
}
输出结果:
处理前的集合:[m-k-l-a, 1-3-5] 处理后的集合:[m, k, l, a, 1, 3, 5]
3.5 归约(reduce)
推荐阅读:最新 Java 核心技术教程,都在这了!
归约,也称缩减,顾名思义,是把一个流缩减成一个值,能实现对集合求和、求乘积和求最值操作。
案例一:求Integer集合的元素之和、乘积和最大值。
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = Arrays.asList(1, 3, 2, 8, 11, 4);
// 求和方式1
Optional sum = list.stream().reduce((x, y) -> x + y);
// 求和方式2
Optional sum2 = list.stream().reduce(Integer::sum);
// 求和方式3
Integer sum3 = list.stream().reduce(0, Integer::sum);
// 求乘积
Optional product = list.stream().reduce((x, y) -> x * y);
// 求最大值方式1
Optional max = list.stream().reduce((x, y) -> x > y ? x : y);
// 求最大值写法2
Integer max2 = list.stream().reduce(1, Integer::max);
System.out.println(“list求和:” + sum.get() + “,” + sum2.get() + “,” + sum3);
System.out.println(“list求积:” + product.get());
System.out.println(“list求和:” + max.get() + “,” + max2);
}
}
输出结果:
list求和:29,29,29 list求积:2112 list求和:11,11
案例二:求所有员工的工资之和和最高工资。
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List personList = new ArrayList();
personList.add(new Person(“Tom”, 8900, 23, “male”, “New York”));
personList.add(new Person(“Jack”, 7000, 25, “male”, “Washington”));
personList.add(new Person(“Lily”, 7800, 21, “female”, “Washington”));
personList.add(new Person(“Anni”, 8200, 24, “female”, “New York”));
personList.add(new Person(“Owen”, 9500, 25, “male”, “New York”));
personList.add(new Person(“Alisa”, 7900, 26, “female”, “New York”));
// 求工资之和方式1:
Optional sumSalary = personList.stream().map(Person::getSalary).reduce(Integer::sum);
// 求工资之和方式2:
Integer sumSalary2 = personList.stream().reduce(0, (sum, p) -> sum += p.getSalary(),
(sum1, sum2) -> sum1 + sum2);
// 求工资之和方式3:
Integer sumSalary3 = personList.stream().reduce(0, (sum, p) -> sum += p.getSalary(), Integer::sum);
// 求最高工资方式1:
Integer maxSalary = personList.stream().reduce(0, (max, p) -> max > p.getSalary() ? max : p.getSalary(),
Integer::max);
// 求最高工资方式2:
Integer maxSalary2 = personList.stream().reduce(0, (max, p) -> max > p.getSalary() ? max : p.getSalary(),
(max1, max2) -> max1 > max2 ? max1 : max2);
System.out.println(“工资之和:” + sumSalary.get() + “,” + sumSalary2 + “,” + sumSalary3);
System.out.println(“最高工资:” + maxSalary + “,” + maxSalary2);
}
}
输出结果:
工资之和:49300,49300,49300 最高工资:9500,9500
3.6 收集(collect)
collect,收集,可以说是内容最繁多、功能最丰富的部分了。从字面上去理解,就是把一个流收集起来,最终可以是收集成一个值也可以收集成一个新的集合。
collect主要依赖java.util.stream.Collectors类内置的静态方法。
3.6.1 归集(toList/toSet/toMap)
因为流不存储数据,那么在流中的数据完成处理后,需要将流中的数据重新归集到新的集合里。toList、toSet和toMap比较常用,另外还有toCollection、toConcurrentMap等复杂一些的用法。
下面用一个案例演示toList、toSet和toMap:
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = Arrays.asList(1, 6, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 6, 20);
List listNew = list.stream().filter(x -> x % 2 == 0).collect(Collectors.toList());
Set set = list.stream().filter(x -> x % 2 == 0).collect(Collectors.toSet());
List personList = new ArrayList();
personList.add(new Person(“Tom”, 8900, 23, “male”, “New York”));
personList.add(new Person(“Jack”, 7000, 25, “male”, “Washington”));
personList.add(new Person(“Lily”, 7800, 21, “female”, “Washington”));
personList.add(new Person(“Anni”, 8200, 24, “female”, “New York”));
Map<?, Person> map = personList.stream().filter(p -> p.getSalary() > 8000)
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getName, p -> p));
System.out.println(“toList:” + listNew);
System.out.println(“toSet:” + set);
System.out.println(“toMap:” + map);
}
}
运行结果:
toList:[6, 4, 6, 6, 20] toSet:[4, 20, 6] toMap:{Tom=mutest.Person@5fd0d5ae, Anni=mutest.Person@2d98a335}
3.6.2 统计(count/averaging)
Collectors提供了一系列用于数据统计的静态方法:
-
计数:
count -
平均值:
averagingInt、averagingLong、averagingDouble -
最值:
maxBy、minBy -
求和:
summingInt、summingLong、summingDouble -
统计以上所有:
summarizingInt、summarizingLong、summarizingDouble
案例:统计员工人数、平均工资、工资总额、最高工资。
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List personList = new ArrayList();
personList.add(new Person(“Tom”, 8900, 23, “male”, “New York”));
personList.add(new Person(“Jack”, 7000, 25, “male”, “Washington”));
personList.add(new Person(“Lily”, 7800, 21, “female”, “Washington”));
// 求总数
Long count = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.counting());
// 求平均工资
Double average = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Person::getSalary));
// 求最高工资
Optional max = personList.stream().map(Person::getSalary).collect(Collectors.maxBy(Integer::compare));
// 求工资之和
Integer sum = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.summingInt(Person::getSalary));
// 一次性统计所有信息
DoubleSummaryStatistics collect = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingDouble(Person::getSalary));
System.out.println(“员工总数:” + count);
System.out.println(“员工平均工资:” + average);
System.out.println(“员工工资总和:” + sum);
System.out.println(“员工工资所有统计:” + collect);
}
}
运行结果:
员工总数:3 员工平均工资:7900.0 员工工资总和:23700 员工工资所有统计:DoubleSummaryStatistics{count=3, sum=23700.000000,min=7000.000000, average=7900.000000, max=8900.000000}
3.6.3 分组(partitioningBy/groupingBy)
-
分区:将
stream按条件分为两个Map,比如员工按薪资是否高于8000分为两部分。 -
分组:将集合分为多个Map,比如员工按性别分组。有单级分组和多级分组。
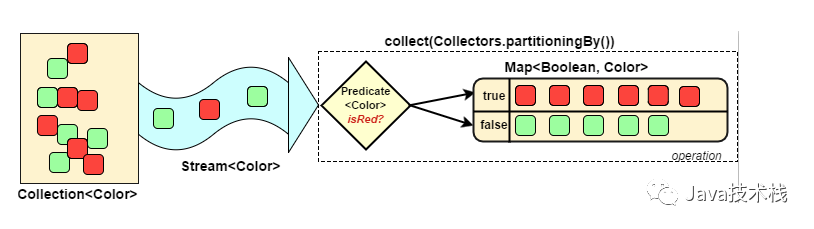
案例:将员工按薪资是否高于8000分为两部分;将员工按性别和地区分组
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List personList = new ArrayList();
personList.add(new Person(“Tom”, 8900, “male”, “New York”));
personList.add(new Person(“Jack”, 7000, “male”, “Washington”));
personList.add(new Person(“Lily”, 7800, “female”, “Washington”));
personList.add(new Person(“Anni”, 8200, “female”, “New York”));
personList.add(new Person(“Owen”, 9500, “male”, “New York”));
personList.add(new Person(“Alisa”, 7900, “female”, “New York”));
// 将员工按薪资是否高于8000分组
Map<Boolean, List> part = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(x -> x.getSalary() > 8000));
// 将员工按性别分组
Map<String, List> group = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getSex));
// 将员工先按性别分组,再按地区分组
Map<String, Map<String, List>> group2 = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getSex, Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getArea)));
System.out.println(“员工按薪资是否大于8000分组情况:” + part);
System.out.println(“员工按性别分组情况:” + group);
System.out.println(“员工按性别、地区:” + group2);
}
}
输出结果:
员工按薪资是否大于8000分组情况:{false=[mutest.Person@2d98a335, mutest.Person@16b98e56, mutest.Person@7ef20235], true=[mutest.Person@27d6c5e0, mutest.Person@4f3f5b24, mutest.Person@15aeb7ab]}
员工按性别分组情况:{female=[mutest.Person@16b98e56, mutest.Person@4f3f5b24, mutest.Person@7ef20235], male=[mutest.Person@27d6c5e0, mutest.Person@2d98a335, mutest.Person@15aeb7ab]}
员工按性别、地区:{female={New York=[mutest.Person@4f3f5b24, mutest.Person@7ef20235], Washington=[mutest.Person@16b98e56]}, male={New York=[mutest.Person@27d6c5e0, mutest.Person@15aeb7ab], Washington=[mutest.Person@2d98a335]}}
3.6.4 接合(joining)
joining可以将stream中的元素用特定的连接符(没有的话,则直接连接)连接成一个字符串。
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List personList = new ArrayList();
personList.add(new Person(“Tom”, 8900, 23, “male”, “New York”));
personList.add(new Person(“Jack”, 7000, 25, “male”, “Washington”));
personList.add(new Person(“Lily”, 7800, 21, “female”, “Washington”));
String names = personList.stream().map(p -> p.getName()).collect(Collectors.joining(“,”));
System.out.println(“所有员工的姓名:” + names);
List list = Arrays.asList(“A”, “B”, “C”);
String string = list.stream().collect(Collectors.joining(“-”));
System.out.println(“拼接后的字符串:” + string);
}
}
运行结果:
所有员工的姓名:Tom,Jack,Lily 拼接后的字符串:A-B-C
3.6.5 归约(reducing)
Collectors类提供的reducing方法,相比于stream本身的reduce方法,增加了对自定义归约的支持。
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List personList = new ArrayList();
personList.add(new Person(“Tom”, 8900, 23, “male”, “New York”));
personList.add(new Person(“Jack”, 7000, 25, “male”, “Washington”));
personList.add(new Person(“Lily”, 7800, 21, “female”, “Washington”));
// 每个员工减去起征点后的薪资之和(这个例子并不严谨,但一时没想到好的例子)
Integer sum = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.reducing(0, Person::getSalary, (i, j) -> (i + j - 5000)));
System.out.println(“员工扣税薪资总和:” + sum);
// stream的reduce
Optional sum2 = personList.stream().map(Person::getSalary).reduce(Integer::sum);
System.out.println(“员工薪资总和:” + sum2.get());
}
}
运行结果:
员工扣税薪资总和:8700 员工薪资总和:23700
3.7 排序(sorted)
sorted,中间操作。有两种排序:
-
sorted():自然排序,流中元素需实现Comparable接口
-
sorted(Comparator com):Comparator排序器自定义排序
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List personList = new ArrayList();
personList.add(new Person(“Sherry”, 9000, 24, “female”, “New York”));
personList.add(new Person(“Tom”, 8900, 22, “male”, “Washington”));
personList.add(new Person(“Jack”, 9000, 25, “male”, “Washington”));
personList.add(new Person(“Lily”, 8800, 26, “male”, “New York”));
personList.add(new Person(“Alisa”, 9000, 26, “female”, “New York”));
// 按工资升序排序(自然排序)
List newList = personList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getSalary)).map(Person::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 按工资倒序排序
List newList2 = personList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getSalary).reversed())
.map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 先按工资再按年龄升序排序
List newList3 = personList.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getSalary).thenComparing(Person::getAge)).map(Person::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 先按工资再按年龄自定义排序(降序)
List newList4 = personList.stream().sorted((p1, p2) -> {
if (p1.getSalary() == p2.getSalary()) {
return p2.getAge() - p1.getAge();
} else {
return p2.getSalary() - p1.getSalary();
}
}).map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(“按工资升序排序:” + newList);
System.out.println(“按工资降序排序:” + newList2);
System.out.println(“先按工资再按年龄升序排序:” + newList3);
System.out.println(“先按工资再按年龄自定义降序排序:” + newList4);
}
}
按工资自然排序:[Lily, Tom, Sherry, Jack, Alisa] 按工资降序排序:[Sherry, Jack, Alisa,Tom, Lily] 先按工资再按年龄自然排序:[Sherry, Jack, Alisa, Tom, Lily] 先按工资再按年龄自定义降序排序:[Alisa, Jack, Sherry, Tom, Lily]
3.8 提取/组合
流也可以进行合并、去重、限制、跳过等操作。
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] arr1 = { “a”, “b”, “c”, “d” };
String[] arr2 = { “d”, “e”, “f”, “g” };
Stream stream1 = Stream.of(arr1);
Stream stream2 = Stream.of(arr2);
// concat:合并两个流 distinct:去重
List newList = Stream.concat(stream1, stream2).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
// limit:限制从流中获得前n个数据
List collect = Stream.iterate(1, x -> x + 2).limit(10).collect(Collectors.toList());
// skip:跳过前n个数据
List collect2 = Stream.iterate(1, x -> x + 2).skip(1).limit(5).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(“流合并:” + newList);
System.out.println(“limit:” + collect);
System.out.println(“skip:” + collect2);
}
}
小编13年上海交大毕业,曾经在小公司待过,也去过华为、OPPO等大厂,18年进入阿里一直到现在。
深知大多数初中级Java工程师,想要提升技能,往往是自己摸索成长,但自己不成体系的自学效果低效又漫长,而且极易碰到天花板技术停滞不前!
因此收集整理了一份《2024年最新Java开发全套学习资料》送给大家,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助到想自学提升又不知道该从何学起的朋友,同时减轻大家的负担。

由于文件比较大,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,每个节点里面都包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、讲解视频
如果你觉得这些内容对你有帮助,可以添加下面V无偿领取!(备注Java)

总结
谈到面试,其实说白了就是刷题刷题刷题,天天作死的刷。。。。。
为了准备这个“金三银四”的春招,狂刷一个月的题,狂补超多的漏洞知识,像这次美团面试问的算法、数据库、Redis、设计模式等这些题目都是我刷到过的
并且我也将自己刷的题全部整理成了PDF或者Word文档(含详细答案解析)

66个Java面试知识点
架构专题(MySQL,Java,Redis,线程,并发,设计模式,Nginx,Linux,框架,微服务等)+大厂面试题详解(百度,阿里,腾讯,华为,迅雷,网易,中兴,北京中软等)

算法刷题(PDF)

摸索成长,但自己不成体系的自学效果低效又漫长,而且极易碰到天花板技术停滞不前!**
因此收集整理了一份《2024年最新Java开发全套学习资料》送给大家,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助到想自学提升又不知道该从何学起的朋友,同时减轻大家的负担。
[外链图片转存中…(img-30iPIVxy-1710687075209)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-1oZ5jd5S-1710687075210)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-jiO1dqb9-1710687075210)]
由于文件比较大,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,每个节点里面都包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、讲解视频
如果你觉得这些内容对你有帮助,可以添加下面V无偿领取!(备注Java)
[外链图片转存中…(img-ETunH263-1710687075210)]
总结
谈到面试,其实说白了就是刷题刷题刷题,天天作死的刷。。。。。
为了准备这个“金三银四”的春招,狂刷一个月的题,狂补超多的漏洞知识,像这次美团面试问的算法、数据库、Redis、设计模式等这些题目都是我刷到过的
并且我也将自己刷的题全部整理成了PDF或者Word文档(含详细答案解析)
[外链图片转存中…(img-YhDGJ1Ku-1710687075211)]
66个Java面试知识点
架构专题(MySQL,Java,Redis,线程,并发,设计模式,Nginx,Linux,框架,微服务等)+大厂面试题详解(百度,阿里,腾讯,华为,迅雷,网易,中兴,北京中软等)
[外链图片转存中…(img-ZyrWseZL-1710687075211)]
算法刷题(PDF)
[外链图片转存中…(img-XhXK8hUA-1710687075211)]























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








