- 脏读(Dirty Read):一个事务读取了另一个事务尚未提交的数据,如果另一个事务回滚了操作,那么第一个事务读取的数据就是无效的。
- 不可重复读(Non-Repeatable Read):一个事务在读取某一行数据时,另一个事务修改了该行数据并提交了事务,导致第一个事务多次读取同一数据时得到的结果不一致。
- 幻读(Phantom Read):一个事务在读取一组数据时,另一个事务插入了符合该条件的新数据并提交了事务,导致第一个事务再次读取同一数据时得到的结果不一致。
这三种问题可以通过设置不同的事务隔离级别来避免或减少发生。例如,READ COMMITTED隔离级别可以避免脏读问题,REPEATABLE READ隔离级别可以避免脏读和不可重复读问题,而SERIALIZABLE隔离级别可以避免所有并发问题。
2.2、基本原理
由上诉ChatGPT的答复,以及自己以往Spring事务的使用可知。Spring事务管理就是基于AOP实现,主要作用就是统一封装非功能性需求。Spring事务的本质其实就是数据库对事务的支持,没有数据库的事务支持,Spring也无法提供事务功能。
如果我们纯操作JDBC,那么我们可以按照如下步骤进行事务控制:
- Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection();获取数据库连接
- 开启事务是否自动提交,conn.setAutoCommit(true/false)
- JDBC操作
- 提交事务conn.commit()或事务回滚conn.rollback()
- 关闭连接conn.close()
如果使用了Spring事务,我们就不需要手动开启或关闭事务操作(上述第2步和第4步)。而是交由Spring自己完成。那么Spring使用事务的方式有哪些呢?在 Spring 中,我们可以通过声明式事务管理和编程式事务管理两种方式来管理事务。
- 声明式事务管理是指将事务的定义和管理与业务逻辑分离,通过配置文件或注解等方式来实现事务管理。在 Spring 中,可以使用 @Transactional 注解来声明事务。
- 编程式事务管理是指在代码中通过编程的方式来控制事务,即在代码中手动开启、提交和回滚事务。Spring 提供了 TransactionTemplate 类来实现编程式事务管理。
示例代码如下:
// 声明式事务
@Service
public class TestServiceImpl {
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void reduce(){
......
}
}
// 编程式事务
@Service
public class TestServiceImpl {
@Autowired
TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
public void reduce(){
transactionTemplate.execute(status -> {
......
});
}
}
真正的数据库层的事务提交和回滚是通过binglog或redo log实现的。
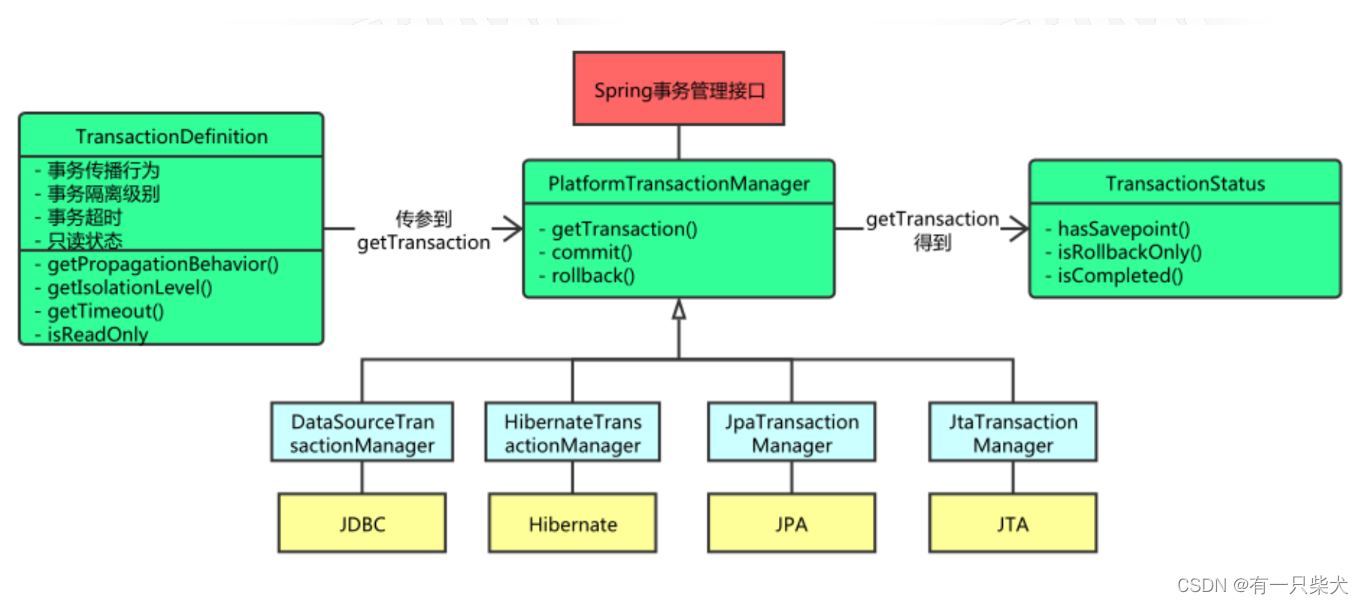
网上借来一张Spring事务API架构图:
3、事务嵌套
前面2章节都是从理论知识的角度阐述了事务的一些基本特性。显然这些背诵的八股文一下子就忘记了。接下来我们以实际业务的角度来分析一下几种传播机制。且以我们平时最常见到的调用方式来说明:那就是事务嵌套。
看一段代码:
@Service
class OrderService {
@Resource
ReduceService reduceService;
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void createOrder(){
// 下单
this.createOrder0();
// 扣除库存
reduceService.reduce();
}
}
@Service
class ReduceService {
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void reduce(){
......
}
}
这时候,OrderService的createOrder()调用ReduceService的reduce()方法,两个方法都声明了事务,这时候就形成了事务嵌套。
3.1、PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
当执行orderService.createOrder()时,spring已经发起事务,这时候调用reduceService.reduce()时,reduceService.reduce()发现自己已经运行在事务内部,就会直接使用外部事务。如果发现外部没有事务,那么就会给reduce()方法新建事务。
当orderService.createOrder()或reduceService.reduce()发生异常时,事务都会被回滚。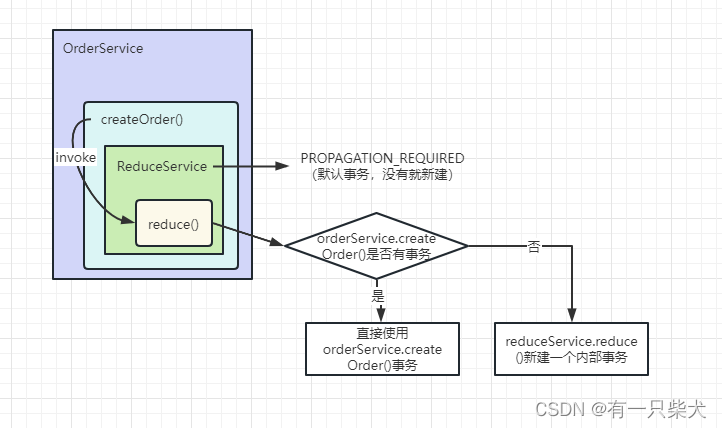
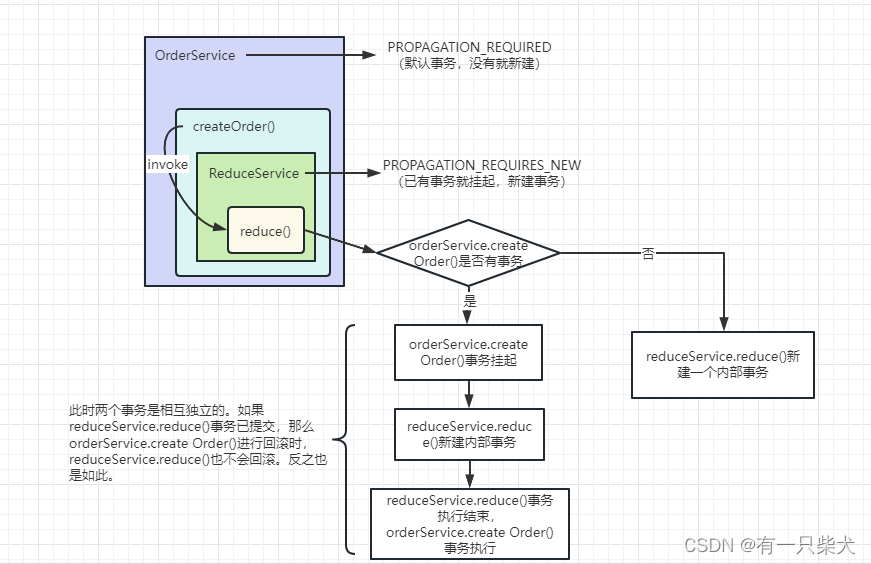
3.2、PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW
当reduceService.reduce()设置了PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW,orderService.createOrder()属性为PROPAGATION_REQUIRED。那么当执行到reduce()方法时,会判断外部是否有事务,如果有,则会挂起外部事务,然后自身创建一个新的内部事务,等到内部事务执行结束后,才会继续执行被挂起的外部事务。
这样的话,由于reduce()是新发起一个事务,且与外部事务是独立的。当createOrder()发生异常时,如果reduce()事务被提交了,那么是reduce()不会回滚的。相应的,如果reduce()抛出异常,被createOrder()捕获,那么createOrder()的事务仍然可能提交,取决于外部事务的回滚操作。
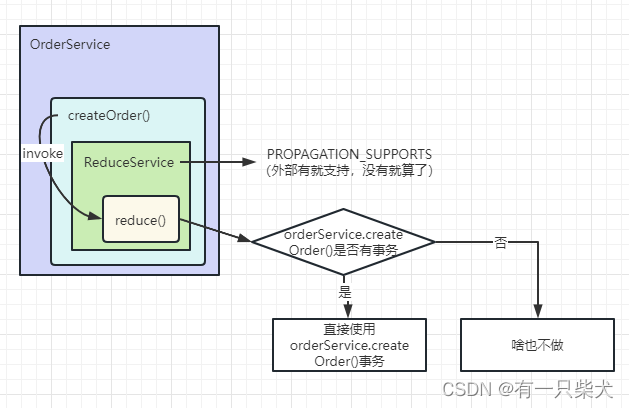
3.3、PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS
与PROPAGATION_REQUIRED类似,只是当执行到reduceService.reduce()方法时,会判断createOrder()是否开启了事务,如果是的话,那么直接支持该事务。如果没有的话,那么自己也不支持事务。这个事务属性是完全取决于外部的事务。
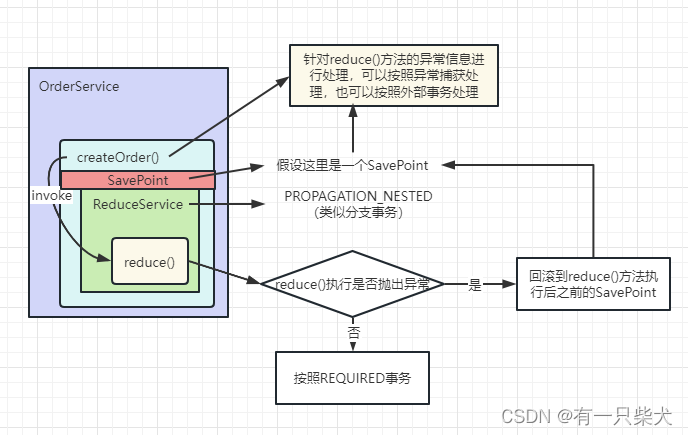
3.4、PROPAGATION_NESTED
当执行到ReduceService.reduce()方法时,如果reduce()出现内部异常,则reduce()会回滚到他执行之前的SavePoint,因此是不会产生脏数据的,相当于该方法从未执行过。
此时createOrder()方法可以直接try-catch异常,然后进行分支逻辑事务处理。如:
@Service
class OrderService {
@Resource
ReduceService reduceService;
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void createOrder(){
// 下单
this.createOrder0();
// 扣除库存
try {
reduceService.reduce();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 如果扣除异常,则取消订单
this.cancelOrder()
return ;
}
// 进行下一步操作
doSomething();
}
}
@Service
class ReduceService {
@Transactional(propagation = PROPAGATION.NESTED, rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void reduce(){
......
}
}
也可以根据外部事务的具体配置决定要提交还是回滚。不过该方式只对DataSourceTransactionManager事务管理器有效。
4、源码看事务
Spring中通过注解@EnableTransactionManagement开启事务,那么我们从这个注解开始入手:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector.class)
public @interface EnableTransactionManagement {
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY;
int order() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
可以看到@Import了TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector,而这个类实现了ImportSelector接口,提供了实现方式PROXY和ASPECTJ。默认PROXY
public class TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector extends AdviceModeImportSelector<EnableTransactionManagement> {
/**
* Returns {@link ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration} or
* {@code AspectJ(Jta)TransactionManagementConfiguration} for {@code PROXY}
* and {@code ASPECTJ} values of {@link EnableTransactionManagement#mode()},
* respectively.
*/
@Override
protected String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) {
switch (adviceMode) {
case PROXY:
// AutoProxyRegistrar : 主要是注册了 InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 自动代理创建器。
// 而 InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 的逻辑基本上和 Aop 的逻辑相同
// ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration : 注册了事务实现的核心 Bean,
// 包括 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 、 TransactionAttributeSource 、 TransactionInterceptor 等
return new String[] {AutoProxyRegistrar.class.getName(),
ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration.class.getName()};
case ASPECTJ:
return new String[] {determineTransactionAspectClass()};
default:
return null;
}
}
private String determineTransactionAspectClass() {
return (ClassUtils.isPresent("javax.transaction.Transactional", getClass().getClassLoader()) ?
TransactionManagementConfigUtils.JTA_TRANSACTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME :
TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME);
}
}
- AutoProxyRegistrar:就是完成事务代理类创建的部分,也就是我们熟悉的AOP代理创建注册的流程,可以跟进查看源码org.springframework.context.annotation.AutoProxyRegistrar#registerBeanDefinitions
- ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration:注册事务的实现核心
查看源码org.springframework.transaction.annotation.ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public class ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration extends AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration {
// 设置了切面拦截方法,以及切点
@Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor(
TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource, TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor) {
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor();
advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);
advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor);
if (this.enableTx != null) {
advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
}
return advisor;
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource() {
return new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource();
}
// 设置事务拦截器,增强式事务的逻辑就是在这里
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor(TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource) {
TransactionInterceptor interceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
interceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);
if (this.txManager != null) {
interceptor.setTransactionManager(this.txManager);
}
return interceptor;
}
}
而TransactionInterceptor这个类,就是我们切面的实现类,用于事务方法的拦截,然后通过Spring事务管理器PlatformTransactionManager进行管理。
public class TransactionInterceptor extends TransactionAspectSupport implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
public TransactionInterceptor() {}
/**
* 创建一个新的事务拦截器TransactionInterceptor.
* @param ptm 默认的事务管理器,通过该事务管理器进行实际的事务管理
* @param tas properties形式的事务属性
* @since 5.2.5
* @see #setTransactionManager
* @see #setTransactionAttributeSource
*/
public TransactionInterceptor(TransactionManager ptm, TransactionAttributeSource tas) {
setTransactionManager(ptm);
setTransactionAttributeSource(tas);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// 配到父类TransactionAspectSupport的invokeWithinTransaction方法
// 第三个参数是InvocationCallback接口,可以保证在父类TransactionAspectSupport#invokeWithinTransaction方法中回调到当前方法的拦截器链条
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, new CoroutinesInvocationCallback() {
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceedWithInvocation() throws Throwable {
return invocation.proceed();
}
@Override
public Object getTarget() {
return invocation.getThis();
}
@Override
public Object[] getArguments() {
return invocation.getArguments();
}
});
}
......
}
查看org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport#invokeWithinTransaction
@Nullable
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// 获取事务属性源TransactionAttributeSource
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
// 获取当前调用的方法的事务属性,如果TransactionAttribute为null,则该方法就是非事务方法
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
// 获取事务管理器TransactionManager
final TransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
// 判断不同的事务管理器
if (this.reactiveAdapterRegistry != null && tm instanceof ReactiveTransactionManager) {
// ReactiveTransactionManager事务管理器不常用,这里省略
......
}
// 获取到常用的PlatformTransactionManager事务管理器
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = asPlatformTransactionManager(tm);
//连接点识别符,也就是事务所作用的方法,如OrderService.createOrder()
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
// 创建一个标准事务
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
// 调用拦截器链的下一个拦截器,最终目标方法会被调用
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
// 清除事务信息
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus();
if (status != null && txAttr != null) {
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
}
// 提交事务
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
else {
......
}
}
接着我们从createTransactionIfNecessary()跟进去会发现org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport#prepareTransactionInfo:
protected TransactionInfo prepareTransactionInfo(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,
@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, String joinpointIdentification,
@Nullable TransactionStatus status) {
TransactionInfo txInfo = new TransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
if (txAttr != null) {
// We need a transaction for this method...
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Getting transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() + "]");
}
// The transaction manager will flag an error if an incompatible tx already exists.
txInfo.newTransactionStatus(status);
}
// 如果没有事务属性,则不需要创建事务
else {
// The TransactionInfo.hasTransaction() method will return false. We created it only
// to preserve the integrity of the ThreadLocal stack maintained in this class.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No need to create transaction for [" + joinpointIdentification +
"]: This method is not transactional.");
}
}
// We always bind the TransactionInfo to the thread, even if we didn't create
// a new transaction here. This guarantees that the TransactionInfo stack
// will be managed correctly even if no transaction was created by this aspect.
// 将TransactionInfo绑定到当前线程,即使我们在这里没有创建一个新的事务
// 这保证了TransactionInfo堆栈将被正确管理,即使这个aspect没有创建任何事务。
// 而这里,便是我们经常提到了Spring事务是绑定到了TreadLocal进行管理的地方
txInfo.bindToThread();
return txInfo;
}
org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport#commitTransactionAfterReturning这里便是事务提交相关的处理:
protected void commitTransactionAfterReturning(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
# 惊喜
最后还准备了一套上面资料对应的面试题(有答案哦)和面试时的高频面试算法题(如果面试准备时间不够,那么集中把这些算法题做完即可,命中率高达85%+)


framework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport#commitTransactionAfterReturning这里便是事务提交相关的处理:
protected void commitTransactionAfterReturning(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
惊喜
最后还准备了一套上面资料对应的面试题(有答案哦)和面试时的高频面试算法题(如果面试准备时间不够,那么集中把这些算法题做完即可,命中率高达85%+)
[外链图片转存中…(img-7AY1Qeco-1714521670196)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-Ucy9993b-1714521670196)]





















 434
434











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








