注
意
观
察
在
整
个
r
e
h
a
s
h
过
程
中
,
字
典
的
r
e
h
a
s
h
i
d
x
属
性
是
如
何
变
化
的
\color{#ef246f}{注意观察在整个 rehash 过程中, 字典的 rehashidx 属性是如何变化的}
注意观察在整个rehash过程中,字典的rehashidx属性是如何变化的
- 为 ht[1] 分配空间, 让字典同时持有 ht[0] 和 ht[1] 两个哈希表。
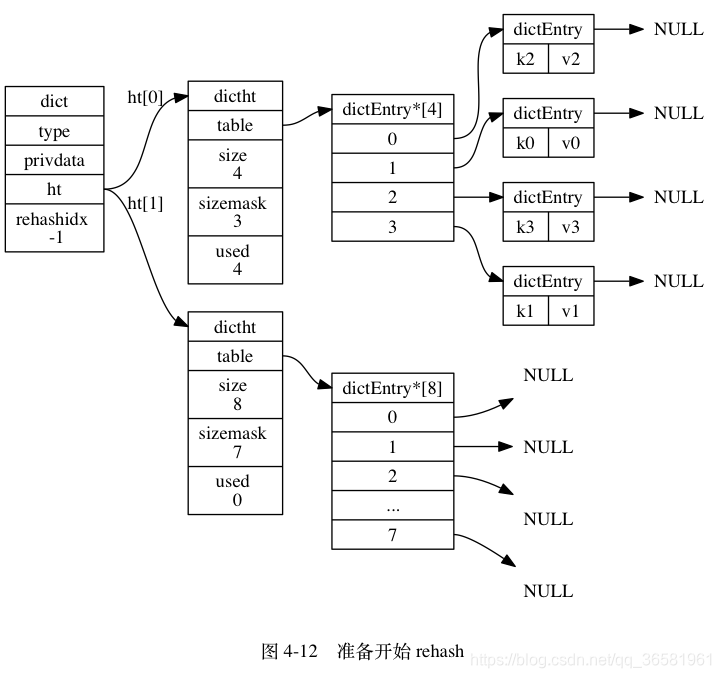
- 在字典中维持一个索引计数器变量 rehashidx , 并将它的值设置为 0 , 表示 rehash 工作正式开始。
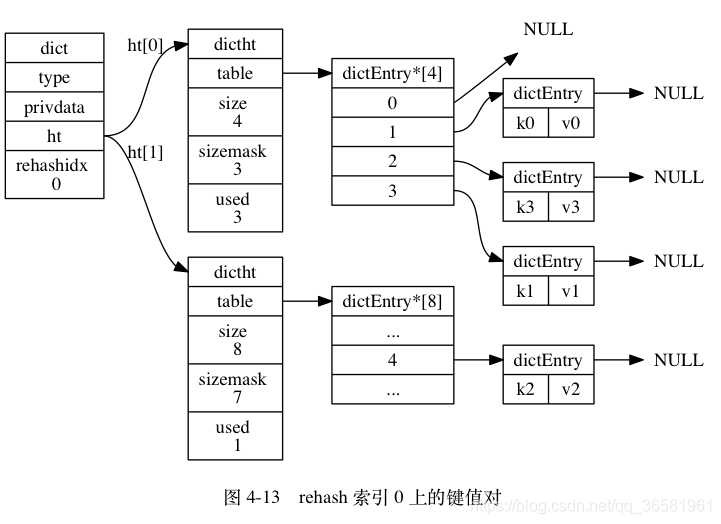
- 在 rehash 进行期间, 每次对字典执行添加、删除、查找或者更新操作时, 程序除了执行指定的操作以外, 还会顺带将 ht[0] 哈希表在 rehashidx 索引上的所有键值对 rehash 到 ht[1] , 当 rehash 工作完成之后, 程序将 rehashidx 属性的值增一。
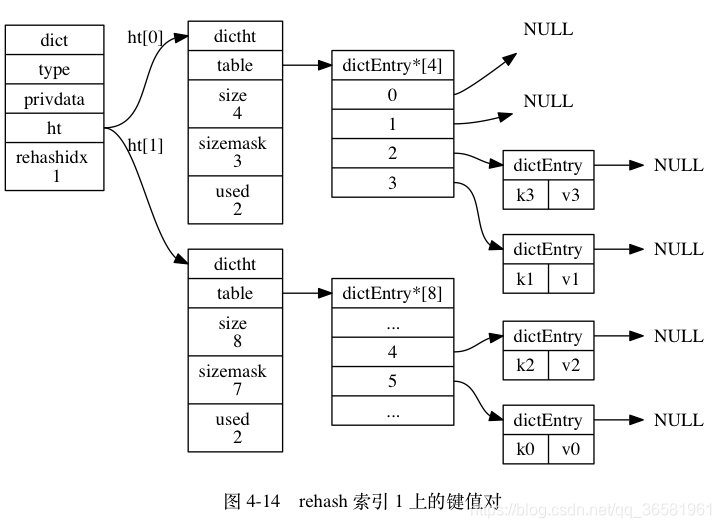
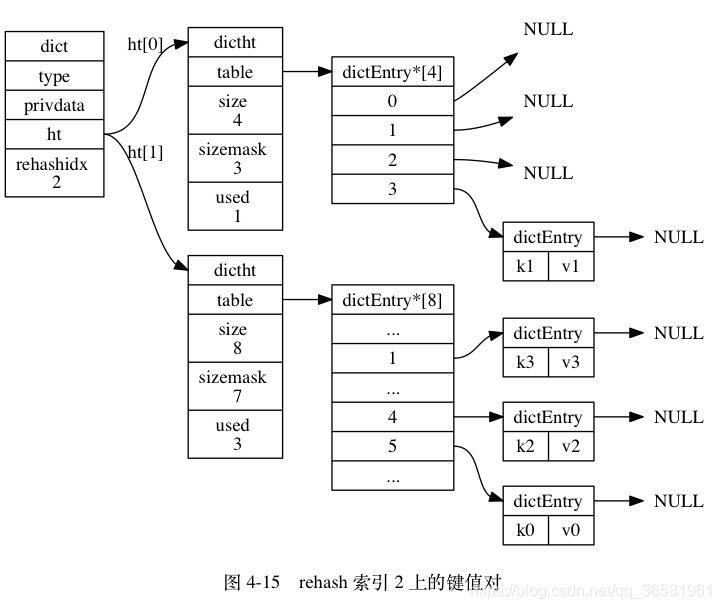
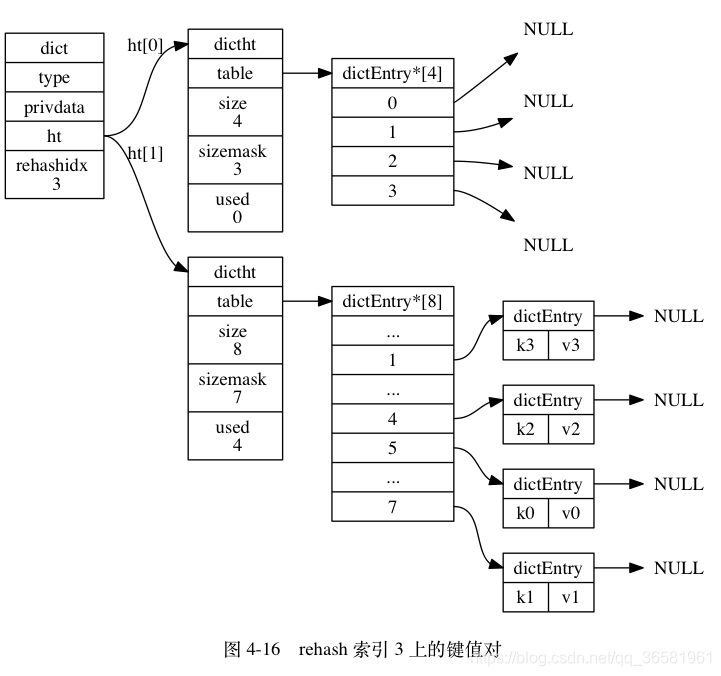
- 随着字典操作的不断执行, 最终在某个时间点上, ht[0] 的所有键值对都会被 rehash 至 ht[1] , 这时程序将 rehashidx 属性的值设为 -1 , 表示 rehash 操作已完成。
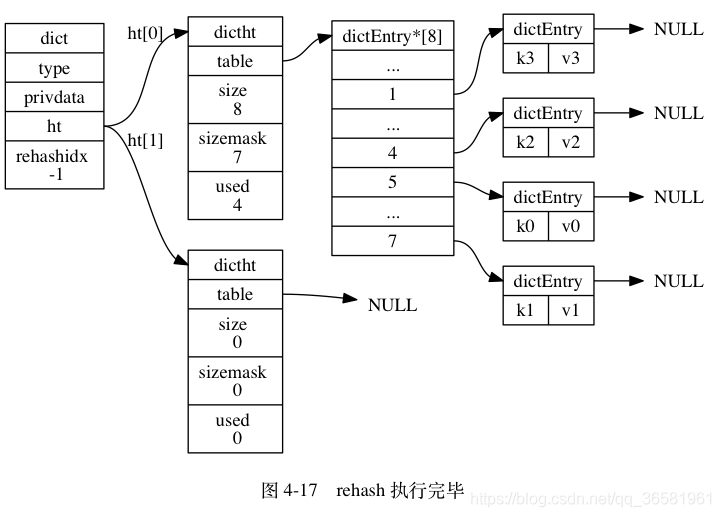
渐进式 rehash 的好处在于它采取分而治之的方式, 将 rehash 键值对所需的计算工作均滩到对字典的每个添加、删除、查找和更新操作上, 从而避免了集中式 rehash 而带来的庞大计算量。
因为在进行渐进式 rehash 的过程中, 字典会同时使用 ht[0] 和 ht[1] 两个哈希表, 所以在渐进式 rehash 进行期间, 字典的删除(delete)、查找(find)、更新(update)等操作会在两个哈希表上进行: 比如说, 要在字典里面查找一个键的话, 程序会先在 ht[0] 里面进行查找, 如果没找到的话, 就会继续到 ht[1] 里面进行查找, 诸如此类。
另外, 在渐进式 rehash 执行期间, 新添加到字典的键值对一律会被保存到 ht[1] 里面, 而 ht[0] 则不再进行任何添加操作: 这一措施保证了 ht[0] 包含的键值对数量会只减不增, 并随着 rehash 操作的执行而最终变成空表。
源码阅读
创建并初始化字典
/* 创建并初始化字典 */
dict *dictCreate(dictType *type,
void *privDataPtr)
{
dict *d = zmalloc(sizeof(*d));
_dictInit(d,type,privDataPtr);
return d;
}
/* Initialize the hash table */
int _dictInit(dict *d, dictType *type,
void *privDataPtr)
{
_dictReset(&d->ht[0]);
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
d->type = type;
d->privdata = privDataPtr;
d->rehashidx = -1;//赋值为-1,表示未进行hash
d->iterators = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}
//重置hash表
static void _dictReset(dictht *ht)
{
ht->table = NULL;
ht->size = 0;
ht->sizemask = 0;
ht->used = 0;
}
由dictCreate创建一个字典d,并将d传入_dictInit函数。而_dictInit函数将负责d初始化操作。在_dictInit内部调用 _dictReset初始化ht[0]和ht[1]数据结构。
从_dictReset函数我们可以看到,新建dict时未对ht[0]、ht[1]分配空间,那么系统会在什么时候进行分配操作呢? 答案是在调用dictAdd操作时.
字典添加
int dictAdd(dict *d, void *key, void *val)
{
dictEntry *entry = dictAddRaw(d,key);
if (!entry) return DICT_ERR;
dictSetVal(d, entry, val);
return DICT_OK;
}
dictAddRaw会检查d是否存在key,如果存在,则返回NULL,否则创建key节点。
dictSetVal:顾名思义,设置节点的值。
dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key)
{
int index;
dictEntry *entry;
dictht *ht;
//判断是否在进行rehash操作
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
//检查key是否存在,如果存在,则返回NULL
if ((index = _dictKeyIndex(d, key)) == -1)
return NULL;
//判断rehash是否正在进行,如果正在进行,则往ht[1]添加数据,否则添加至ht[0]
ht = dictIsRehashing(d) ? &d->ht[1] : &d->ht[0];
//创建key节点
entry = zmalloc(sizeof(*entry));
//将节点的指针指向对应的链表头部
entry->next = ht->table[index];
//添加节点至链表头部
ht->table[index] = entry;
//更新used值
ht->used++;
//设置节点信息
dictSetKey(d, entry, key);
return entry;
}
从上面可以看出,代码执行顺序:dictIsRehashing->_dictKeyIndex->dictIsRehashing->dictSetKey.细心的童鞋可能注意到,该函数内部调用两次dictIsRehashing。难道在_dictKeyIndex函数期间dict结构会发生变化么?
追踪下_dictKeyIndex代码:
static int _dictKeyIndex(dict *d, const void *key)
{
unsigned int h, idx, table;
dictEntry *he;
if (_dictExpandIfNeeded(d) == DICT_ERR)
return -1;
//计算key hash值
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
//查找key,如果存在,则返回-1,否则返回hash索引
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
//计算hash索引
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
//从hash索引对应的链表中搜索
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
while(he) {
if (key==he->key || dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key))
return -1;
he = he->next;
}
//如果rehash未进行,则只需搜索ht[0]
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break;
}
return idx;
}
从_dictKeyIndex内部,可以看到_dictExpandIfNeeded函数。根据字面意思推测,这个应该与dict空间有关联(即ht->size)。继续追踪_dictExpandIfNeeded代码
//判断dict是否需要扩展空间
static int _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d)
{
//rehash正在进行,则不进行操作
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_OK;
//如果size=0,则设置默认大小
if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return dictExpand(d, DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE);
//当负载因子(used/size)>=1时,对以下两种情况扩展空间。
//1. dict_can_resize=1
//2. 达到强制resize条件时(used/size>dict_force_resize_ratio)。
if (d->ht[0].used >= d->ht[0].size &&
(dict_can_resize ||
d->ht[0].used/d->ht[0].size > dict_force_resize_ratio))
{
return dictExpand(d, d->ht[0].used*2);
}
return DICT_OK;
}
对于新建的dict,执行的代码为dictExpand(d, DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE)。DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE在dict.h文件被定义,值为4.我们再追踪下dictExpand函数。
int dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size)
{
//dict的扩展空间大小:最小一个>=size的2^N数
unsigned long realsize = _dictNextPower(size);
…省略部分代码…
//设置dict大小
n.size = realsize;
//设置hash掩码
n.sizemask = realsize-1;
//初始化table空间
n.table = zcalloc(realsize*sizeof(dictEntry*));
n.used = 0;
//如果dict是否为空(初始化操作),则将n设置为ht[0]
if (d->ht[0].table == NULL) {
d->ht[0] = n;
return DICT_OK;
}
//将n赋给ht[1],并设置rehash索引
d->ht[1] = n;
d->rehashidx = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}
从上面的代码可以看出,ht[0]和ht[1]的内存分配都是在这里进行的。对于一个为空的dict,系统会为ht[0]分配空间。对于一个非空的dict,系统则为ht[1]分配空间,并重置rehashidx标识。
现在应该知道dictAddRaw函数内部执行_dictKeyIndex之后再次调用 dictIsRehashing的原因了吧。
好了,总结下dictAdd的流程:dictAdd->dictAddRaw->_dictKeyIndex->_dictExpandIfNeeded->dictExpand。
字典替换
dictReplace:顾名思义,替换功能,分为两种情形:当key不存在,则进行创建;当key存在,则修改key的值。代码执行流程:dictAdd->dictFind->dictSetVal
int dictReplace(dict *d, void *key, void *val)
{
dictEntry *entry, auxentry;
//如果key不存在,则进行创建
if (dictAdd(d, key, val) == DICT_OK)
return 1;
//如果key存在,则找到相应的节点
entry = dictFind(d, key);
//修改节点的值
dictSetVal(d, entry, val);
…省略部分代码…
}
字典删除
dictDelete
/* Remove an element, returning DICT_OK on success or DICT_ERR if the
* element was not found. */
int dictDelete(dict *ht, const void *key) {
return dictGenericDelete(ht,key,0) ? DICT_OK : DICT_ERR;
}
扩大或者缩小空间
dictResize—>dictExpand
/* Resize the table to the minimal size that contains all the elements,
* but with the invariant of a USED/BUCKETS ratio near to <= 1 */
// 缩小hashtable空间 触发rehash的条件
int dictResize(dict *d)
{
int minimal;
if (!dict_can_resize || dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_ERR;
minimal = d->ht[0].used;
if (minimal < DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE)
minimal = DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE; // 4
return dictExpand(d, minimal);
}
/* Expand or create the hash table */
int dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size)
{
/* the size is invalid if it is smaller than the number of
* elements already inside the hash table */
if (dictIsRehashing(d) || d->ht[0].used > size)
return DICT_ERR;
dictht n; /* the new hash table */
// 它不断计算 2 的乘幂,直到遇到大于等于 size 参数的乘幂,就返回这个乘幂作为哈希表的大小 这个地方有点意思的
unsigned long realsize = _dictNextPower(size); //比size大的2**n
/* Rehashing to the same table size is not useful. */
if (realsize == d->ht[0].size) return DICT_ERR;
/* Allocate the new hash table and initialize all pointers to NULL */
n.size = realsize;
n.sizemask = realsize-1;
n.table = zcalloc(realsize*sizeof(dictEntry*));
n.used = 0;
/* Is this the first initialization? If so it’s not really a rehashing
* we just set the first hash table so that it can accept keys. */
// 如果0号哈希表为空 那么这是第一次初始化
// 程序将新的哈希表赋给0号哈希表的指针 然后字典处理键值对
if (d->ht[0].table == NULL) {
d->ht[0] = n;
return DICT_OK;
}
/* Prepare a second hash table for incremental rehashing */
d->ht[1] = n;
d->rehashidx = 0; // 标记可以rehash
return DICT_OK;
}
_dictKeyIndex——>_dictExpandIfNeeded——>dictExpand
/* Returns the index of a free slot that can be populated with
* a hash entry for the given ‘key’.
* If the key already exists, -1 is returned
* and the optional output parameter may be filled.
*
* Note that if we are in the process of rehashing the hash table, the
* index is always returned in the context of the second (new) hash table. */
static long _dictKeyIndex(dict *d, const void *key, uint64_t hash, dictEntry **existing)
{
unsigned long idx, table;
dictEntry *he;
if (existing) *existing = NULL;
/* Expand the hash table if needed */
if (_dictExpandIfNeeded(d) == DICT_ERR)
return -1;
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
idx = hash & d->ht[table].sizemask;
/* Search if this slot does not already contain the given key */
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
while(he) {
if (key==he->key || dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key)) {
if (existing) *existing = he;
return -1;
}
he = he->next;
}
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break;
}
return idx;
}
static int _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d)
{
/* Incremental rehashing already in progress. Return. */
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_OK;
/* If the hash table is empty expand it to the initial size. */
if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return dictExpand(d, DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE);
/* If we reached the 1:1 ratio, and we are allowed to resize the hash
* table (global setting) or we should avoid it but the ratio between
* elements/buckets is over the “safe” threshold, we resize doubling
* the number of buckets. */
if (d->ht[0].used >= d->ht[0].size &&
(dict_can_resize ||
d->ht[0].used/d->ht[0].size > dict_force_resize_ratio))
{
return dictExpand(d, d->ht[0].used*2);
}
return DICT_OK;
}
渐进式的rehash
dictRehashMilliseconds:一个定时器调用rehash
/* Rehash for an amount of time between ms milliseconds and ms+1 milliseconds */
int dictRehashMilliseconds(dict *d, int ms) {
long long start = timeInMilliseconds();
int rehashes = 0;
// 在给定的毫秒数 以100为单位
while(dictRehash(d,100)) {
rehashes += 100;
if (timeInMilliseconds()-start > ms) break;
}
return rehashes;
}
_dictRehashStep:在添加 查找 删除的时候会调用这个方法,平摊这dictAddRaw 、dictGetRandomKey 、dictFind 、dictGenericDelete这些函数,这样可以避免集中式的rehash,出现进程阻塞的情况。
/* This function performs just a step of rehashing, and only if there are
* no safe iterators bound to our hash table. When we have iterators in the
* middle of a rehashing we can’t mess with the two hash tables otherwise
* some element can be missed or duplicated.
*
* This function is called by common lookup or update operations in the
* dictionary so that the hash table automatically migrates from H1 to H2
* while it is actively used. */
static void _dictRehashStep(dict *d) {
if (d->iterators == 0) dictRehash(d,1);
}
注
意
!
注
意
!
注
意
!
最
为
核
心
的
东
西
来
自我介绍一下,小编13年上海交大毕业,曾经在小公司待过,也去过华为、OPPO等大厂,18年进入阿里一直到现在。
深知大多数Go语言工程师,想要提升技能,往往是自己摸索成长或者是报班学习,但对于培训机构动则几千的学费,着实压力不小。自己不成体系的自学效果低效又漫长,而且极易碰到天花板技术停滞不前!
因此收集整理了一份《2024年Go语言全套学习资料》,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助到想自学提升又不知道该从何学起的朋友,同时减轻大家的负担。


既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,基本涵盖了95%以上Golang知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较大,这里只是将部分目录大纲截图出来,每个节点里面都包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
如果你觉得这些内容对你有帮助,可以添加V获取:vip1024b (备注Go)

一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远。不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎扫码加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
因此收集整理了一份《2024年Go语言全套学习资料》,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助到想自学提升又不知道该从何学起的朋友,同时减轻大家的负担。
[外链图片转存中…(img-XNFDuSNt-1712985720694)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-VEj5HcMu-1712985720696)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-LzeW63vQ-1712985720696)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-VsUwQaZm-1712985720697)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-e4vFfAv7-1712985720697)]
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,基本涵盖了95%以上Golang知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较大,这里只是将部分目录大纲截图出来,每个节点里面都包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
如果你觉得这些内容对你有帮助,可以添加V获取:vip1024b (备注Go)
[外链图片转存中…(img-kedTrxO1-1712985720698)]
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远。不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎扫码加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!






















 620
620











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








