小结:
Prim算法是一种基**于贪心思想求解加权无向图的最小生成树**的算法
Prim算法的时间复杂度为T(n)= O(V^2),适合于处理稠密图;
Kurskal
并查集 + 最小生成树 --> Kruskal算法
克鲁斯卡尔算法
一种用来查找最小生成树的算法
由Joseph Kruskal于1956年发表【Joseph Bernard Kruskal,1928年1月29日-2010年9月19日,美国数学家、统计学家、计算机科学家、心理测量学专家】
设计思路
(1) 将边按权值从小到大排序后逐个判断,如果当前的边加入以后不会产生环,那么就把当前边作为生成树的一条边
(2) 一共选取(V-1)条边(V为顶点数),最终得到的结果就是最小生成树
数据结构:并查集
数据结构定义和初始化
/* 定义边(x,y),权为w */
struct edge
{
int x, y;
int w;
};
edge e[MAX * MAX];
int rank[MAX];/* rank[x]表示x的秩 */
int father[MAX];/* father[x]表示x的父结点 */
int sum; /*存储最小生成树的总权重 */
/* 比较函数,按权值非降序排序 */
bool cmp(const edge a, const edge b)
{
return a.w < b.w;
}
并查集
/* 初始化集合 */
void make_set(int x)
{
father[x] = x;
rank[x] = 0;
}
/* 查找x元素所在的集合,回溯时压缩路径 */
int find_set(int x)
{
if (x != father[x])
{
father[x] = find_set(father[x]);
}
return father[x];
}
/* 合并x,y所在的集合 */
int union_set(int x, int y, int w)
{
x = find_set(x);
y = find_set(y);
if (x == y) return 0;//不合并返回0
if (rank[x] > rank[y])
{
father[y] = x;
}
else
{
if (rank[x] == rank[y])
{
rank[y]++;
}
father[x] = y;
}
sum += w; //记录权重
return 1;//合并返回1, 标记出边(x,y)是否可以加入生成树中
}
时间复杂度分析
边排序所需时间:T(n) = O(ElogE)
Kruskal算法的实现通常使用并查集来快速判断两个顶点是否属于同一个集合。**最坏的情况可能要枚举完所有的边,此时要循环|E|次,**所以这一步的时间复杂度为O(Eα(V))【采用路径压缩后,每一次查询所用的时间复杂度为增长极为缓慢的Ackerman函数的反函数——α(x) ,其增长非常慢,可以视为常数】
T(n)= O(Eα(V)) + O(ElogE) = O(ElogE) -->稀疏图
例题HDU-1301
题目描述

The Head Elder of the tropical island of Lagrishan has a problem. A burst of foreign aid money was spent on extra roads between villages some years ago. But the jungle overtakes roads relentlessly, so the large road network is too expensive to maintain. The Council of Elders must choose to stop maintaining some roads. The map above on the left shows all the roads in use now and the cost in aacms per month to maintain them. Of course there needs to be some way to get between all the villages on maintained roads, even if the route is not as short as before. The Chief Elder would like to tell the Council of Elders what would be the smallest amount they could spend in aacms per month to maintain roads that would connect all the villages. The villages are labeled A through I in the maps above. The map on the right shows the roads that could be maintained most cheaply, for 216 aacms per month. Your task is to write a program that will solve such problems.
The input consists of one to 100 data sets, followed by a final line containing only 0. Each data set starts with a line containing only a number n, which is the number of villages, 1 < n < 27, and the villages are labeled with the first n letters of the alphabet, capitalized. Each data set is completed with n-1 lines that start with village labels in alphabetical order. There is no line for the last village. Each line for a village starts with the village label followed by a number, k, of roads from this village to villages with labels later in the alphabet. If k is greater than 0, the line continues with data for each of the k roads. The data for each road is the village label for the other end of the road followed by the monthly maintenance cost in aacms for the road. Maintenance costs will be positive integers less than 100. All data fields in the row are separated by single blanks. The road network will always allow travel between all the villages. The network will never have more than 75 roads. No village will have more than 15 roads going to other villages (before or after in the alphabet). In the sample input below, the first data set goes with the map above.
The output is one integer per line for each data set: the minimum cost in aacms per month to maintain a road system that connect all the villages. Caution: A brute force solution that examines every possible set of roads will not finish within the one minute time limit.
翻译:热带岛屿拉格里山的首长有个问题。几年前,大量的外援花在了村庄之间的额外道路上。但是丛林不断地超越道路,因此庞大的道路网太昂贵而无法维护。老年人理事会必须选择停止维护一些道路。左上方的地图显示了目前正在使用的所有道路,以及每月维护这些道路的费用。当然,即使路线不像以前那么短,也需要采取某种方式在所有村庄之间保持通行。长老院长想告诉长老委员会每月要花多少钱才能维持连接所有村庄的道路。在上面的地图中,这些村庄被标记为A到I。右边的地图显示了可以最便宜地维护的道路,每月可节省216英亩。您的任务是编写一个解决此类问题的程序。
输入由1到100个数据集组成,后面是仅包含0的最后一行。每个数据集都从仅包含数字n的行开始,n是村庄的数目,1 <n <27,并标记了村庄字母的前n个字母大写。每个数据集都以n-1行完成,这些行以字母顺序的村庄标签开头。最后一个村庄没有电话。村庄的每条线均以村庄标签开头,后跟从该村庄到带有字母标签的村庄的道路的数量k。如果k大于0,则该行以k条道路中的每条道路的数据继续。每条道路的数据是道路另一端的村庄标签,其后是道路的每月维护成本(以acms为单位)。维护成本将为小于100的正整数。该行中的所有数据字段均由单个空格分隔。公路网将始终允许所有村庄之间的旅行。该网络永远不会超过75条道路。到其他村庄的村庄中,没有一条道路会超过15条(在字母表中的前后)。在下面的示例输入中,第一个数据集与上面的地图一起显示。
每个数据集的输出为每行一个整数:维护连接所有村庄的道路系统的每月最低费用(以aacms计)。警告:检查每条可能的道路的暴力解决方案都不会在一分钟的时间内完成。
输入
9
A 2 B 12 I 25
B 3 C 10 H 40 I 8
C 2 D 18 G 55
D 1 E 44
E 2 F 60 G 38
F 0
G 1 H 35
H 1 I 35
3
A 2 B 10 C 40
B 1 C 20
0
输出
216
30
上代码,这是Kruskal算法的。
#include “bits/stdc++.h”
using namespace std;
const int maxx = 105;
int father[maxx];
int ran[maxx];
int ans = 0;
struct node
{
int x, y;
int v;
} qq[30];
inline bool cmp(node a, node b)
{
return a.v < b.v;
}
inline void make_set(int x)
{
father[x] = x;
ran[x] = 0;
}
inline int find(int x)
{ //压缩路径的查找
if (father[x] == x)
{ //如果自己的父节点是自己,那么x 结点就是根结点
return x;
}
return find(father[x]); // 返回父结点的根结点
}
inline int merge(int x, int y, int v)//按秩合并
{
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
if (x == y)
return 0;
ans += v;
if (ran[x] > ran[y])
{
father[y] = x;
}
else
{
father[x] = y;
if (ran[x] == ran[y])
{
ran[y]++;
}
}
return 1;
}
int main()
{
int n, m;
while (cin >> n && n)
{
ans = 0;
m = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
make_set(i);
}
int x, y;
int v;
char a, b;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
cin >> a >> x;
for (int j = 0; j < x; j++)
{
cin >> b >> v;
qq[j + m].x = a - ‘A’;
qq[j + m].y = b - ‘A’;
qq[j + m].v = v;
/* code */
}
m += x;
}
sort(qq, qq + m, cmp);
int s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
if (merge(qq[i].x, qq[i].y, qq[i].v))
{
文末
js前端的重头戏,值得花大部分时间学习。
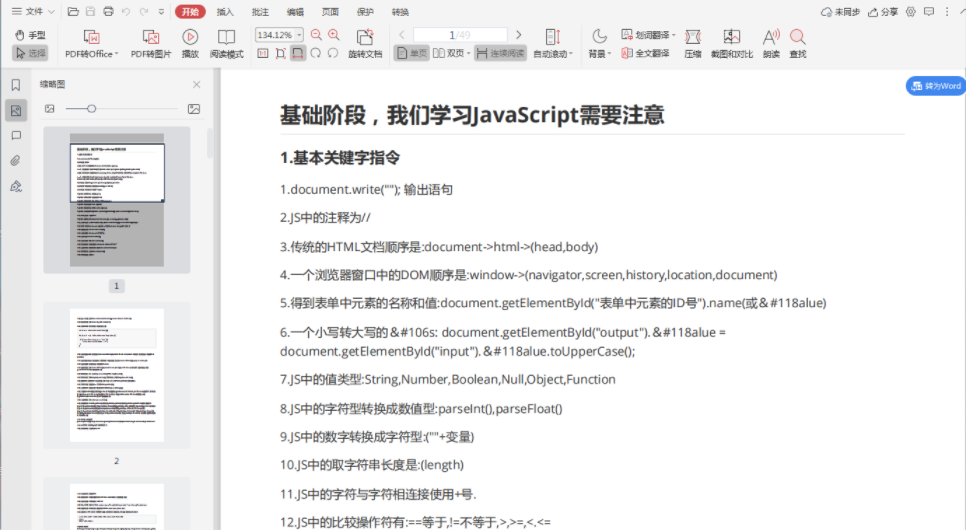
推荐通过书籍学习,《 JavaScript 高级程序设计(第 4 版)》你值得拥有。整本书内容质量都很高,尤其是前十章语言基础部分,建议多读几遍。
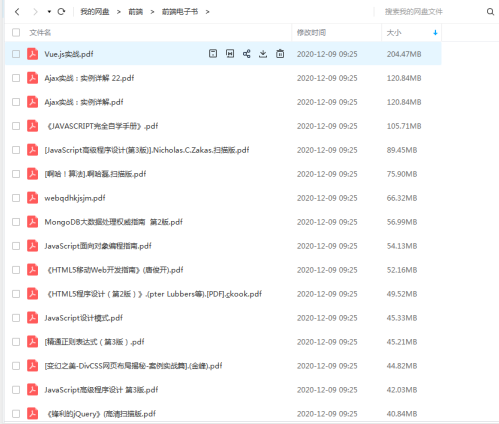
开源分享:【大厂前端面试题解析+核心总结学习笔记+真实项目实战+最新讲解视频】
另外,大推一个网上教程 现代 JavaScript 教程 ,文章深入浅出,很容易理解,上面的内容几乎都是重点,而且充分发挥了网上教程的时效性和资料链接。
学习资料在精不在多,二者结合,定能构建你的 JavaScript 知识体系。
面试本质也是考试,面试题就起到很好的考纲作用。想要取得优秀的面试成绩,刷面试题是必须的,除非你样样精通。
这是288页的前端面试题
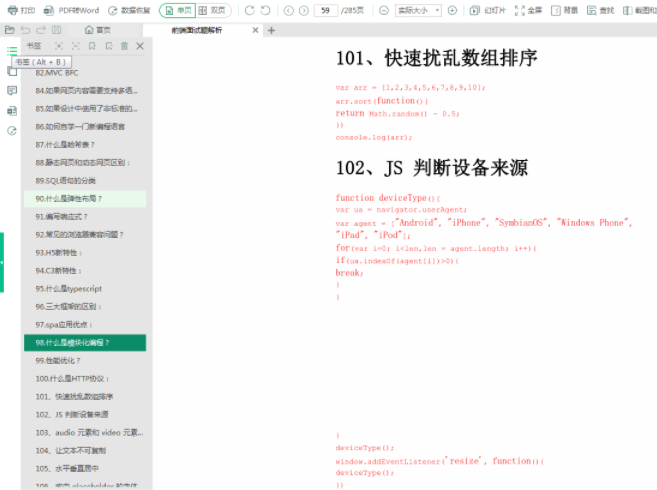






















 194
194

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








