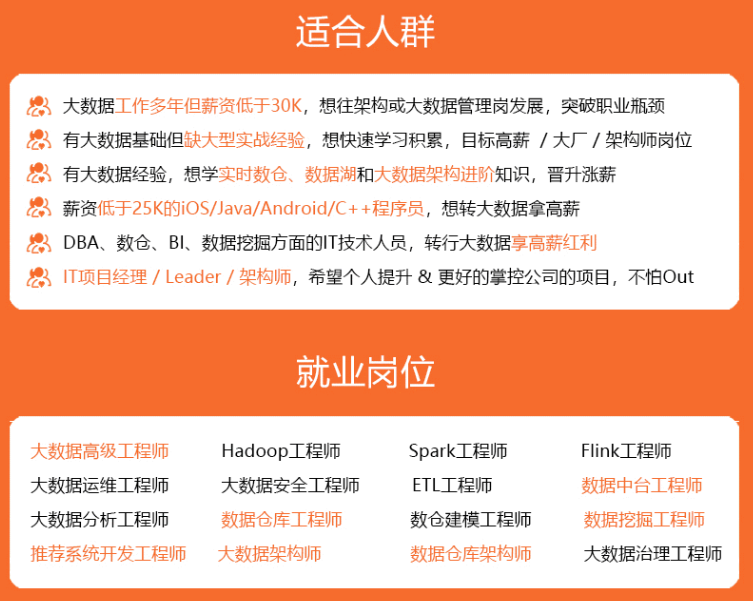
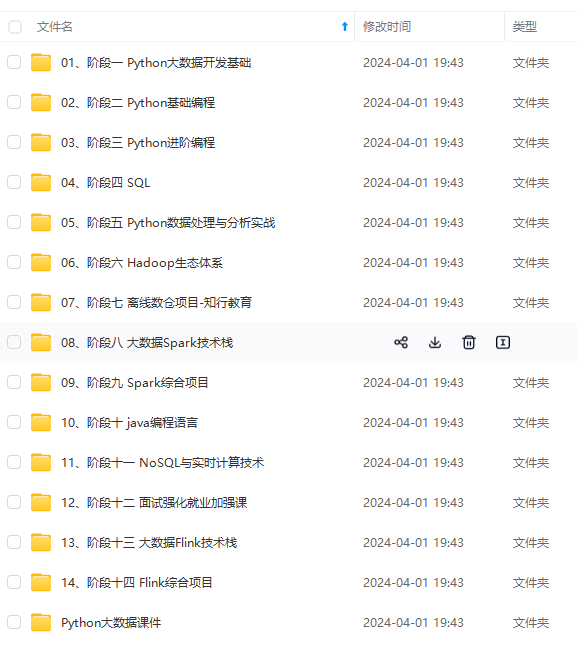
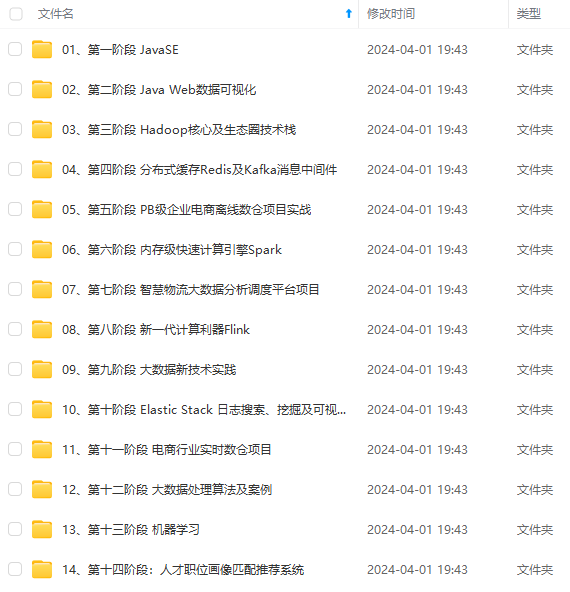
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上大数据知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
Why Data Mining? • The Explosive Growth of Data: from terabytes to petabytes — Data collection and data availability ◦ Automated data collection tools, database systems, Web, computerized society — Major sources of abundant data ◦ Business: Web, e-commerce, transactions, stocks, . . . ◦ Science: Remote sensing, bioinformatics, scientific simulation, . . . ◦ Society and everyone: news, digital cameras, YouTube • We are drowning in data, but starving for knowledge! • “Necessity is the mother of invention” – Data mining—Automated analysis of massive data sets
What Is Data Mining? • Data mining (knowledge discovery from data) — Extraction of interesting (non-trivial, implicit, previously unknown and potentially useful) patterns or knowledge from huge amount of data 数据挖掘(从数据中发现知识)–从海量数据中提取有趣的(非次要的、隐含的、以前未知的和潜在有用的)模式或知识- • Alternative names — Knowledge discovery (mining) in databases (KDD), knowledge extraction, data/pattern analysis, data archeology, data dredging, information harvesting, business intelligence, etc. Data mining – searching for knowledge (interesting patterns) in data.
Origins of Data Mining • Draws ideas from machine learning/AI, pattern recognition, statistics, visualization and database systems • Traditional techniques may be unsuitable due to data that is — Large-scale — High dimensional — Heterogeneous — Complex — Distributed • A key component of the emerging field of data science and data-driven discovery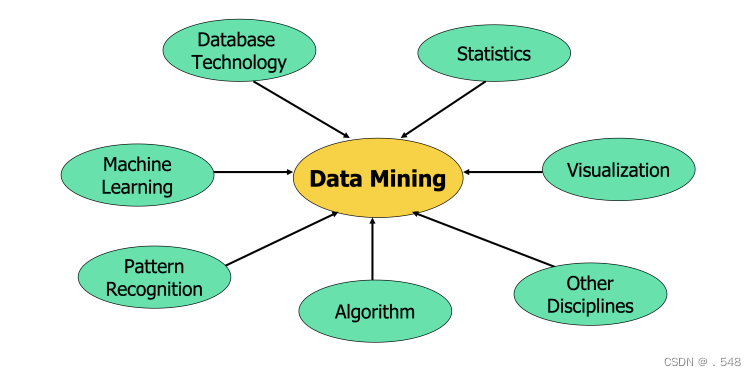 • Data mining: the core of knowledge discovery process A KDD Process
• Data mining: the core of knowledge discovery process A KDD Process
KDD Process: A Typical View from ML and Statistics • This is a view from typical machine learning and statistics communities 来自机器学习和统计学界的典型观点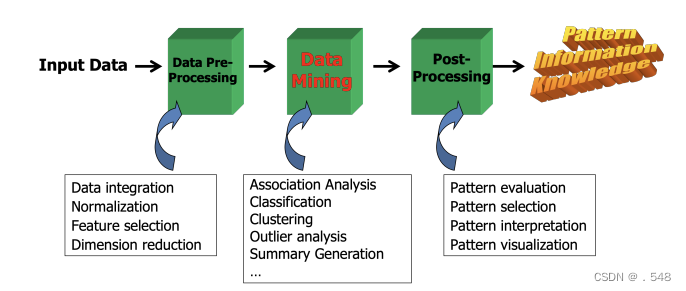 KDD Process: Several Key Steps • Learning the application domain 学习应用领域— relevant prior knowledge and goals of application • Creating a target data set创建目标数据集: data selection • Data cleaning and preprocessing数据清理和预处理: (may take 60% of effort!) • Data reduction and transformation数据缩减和转换 — Find useful features查找有用特征, dimensionality/variable reduction, invariant representation • Choosing functions of data mining选择数据挖掘功能 — summarization, classification, regression, association, clustering • Choosing the mining algorithm(s)选择挖掘算法 • Data mining: search for patterns of interest • Pattern evaluation and knowledge presentation 模式评估和知识展示— visualization, transformation, removing redundant patterns, etc. • Use of discovered knowledge
KDD Process: Several Key Steps • Learning the application domain 学习应用领域— relevant prior knowledge and goals of application • Creating a target data set创建目标数据集: data selection • Data cleaning and preprocessing数据清理和预处理: (may take 60% of effort!) • Data reduction and transformation数据缩减和转换 — Find useful features查找有用特征, dimensionality/variable reduction, invariant representation • Choosing functions of data mining选择数据挖掘功能 — summarization, classification, regression, association, clustering • Choosing the mining algorithm(s)选择挖掘算法 • Data mining: search for patterns of interest • Pattern evaluation and knowledge presentation 模式评估和知识展示— visualization, transformation, removing redundant patterns, etc. • Use of discovered knowledge
Data Mining and Business Intelligence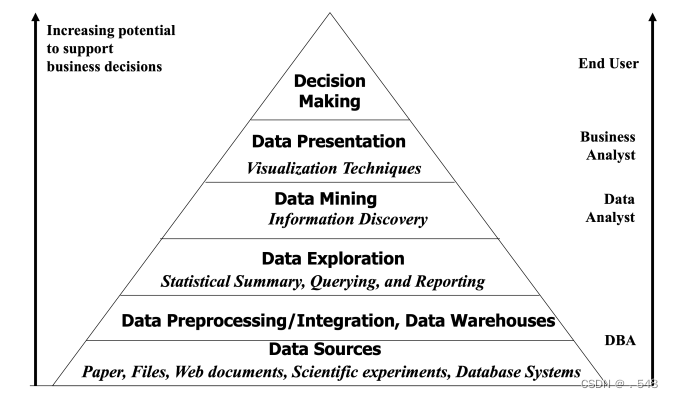
Multi-Dimensional View of Data Mining • Data to be mined — Relational, data warehouse, transactional, stream, object-oriented/relational, active, spatial, time-series, text, multi-media, heterogeneous, legacy, WWW 需要挖掘的数据 - 关系型、数据仓库型、事务型、数据流型、面向对象/关系型、活动型、空间型、时间序列型、文本型、多媒体型、异构型、遗留型、WWW• Knowledge to be mined — Characterization, discrimination, association, classification, clustering, trend/deviation, outlier analysis, etc.需要挖掘的知识 - 特征、鉴别、关联、分类、聚类、趋势/差异、异常值分析等 - 多种/集成功能和多层次挖掘 — Multiple/integrated functions and mining at multiple levels多种/集成功能和多层次挖掘 • Techniques utilized — Database-oriented, data warehouse (OLAP), machine learning, statistics, visualization, etc.使用的技术 - 面向数据库、数据仓库(OLAP)、机器学习、统计、可视化等 • Applications adapted — Retail, telecommunication, banking, fraud analysis, bio-data mining, stock market analysis, text mining, Web mining, etc.适应的应用 - 零售、电信、银行、欺诈分析、生物数据挖掘、股票市场分析、文本挖掘、网络挖掘等
Data Mining: Classification Schemes • General functionality — Descriptive data mining — Predictive data mining 一般功能 - 描述性数据挖掘 - 预测性数据挖掘• Different views lead to different classifications — Data view: Kinds of data to be mined 数据观点: 要挖掘的数据类型— Knowledge view: Kinds of knowledge to be discovered 知识观点: 有待发现的知识种类 — Method view: Kinds of techniques utilized 方法观点:使用的技术种类— Application view: Kinds of applications adapted应用观点: 适应的应用程序类型
Data Mining: On What Kinds of Data? • Database-oriented data sets and applications — Relational database, data warehouse, transactional database面向数据库的数据集和应用 - 关系数据库、数据仓库、事务数据库 • Advanced data sets and advanced applications — Data streams and sensor data — Time-series data, temporal data, sequence data (incl. bio-sequences) — Structure data, graphs, social networks and multi-linked data — Object-relational databases — Heterogeneous databases and legacy databases — Spatial data and spatiotemporal data — Multimedia database — Text databases — The World-Wide Web高级数据集和高级应用 - 数据流和传感器数据 - 时间序列数据、时间数据、序列数据(包括生物序列) - 结构数据、图形、社交网络和多链接数据 - 对象关系数据库 - 异构数据库和传统数据库 - 空间数据和时空数据 - 多媒体数据库 - 文本数据库 - 万维网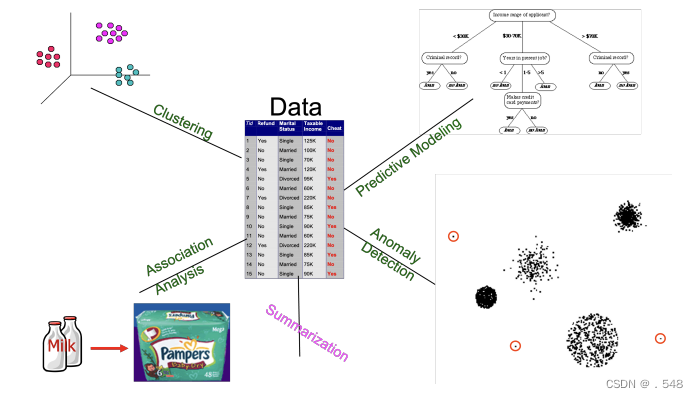 Data Mining Tasks • Prediction Methods — Use some variables to predict unknown or future values of other variables预测方法 - 使用某些变量预测其他变量的未知值或未来值 • Description Methods — Find human-interpretable patterns that describe the data; create summaries描述方法 - 找出描述数据的人类可解释模式;创建摘要
Data Mining Tasks • Prediction Methods — Use some variables to predict unknown or future values of other variables预测方法 - 使用某些变量预测其他变量的未知值或未来值 • Description Methods — Find human-interpretable patterns that describe the data; create summaries描述方法 - 找出描述数据的人类可解释模式;创建摘要
Data Mining Tasks • Classification [Predictive] • Clustering [Descriptive] • Association Rule Discovery [Descriptive] • Sequential Pattern Discovery [Descriptive] • Regression [Predictive] • Deviation Detection / Anomaly Detection [Predictive]数据挖掘任务 - 分类[预测性] - 聚类[描述性] - 关联规则发现[描述性] - 序列模式发现[描述性] - 回归[预测性] - 偏差检测/异常检测[预测性]
Data Mining Functions: (1) Generalization • Information integration and data warehouse construction — Data cleaning, transformation, integration, and multidimensional data model信息集成和数据仓库建设–数据清理、转换、集成和多维数据模型 • Data cube technology — Scalable methods for computing (i.e., materializing) multidimensional aggregates — OLAP (online analytical processing) 数据立方体技术–计算(即具体化)多维集合的可扩展方法–OLAP(在线分析处理)• Multidimensional concept description: Characterization and discrimination — Generalize, summarize, and contrast data characteristics, e.g., dry v.s. wet regions多维概念描述: 特征描述和判别 - 归纳、总结和对比数据特征,如干燥地区和潮湿地区
Data Mining Functions: (2) Association and Correlation Analysis • Frequent patterns (or frequent itemsets) — What items are frequently purchased together in your Walmart? • Association, correlation vs. causality — A typical association rule - 关联性、相关性与因果性 - 一个典型的关联规则◦ Diaper → Beer [0.5%, 75%] (support, confidence) — Are strongly associated items also strongly correlated? • How to mine such patterns and rules efficiently in large datasets? • How to use such patterns for classification, clustering, and other applications?
Association Rule Discovery: Definition • Given a set of records each of which contain some number of items from a given collection; — Produce dependency rules which will predict occurrence of an item based on occurrences of other items. 给定一组记录,其中每条记录都包含给定集合中的若干项目; - 生成依赖规则,根据其他项目的出现情况预测某个项目的出现情况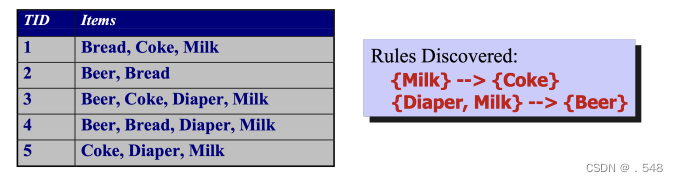 Data Mining Functions: (3) Classification and Prediction • Classification and prediction — Construct models (functions) based on some training examples — Describe and distinguish classes or concepts for future prediction ◦ e.g., classify countries based on (climate), or classify cars based on (gas mileage) 分类和预测 - 基于一些训练实例构建模型(函数) - 描述和区分类别或概念,用于未来预测 — Predict some unknown or missing numerical values 预测一些未知或缺失的数值• Typical methods — Decision trees, na¨ıve Bayesian classification, support vector machines, neural networks, rule-based classification, pattern-based classification, logistic regression, … 典型方法 - 决策树、贝叶斯分类法、支持向量机、神经网络、基于规则的分类法、基于模式的分类法、逻辑回归法…• Typical applications — Credit card fraud detection, direct marketing, classifying stars, diseases, web-pages, …典型应用 - 信用卡欺诈检测、直销、明星分类、疾病分类、网页分类.
Data Mining Functions: (3) Classification and Prediction • Classification and prediction — Construct models (functions) based on some training examples — Describe and distinguish classes or concepts for future prediction ◦ e.g., classify countries based on (climate), or classify cars based on (gas mileage) 分类和预测 - 基于一些训练实例构建模型(函数) - 描述和区分类别或概念,用于未来预测 — Predict some unknown or missing numerical values 预测一些未知或缺失的数值• Typical methods — Decision trees, na¨ıve Bayesian classification, support vector machines, neural networks, rule-based classification, pattern-based classification, logistic regression, … 典型方法 - 决策树、贝叶斯分类法、支持向量机、神经网络、基于规则的分类法、基于模式的分类法、逻辑回归法…• Typical applications — Credit card fraud detection, direct marketing, classifying stars, diseases, web-pages, …典型应用 - 信用卡欺诈检测、直销、明星分类、疾病分类、网页分类.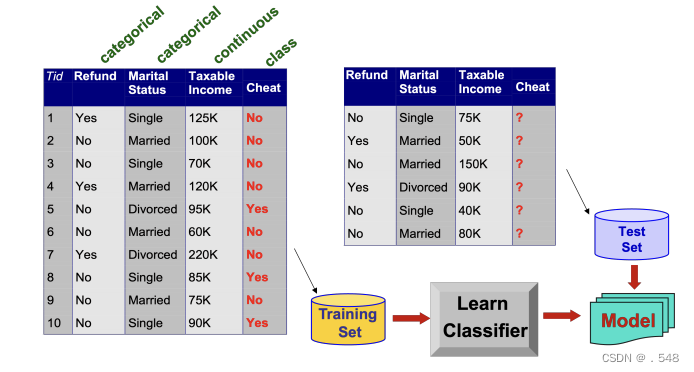 Data Mining Functions: (4) Cluster and Outlier Analysis • Cluster analysis — Unsupervised learning (i.e., Class label is unknown) — Group data to form new categories (i.e., clusters), e.g., cluster houses to find distribution patterns — Principle: Maximizing intra-class similarity & minimizing interclass similarity — Many methods and applications 聚类分析 - 无监督学习(即类标签未知) - 将数据分组以形成新的类别(即聚类),例如,聚类房屋以寻找分布模式 - 原则: 最大化类内相似性,最小化类间相似性 - 许多方法和应用 • Outlier analysis — Outlier: A data object that does not comply with the general behavior of the data — Noise or exception? – One person’s garbage could be another person’s treasure — Methods: by product of clustering or regression analysis, … — Useful in fraud detection, rare events analysis离群值分析 - 离群值: 不符合数据一般行为的数据对象 - 噪音还是异常?- 一个人的垃圾可能是另一个人的宝藏 - 方法:聚类或回归分析的产物… - 在欺诈检测、罕见事件分析中很有用
Data Mining Functions: (4) Cluster and Outlier Analysis • Cluster analysis — Unsupervised learning (i.e., Class label is unknown) — Group data to form new categories (i.e., clusters), e.g., cluster houses to find distribution patterns — Principle: Maximizing intra-class similarity & minimizing interclass similarity — Many methods and applications 聚类分析 - 无监督学习(即类标签未知) - 将数据分组以形成新的类别(即聚类),例如,聚类房屋以寻找分布模式 - 原则: 最大化类内相似性,最小化类间相似性 - 许多方法和应用 • Outlier analysis — Outlier: A data object that does not comply with the general behavior of the data — Noise or exception? – One person’s garbage could be another person’s treasure — Methods: by product of clustering or regression analysis, … — Useful in fraud detection, rare events analysis离群值分析 - 离群值: 不符合数据一般行为的数据对象 - 噪音还是异常?- 一个人的垃圾可能是另一个人的宝藏 - 方法:聚类或回归分析的产物… - 在欺诈检测、罕见事件分析中很有用
Illustrating Clustering • Euclidean Distance Based Clustering in 3-D space说明聚类–基于欧氏距离的三维空间聚类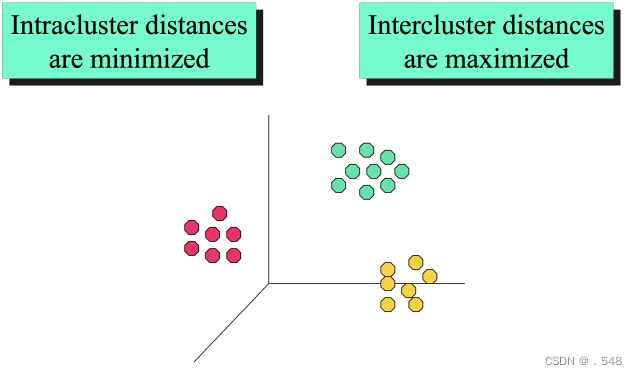 Data Mining Functions: (5) Trend and Evolution Analysis • Sequence, trend and evolution analysis — Trend and deviation analysis: e.g., regression — Sequential pattern mining ◦ e.g., first buy digital camera, then large SD memory cards — Periodicity analysis — Motifs, time-series, and biological sequence analysis ◦ Approximate and consecutive motifs — Similarity-based analysis 序列、趋势和演变分析 - 趋势和偏差分析:如回归 - 序列模式挖掘 ◦ 如先购买数码相机,再购买大型 SD 存储卡 - 周期性分析 - 主题、时间序列和生物序列分析 ◦ 近似和连续主题 • Mining data streams — Ordered, time-varying, potentially infinite, data streams基于相似性的分析 - 挖掘数据流 - 有序、时变、可能无限的数据流
Data Mining Functions: (5) Trend and Evolution Analysis • Sequence, trend and evolution analysis — Trend and deviation analysis: e.g., regression — Sequential pattern mining ◦ e.g., first buy digital camera, then large SD memory cards — Periodicity analysis — Motifs, time-series, and biological sequence analysis ◦ Approximate and consecutive motifs — Similarity-based analysis 序列、趋势和演变分析 - 趋势和偏差分析:如回归 - 序列模式挖掘 ◦ 如先购买数码相机,再购买大型 SD 存储卡 - 周期性分析 - 主题、时间序列和生物序列分析 ◦ 近似和连续主题 • Mining data streams — Ordered, time-varying, potentially infinite, data streams基于相似性的分析 - 挖掘数据流 - 有序、时变、可能无限的数据流
Data Mining Functions: (6) Structure and Network Analysis • Graph mining — Finding frequent subgraphs (e.g., chemical compounds), trees (XML), substructures (web fragments) 图挖掘 - 寻找频繁出现的子图(如化合物)、树(XML)、子结构(网络片段)• Information network analysis — Social networks: actors (objects, nodes) and relationships (edges) 信息网络分析 - 社会网络:行为者(对象、节点)和关系(边)◦ e.g., author networks in CS, terrorist networks — Multiple heterogeneous networks ◦ A person could be multiple information networks: friends, family, classmates, … — Links carry a lot of semantic information: Link mining • Web mining — Web is a big information network: 链接携带大量语义信息: 链接挖掘 - 网络挖掘 - 网络是一个巨大的信息网络from PageRank to Google — Analysis of Web information networks ◦ Web community discovery, opinion mining, usage mining, …
Top-10 Algorithm Finally Selected at ICDM’ 06 1. C4.5 (61 votes) 2. K-Means (60 votes) 3. SVM (58 votes) 4. Apriori (52 votes) 5. EM (48 votes) 6. PageRank (46 votes) 7. AdaBoost (45 votes) 8. kNN (45 votes) 9. Naive Bayes (45 votes) 10. CART (34 votes)
Are All the “Discovered” Patterns Interesting? • Data mining may generate thousands of patterns: Not all of them are interesting — Suggested approach: Human-centered, query-based, focused mining数据挖掘可能会产生成千上万种模式: 并非所有模式都有趣 • Interestingness measures — A pattern is interesting if it is easily understood by humans, valid on new or test data with some degree of certainty, potentially useful, novel, or validates some hypothesis that a user seeks to confirm 建议的方法: 以人为中心、基于查询、有重点的挖掘 - 趣味性衡量标准 - 如果一个模式容易被人类理解、在新数据或测试数据上有一定程度的确定性、潜在有用、新颖或验证了用户试图确认的某些假设,那么这个模式就是有趣的 - 客观与主观趣味性衡量标准 • Objective v.s. subjective interestingness measures — Objective: based on statistics and structures of patterns, e.g., support, confidence, etc. — Subjective: based on user’s belief in the data, e.g., unexpectedness, novelty, actionability, etc.客观:基于模式的统计数据和结构,如支持度、置信度等 - 主观:基于用户对数据的信念,如意外性、新颖性、可操作性等。
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上大数据知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
以戳这里获取](https://bbs.csdn.net/forums/4f45ff00ff254613a03fab5e56a57acb)**





















 475
475











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








