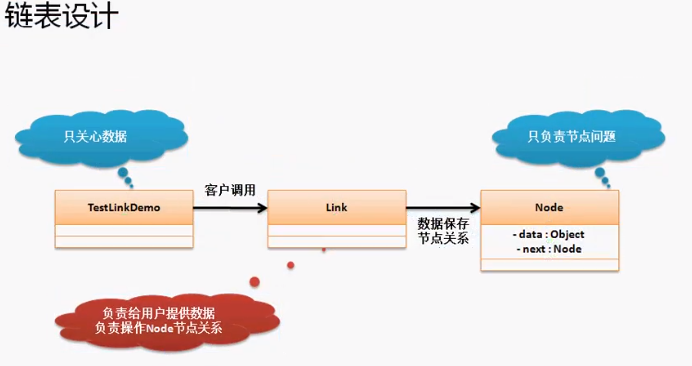
2.2 链表实现结构说明
通过之前的分析,可以发现链表的最大作用类就是Node,但是以上程序都是由用户自己去匹配节点关系的,但是这些节点的匹配工作不应该由用户完成,应该由一个程序专门去负责。
那么专门负责几点操作的类,就成为链表类——Link,负责处理几点关系,而用户不用关心节点的问题,只需关心Link的处理操作即可。
真实开发——标准过程

class Link{//负责对链表的操作
//将Node定义内部类,表示Node类只能为Link类提供服务
private class Node{//负责数据与节点的关系匹配
private Object data;//真正要保存的数据
private Node next;//定义下一个节点
public Node(Object data){
this.data = data;
}
public void setData(Object data){
this.data = data;
}
public Object getData(){
return this.data;
}
}
//以下为Link类
}
public class TestLinkDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
}
}
2.3 增加链表数据—public void add(数据)
通过上面程序的分析,可以发下,对于链表的实现,Node类是整个操作的关键,但是首先来研究一下之前程序的问题:Node是一个单独的类是可以被用户直接使用的,但是这个类由用户直接去使用,没有任何意义,即:这个类有用,但不能让用户去使用,让Link类去使用。
class Link{//负责对链表的操作
//将Node定义内部类,表示Node类只能为Link类提供服务
private class Node{//负责数据与节点的关系匹配
private Object data;//真正要保存的数据
private Node next;//定义下一个节点
public Node(Object data){
this.data = data;
}
public void setData(Object data){
this.data = data;
}
public Object getData(){
return this.data;
}
public void setNext(Node next){
this.next = next;
}
public Node getNext(){
return this.next;
}
//第一次调用:this = Link.root
//第二次调用:this = Link.root.next
//第三次调用:this = Link.root.next.next
public void addNode(Node newNode){//处理节点关系
if(this.next == null){ //当前节点下一个为空
this.next = newNode;
}else{//当前节点的下一个不为空
this.next.addNode(newNode);
}
}
public void nodePrint(){
System.out.println(this.getData());
if (this.getNext()==null)
{
return;
}else{
this.getNext().nodePrint();
}
}
}
//以下为Link类------------------------------------------------
private Node root; //属于根节点,没有根节点就无法数据的保存
//增加数据
public void add(Object data){
if(data == null){//人为追加规定,不允许存放null值
return ;//结束方法调用
}
//如果要想进行数据的保存,那么必须将数据封装在Node类里面
//如果没有封装,则无法确认好节点的先后顺序
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if(this.root == null){
this.root = newNode;//第一个节点设置为根节点
}else{//根节点存在了
this.root.addNode(newNode);
}
}
//输出数据
public void print(){
if (this.root == null){
return;
}
System.out.println(this.root.getData());
if (this.root.getNext()==null){
return;
}
else{
this.root.getNext().nodePrint();
}
}
}
public class TestLinkDemo1{
public static void main(String args[]){
Link link = new Link();
link.add("Hello");
link.add("World");
link.print();
}
}
2.4 增加多个数据—public void addAll(数据数组)
public void addAll(String date[]){
for(int x = 0;x<date.length;x++){
this.add(date[x]);
}
}
2.5 统计数据个数—public int size()
在Link类中定义
private int count;//统计个数
在增加数据的最后一行添加count++
public void add(Object data){
if(data == null){//人为追加规定,不允许存放null值
return ;//结束方法调用
}
//如果要想进行数据的保存,那么必须将数据封装在Node类里面
//如果没有封装,则无法确认好节点的先后顺序
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if(this.root == null){
this.root = newNode;//第一个节点设置为根节点
}else{//根节点存在了
this.root.addNode(newNode);
}
count++;
}
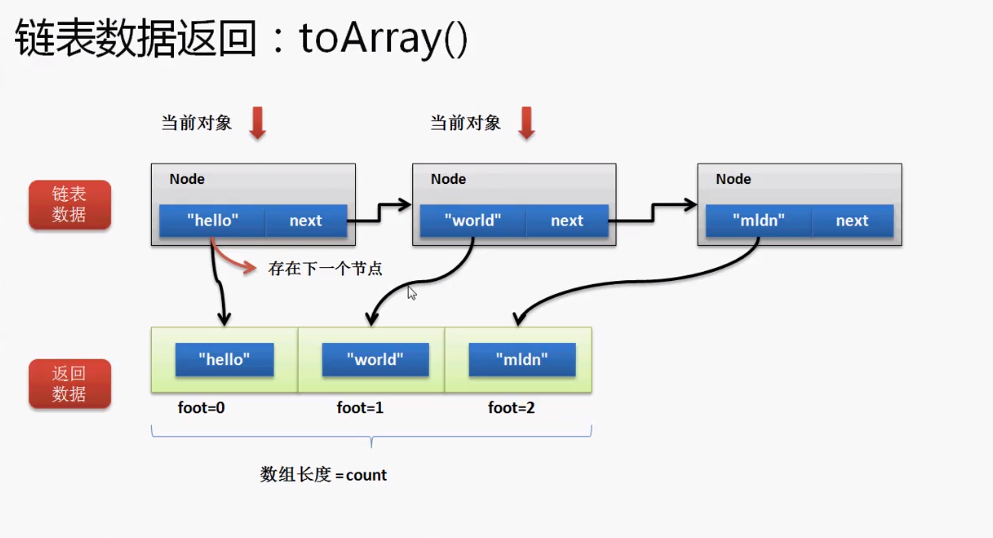
2.6 链表数据转换为对象数组—public Object[] toArray()
对于链表的这种数据结构,最为关键的是两个操作:删除和取得全部数据。
在Link类中定义一个操作数组的脚标:
private int foot = 0;
要把数据保存的数组,Link类和Node类都需要使用,那么可以在Link类中定义返回数组,必须以属性的形式出现,只有这样,Node类才可以访问这个数组并进行操作。
private Object [] retData ; //返回类型
在Link类中增加toArray()方法:
//链表数据转换为对象数组
public Object[] toArray(){
if(this.count == 0){
return null;
}
this.retData = new Object[this.count];
this.root.toArrayNode();
this.foot = 0;//下表清零操作
return this.retData;
}
在Node中增加toArrayNode()方法:
public void toArrayNode(){
Link.this.retData[Link.this.foot++] = this.data;
if(this.next != null){
this.next.toArrayNode();
}
}
不过按照以上的方式进行开发,每一次调用toArray()方法,都要重复的进行数据的的遍历,如果在数据没有修改的情况下,这种做法是一种低效的做法,最好的方法是增加一个修改标记,如果发现数据增加了或删除的话,表示要重新遍历数据。
2.7 链表查询数据—public boolean contains(查找对象)
现在如果想查询某个数据是否存在,那么基本的操作原理:逐个盘查,盘查的具体对象应该交给Node去完成,前提是:有数据存在。
在Link类之中,增加查询操作:
//查找链表的指定数据是否存在
public boolean contains(Object search){
if(search == null && this.root == null)
return false;
return this.root.containsNode(search);
}
在Node类中,完成具体查询,查询流程为:
判断当前节点的内容是否满足于查询内容,如果满足返回ture;
如果当前节点内容不满足,则向后继续查询,如果没有后续节点了,则返回false。
public boolean containsNode(Object search){
if(search.equals(this.data))
return true;
else{
if(this.next != null){//判断下一个节点是否为空
return this.next.containsNode(search);
}
return false;
}
}
2.8 根据索引取得数据—public Object get(int index)
在一个链表之中会有多个节点保存数据,现在要求可以取得指定节点的数据。但是在进行这一操作的过程之中,有一个小问题:如果要取得数据的索引超过了数据的保存个数,那么是无法取得的。
在Link类之中增加一个get(int index)方法:
//根据索引取得数据
public Object get(int index){
if(index >= this.count){
return null;
}
this.foot = 0;
return this.root.getNode(index);
}
在Node类之中增加一个getNdoe(int index)方法:
//第一次this == Link.root
//第二次this == Link.root.next
public Object getNode(int index){
if(Link.this.foot++ == index){
return this.data;
}else{
return this.next.getNode(index);
}
}
2.9 修改指定索引数据—public void set(int index,Object newData)
如果修改数据只需要进行数据的替换。
在Link类之中增加一个set(int index,Object newData)方法:
//修改指定索引数据
public void set(int index,Object newData){
if(index >= this.count){
return ;
}
this.foot = 0;
this.root.setNode(index,newData);
}
在Node类之中增加一个getNode(int index)方法:
public void setNode(int index, Object newData){
if(Link.this.foot ++ == index){//索引相同
this.data = newData;
}else{
if(this.next != null){
this.next.setNode(index,newData);
}
}
}
2.10 删除数据—public void remove(数据)
对于链表之中的内容,之前完成的是增加操作和查询操作,但是从链表之中也会存在删除数据的操作,可是删除数据的操作要分为两种情况讨论:
情况一:删除的数据不是根节点,待删节点的上一个next指向待删节点的next。
所有的处理操作应该交给Node进行处理。
情况二:删除的数据是根节点,下一个节点保存为跟节点。
如果删除的是根节点,意味着Link中的根节点的保存需要发生变化,该操作主要在Link中处理。
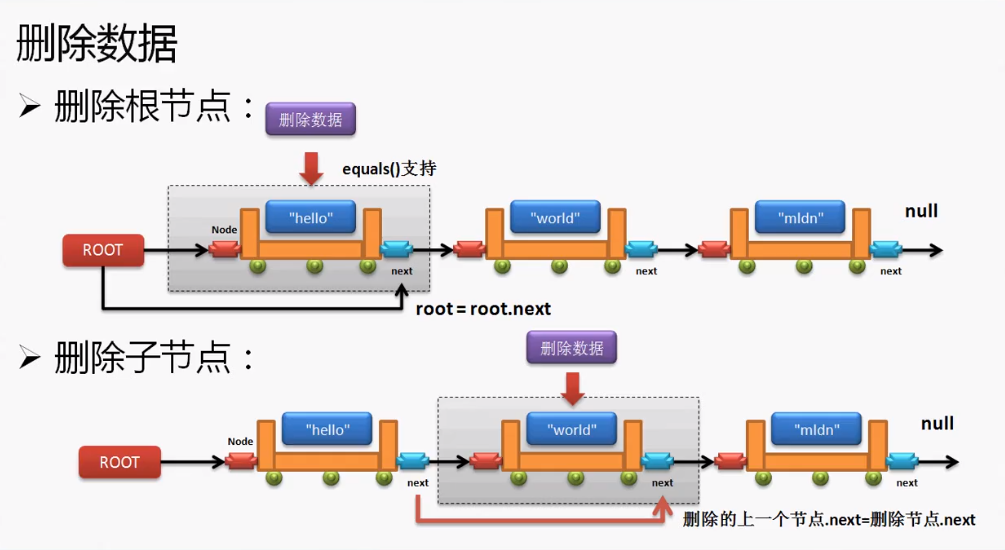
在Link中增加一个删除remove(Object data)方法
//删除数据
public void remove(Object data){
if(this.contains(data)){//如果数据存在则进行数据处理
if(this.root.data.equals(data)){//首先需要判断要删除的数据是否为根节点数据
this.root = this.root.next;//根节点变为下一个节点
}else{//不是根节点
this.root.next.removeNode(this.root,data);
}
this.count --;
}
}
在Node类之中增加一个removeNode(Node previous, Object data)方法:
//第一次:this = Link.root.next、previous= Link.root;
//第二次:this = Link.root.next.next、previous= Link.root.next;
public void removeNode(Node previous, Object data){
if(this.data.equals(data)){//当前节点为要删除的节点
previous.next = this.next;
}else{
this.next.removeNode(this,data);
}
}
Link链表类模板
class Link{//负责链表的操作
//将Node定义内部类,表示Node类只能为Link类提供服务
private class Node{//负责数据与节点的关系匹配
private Object data;//真正要保存的数据
private Node next;//定义下一个节点
public Node(Object data){
this.data = data;
}
public void setData(Object data){
this.data = data;
}
public Object getData(){
return this.data;
}
public void setNext(Node next){
this.next = next;
}
public Node getNext(){
return this.next;
}
//第一次调用:this = Link.root
//第二次调用:this = Link.root.next
//第三次调用:this = Link.root.next.next
public void addNode(Node newNode){//处理节点关系
if(this.next == null){ //当前节点下一个为空
this.next = newNode;
}else{//当前节点的下一个不为空
this.next.addNode(newNode);
}
}
public void nodePrint(){
System.out.println(this.getData());
if (this.getNext()==null)
{
return;
}else{
this.getNext().nodePrint();
}
}
public void toArrayNode(){
Link.this.retData[Link.this.foot++] = this.data;
if(this.next != null){
this.next.toArrayNode();
}
}
public boolean containsNode(Object search){
if(search.equals(this.data))
return true;
else{
if(this.next != null){//判断下一个节点是否为空
return this.next.containsNode(search);
}
return false;
}
}
//第一次this == Link.root
//第二次this == Link.root.next
public Object getNode(int index){
if(Link.this.foot++ == index){
return this.data;
}else{
return this.next.getNode(index);
}
}
public void setNode(int index, Object newData){
if(Link.this.foot ++ == index){//索引相同
this.data = newData;
}else{
if(this.next != null){
this.next.setNode(index,newData);
}
}
}
//第一次:this = Link.root.next、previous= Link.root;
//第二次:this = Link.root.next.next、previous= Link.root.next;
public void removeNode(Node previous, Object data){
if(this.data.equals(data)){//当前节点为要删除的节点
previous.next = this.next;
}else{
this.next.removeNode(this,data);
}
}
}
//以下为Link类------------------------------------------------
private Object [] retData ; //返回类型
private int foot = 0;//操作下标
private int count;//统计个数
private Node root; //属于根节点,没有根节点就无法数据的保存
//增加数据
public void add(Object data){
if(data == null){//人为追加规定,不允许存放null值
return ;//结束方法调用
}
//如果要想进行数据的保存,那么必须将数据封装在Node类里面
//如果没有封装,则无法确认好节点的先后顺序
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if(this.root == null){
this.root = newNode;//第一个节点设置为根节点
}else{//根节点存在了
this.root.addNode(newNode);
}
count++;
}
//判断链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
this.count=0;
return false;
}
//增加多个数据
public void addAll(String date[]){
for(int x = 0;x<date.length;x++){
this.add(date[x]);
}
}
public int size(){
return this.count;
}
//输出数据
public void print(){
if (this.root == null){
return;
}
System.out.println(this.root.getData());
if (this.root.getNext()==null){
return;
}
else{
this.root.getNext().nodePrint();
}
}
//链表数据转换为对象数组
public Object[] toArray(){
if(this.count == 0){
return null;
}
this.retData = new Object[this.count];
this.root.toArrayNode();
this.foot = 0;//下表清零操作
return this.retData;
}
//查找链表的指定数据是否存在
public boolean contains(Object search){
if(search == null && this.root == null)
return false;
return this.root.containsNode(search);
}
//根据索引取得数据
public Object get(int index){
if(index >= this.count){
return null;
}
this.foot = 0;
return this.root.getNode(index);
}
//修改指定索引数据
public void set(int index,Object newData){
if(index >= this.count){
return ;
}
this.foot = 0;
this.root.setNode(index,newData);
}
//删除数据
public void remove(Object data){
if(this.contains(data)){//如果数据存在则进行数据处理
if(this.root.data.equals(data)){//首先需要判断要删除的数据是否为根节点数据
this.root = this.root.next;//根节点变为下一个节点
}else{//不是根节点
this.root.next.removeNode(this.root,data);
}
this.count --;
}
}
}
综合案例
建立宠物商店,包括销售宠物上架、下架、关键字查询,要求程序的关系即可,对于宠物的信息只要有三项:名字、年龄、颜色。
对应的关系:一个宠物商店有多种宠物,如果按照表设计应该属于一对多关系映射,但是现在问题,一方是宠物商店,多方是宠物,但是宠物又分为猫、狗、猪、驴、鱼等。
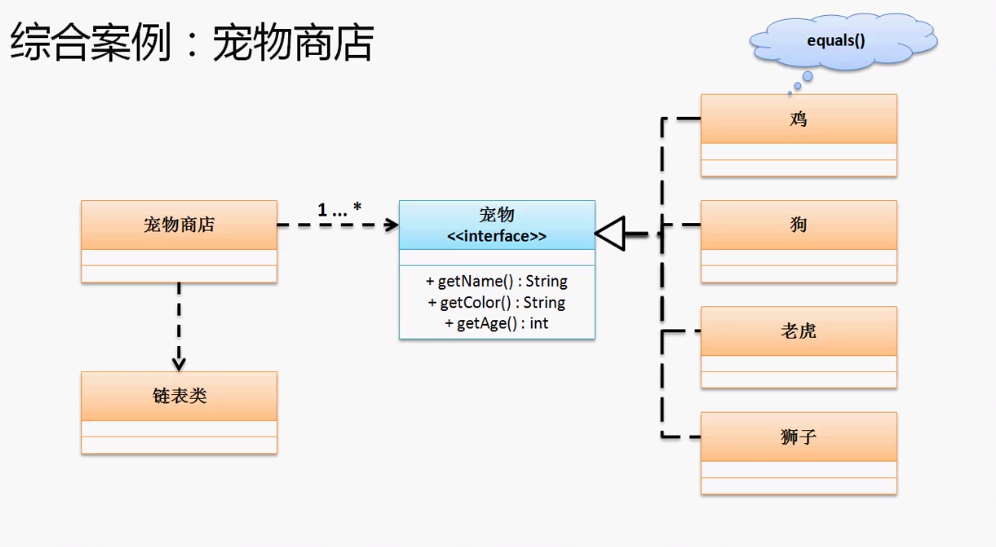
1、建立宠物标准
interface Pet{//定义宠物
public String getName();
public String getColor();
public int getAge();
}
2、对于宠物商店,只关注于宠物的标准,而不关心具体是那种宠物
class PetShop{
private Link pets = new Link();//开辟一个链表,保存宠物信息
public void add(Pet pet){//上架宠物
this.pets.add(pet);
}
public void delete(Pet pet){//下架宠物
this.pets.delete(pet);
}
public Link getPets(){ //得到全部宠物
return this.pets;
}
public Link search(String keyword){//关键字查找
Link result = new Link();
Object [] data = this.pets.toArray();
for(int i = 0; i < data.length ; i++){
Pet pet = (Pet) data[i];
if(pet.getName().contains(keyword) || pet.getColor().contains(keyword)){
result.add(pet); //满足查询结果
}
}
return result;
}
}
3、定义宠物狗
class Dog implements Pet{
private String name;
private String color;
private int age;
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public String getColor(){
return this.color;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(obj == null){
return false;
}
if(this == obj){
return false;
}
if(!(obj instanceof Dog)){
return false;
}
Dog pet = (Dog) obj;
return this.name.equals(pet.name) && this.color.equals(pet.color) && this.age.equals(pet.age);
}
public int getAge(){
return this.age;
}
public Dog(String name, String color, int age){
this.name = name ;
this.color = color;
this.age = age;
}
public String toString(){
return "【狗】名字 = " + this.name +
"颜色 = " + this.color +
"年龄 = " +this.age;
}
}
定义宠物猫
class Cat implements Pet{
private String name;
private String color;
private int age;
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public String getColor(){
return this.color;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(obj == null){
return false;
}
if(this == obj){
return false;
}
if(!(obj instanceof Cat)){
return false;
}
Cat pet = (Cat) obj;
return this.name.equals(pet.name) && this.color.equals(pet.color) && this.age.equals(pet.age);
}
public int getAge(){
return this.age;
}
public Cat(String name, String color, int age){
this.name = name ;
this.color = color;
this.age = age;
}
public String toString(){
return "【猫】名字 = " + this.name +
"颜色 = " + this.color +
"年龄 = " +this.age;
}
}
5、测试类
public class Pets{
public static void main(String args[]){
PetShop ps = new PetShop();
ps.add(new Dog("小黑","黑色",1));
ps.add(new Dog("金毛","金色",2));
ps.add(new Dog("拉布拉多","白色",3));
ps.add(new Dog("萨摩耶","白色",2));
ps.add(new Cat("加菲猫","黄色",3));
ps.add(new Dog("波斯猫","金色",4));
ps.delete(new Dog("萨摩耶","白色",2));
Link all = ps.search("白");
Object [] data = all.toArray();
for(int i = 0 ; i < data.length ; i++){
System.out.println(data[i]);
}
}
}
6、完整代码
class Link{//负责链表的操作
//将Node定义内部类,表示Node类只能为Link类提供服务
private class Node{//负责数据与节点的关系匹配
private Object data;//真正要保存的数据
private Node next;//定义下一个节点
public Node(Object data){
this.data = data;
}
public void setData(Object data){
this.data = data;
}
public Object getData(){
return this.data;
}
public void setNext(Node next){
this.next = next;
}
public Node getNext(){
return this.next;
}
//第一次调用:this = Link.root
//第二次调用:this = Link.root.next
//第三次调用:this = Link.root.next.next
public void addNode(Node newNode){//处理节点关系
if(this.next == null){ //当前节点下一个为空
this.next = newNode;
}else{//当前节点的下一个不为空
this.next.addNode(newNode);
}
}
public void nodePrint(){
System.out.println(this.getData());
if (this.getNext()==null)
{
return;
}else{
this.getNext().nodePrint();
}
}
public void toArrayNode(){
Link.this.retData[Link.this.foot++] = this.data;
if(this.next != null){
this.next.toArrayNode();
}
}
public boolean containsNode(Object search){
if(search.equals(this.data))
return true;
else{
if(this.next != null){//判断下一个节点是否为空
return this.next.containsNode(search);
}
return false;
}
}
//第一次this == Link.root
//第二次this == Link.root.next
public Object getNode(int index){
if(Link.this.foot++ == index){
return this.data;
}else{
return this.next.getNode(index);
}
}
public void setNode(int index, Object newData){
if(Link.this.foot ++ == index){//索引相同
this.data = newData;
}else{
if(this.next != null){
this.next.setNode(index,newData);
}
}
}
//第一次:this = Link.root.next、previous= Link.root;
//第二次:this = Link.root.next.next、previous= Link.root.next;
public void removeNode(Node previous, Object data){
if(this.data.equals(data)){//当前节点为要删除的节点
previous.next = this.next;
}else{
this.next.removeNode(this,data);
}
}
}
//以下为Link类------------------------------------------------
private Object [] retData ; //返回类型
private int foot = 0;//操作下标
private int count;//统计个数
private Node root; //属于根节点,没有根节点就无法数据的保存
//增加数据
public void add(Object data){
if(data == null){//人为追加规定,不允许存放null值
return ;//结束方法调用
}
//如果要想进行数据的保存,那么必须将数据封装在Node类里面
//如果没有封装,则无法确认好节点的先后顺序
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if(this.root == null){
this.root = newNode;//第一个节点设置为根节点
}else{//根节点存在了
this.root.addNode(newNode);
}
count++;
}
//判断链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
this.count=0;
return false;
}
//增加多个数据
public void addAll(String date[]){
for(int x = 0;x<date.length;x++){
this.add(date[x]);
}
}
public int size(){
return this.count;
}
//输出数据
public void print(){
if (this.root == null){
return;
}
System.out.println(this.root.getData());
if (this.root.getNext()==null){
return;
}
else{
this.root.getNext().nodePrint();
}
}
//链表数据转换为对象数组
public Object[] toArray(){
if(this.count == 0){
return null;
}
this.retData = new Object[this.count];
this.root.toArrayNode();
this.foot = 0;//下表清零操作
return this.retData;
}
//查找链表的指定数据是否存在
public boolean contains(Object search){
if(search == null && this.root == null)
return false;
return this.root.containsNode(search);
}
//根据索引取得数据
public Object get(int index){
if(index >= this.count){
return null;
}
this.foot = 0;
return this.root.getNode(index);
}
//修改指定索引数据
public void set(int index,Object newData){
if(index >= this.count){
return ;
}
this.foot = 0;
this.root.setNode(index,newData);
}
//删除数据
public void remove(Object data){
if(this.contains(data)){//如果数据存在则进行数据处理
if(this.root.data.equals(data)){//首先需要判断要删除的数据是否为根节点数据
this.root = this.root.next;//根节点变为下一个节点
}else{//不是根节点
this.root.next.removeNode(this.root,data);
}
this.count --;
}
}
}
interface Pet{//定义宠物
public String getName();
public String getColor();
public int getAge();
}
class PetShop{
private Link pets = new Link();//开辟一个链表,保存宠物信息
public void add(Pet pet){//上架宠物
this.pets.add(pet);
}
public void delete(Pet pet){//下架宠物
this.pets.remove(pet);
}
public Link getPets(){ //得到全部宠物
return this.pets;
}
public Link search(String keyword){//关键字查找
Link result = new Link();
Object [] data = this.pets.toArray();
for(int i = 0; i < data.length ; i++){
Pet pet = (Pet) data[i];
if(pet.getName().contains(keyword) || pet.getColor().contains(keyword)){
result.add(pet); //满足查询结果
### 如何自学黑客&网络安全
#### 黑客零基础入门学习路线&规划
**初级黑客**
**1、网络安全理论知识(2天)**
①了解行业相关背景,前景,确定发展方向。
②学习网络安全相关法律法规。
③网络安全运营的概念。
④等保简介、等保规定、流程和规范。(非常重要)
**2、渗透测试基础(一周)**
①渗透测试的流程、分类、标准
②信息收集技术:主动/被动信息搜集、Nmap工具、Google Hacking
③漏洞扫描、漏洞利用、原理,利用方法、工具(MSF)、绕过IDS和反病毒侦察
④主机攻防演练:MS17-010、MS08-067、MS10-046、MS12-20等
**3、操作系统基础(一周)**
①Windows系统常见功能和命令
②Kali Linux系统常见功能和命令
③操作系统安全(系统入侵排查/系统加固基础)
**4、计算机网络基础(一周)**
①计算机网络基础、协议和架构
②网络通信原理、OSI模型、数据转发流程
③常见协议解析(HTTP、TCP/IP、ARP等)
④网络攻击技术与网络安全防御技术
⑤Web漏洞原理与防御:主动/被动攻击、DDOS攻击、CVE漏洞复现
**5、数据库基础操作(2天)**
①数据库基础
②SQL语言基础
③数据库安全加固
**6、Web渗透(1周)**
①HTML、CSS和JavaScript简介
②OWASP Top10
③Web漏洞扫描工具
④Web渗透工具:Nmap、BurpSuite、SQLMap、其他(菜刀、漏扫等)
恭喜你,如果学到这里,你基本可以从事一份网络安全相关的工作,比如渗透测试、Web 渗透、安全服务、安全分析等岗位;如果等保模块学的好,还可以从事等保工程师。薪资区间6k-15k
到此为止,大概1个月的时间。你已经成为了一名“脚本小子”。那么你还想往下探索吗?
如果你想要入坑黑客&网络安全,笔者给大家准备了一份:282G全网最全的网络安全资料包评论区留言即可领取!
**7、脚本编程(初级/中级/高级)**
在网络安全领域。是否具备编程能力是“脚本小子”和真正黑客的本质区别。在实际的渗透测试过程中,面对复杂多变的网络环境,当常用工具不能满足实际需求的时候,往往需要对现有工具进行扩展,或者编写符合我们要求的工具、自动化脚本,这个时候就需要具备一定的编程能力。在分秒必争的CTF竞赛中,想要高效地使用自制的脚本工具来实现各种目的,更是需要拥有编程能力.
如果你零基础入门,笔者建议选择脚本语言Python/PHP/Go/Java中的一种,对常用库进行编程学习;搭建开发环境和选择IDE,PHP环境推荐Wamp和XAMPP, IDE强烈推荐Sublime;·Python编程学习,学习内容包含:语法、正则、文件、 网络、多线程等常用库,推荐《Python核心编程》,不要看完;·用Python编写漏洞的exp,然后写一个简单的网络爬虫;·PHP基本语法学习并书写一个简单的博客系统;熟悉MVC架构,并试着学习一个PHP框架或者Python框架 (可选);·了解Bootstrap的布局或者CSS。
**8、超级黑客**
这部分内容对零基础的同学来说还比较遥远,就不展开细说了,附上学习路线。
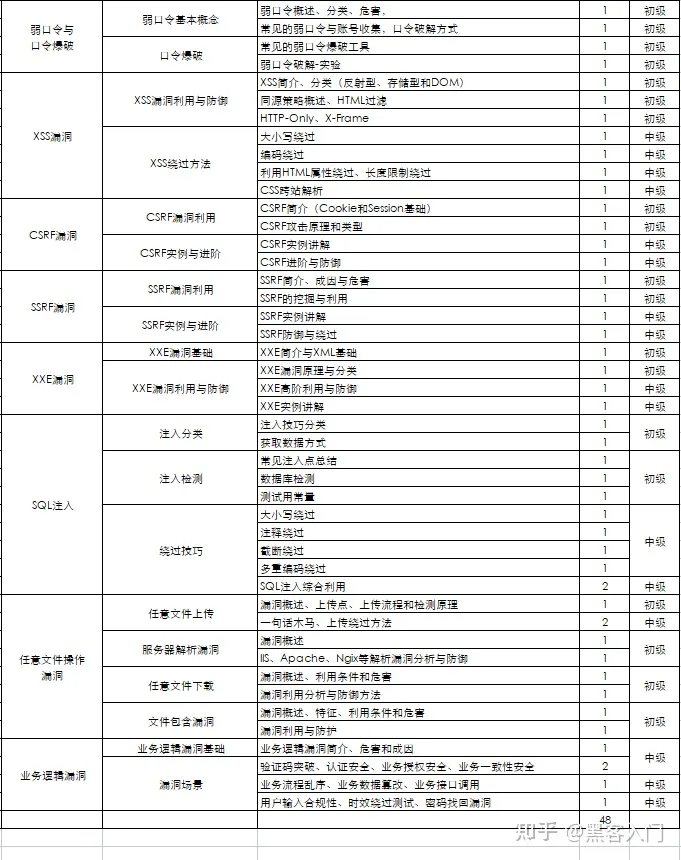
#### 网络安全工程师企业级学习路线

如图片过大被平台压缩导致看不清的话,评论区点赞和评论区留言获取吧。我都会回复的
视频配套资料&国内外网安书籍、文档&工具
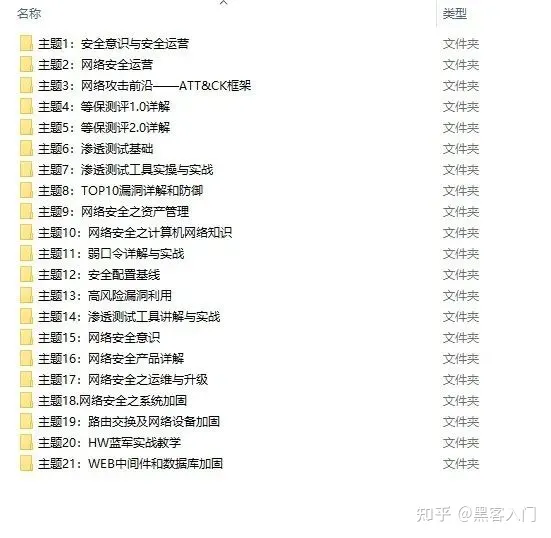
当然除了有配套的视频,同时也为大家整理了各种文档和书籍资料&工具,并且已经帮大家分好类了。

一些笔者自己买的、其他平台白嫖不到的视频教程。
**网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。**
**[需要这份系统化资料的朋友,可以点击这里获取](https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/618540462)**
**一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!**






















 986
986











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








