return cn;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
根据Android系统揭秘(一)-Activity启动流程(上) 一节我们已经知道ActivityManager.getService()其实就是AMS
AMS通知ActivityThread
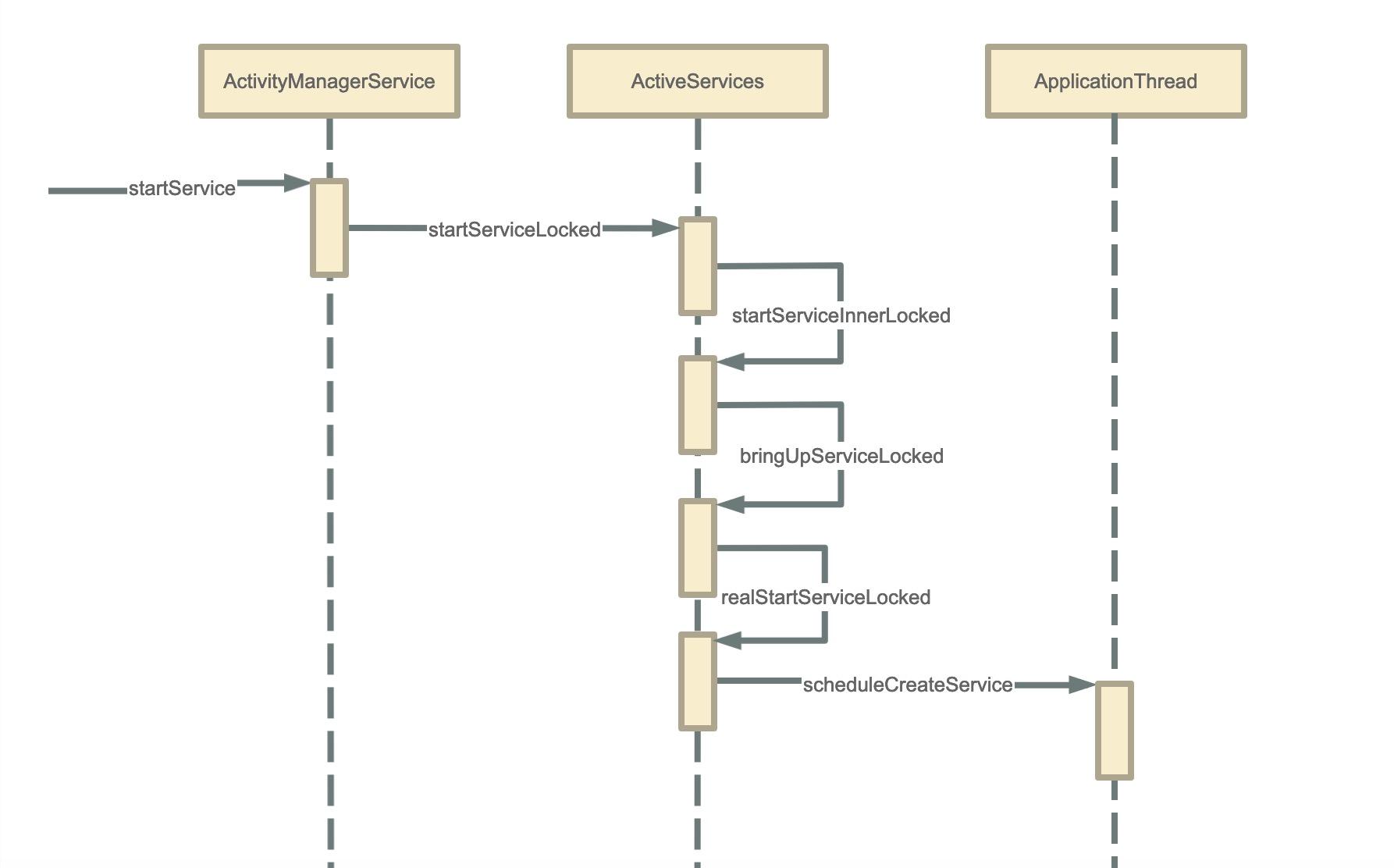
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
final ActiveServices mServices;
@Override
public ComponentName startService(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service,
String resolvedType, boolean requireForeground, String callingPackage, int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
…
synchronized(this) {
final int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
ComponentName res;
try {
res = mServices.startServiceLocked(caller, service,
resolvedType, callingPid, callingUid,
requireForeground, callingPackage, userId);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
return res;
}
}
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
ComponentName startServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType,
int callingPid, int callingUid, boolean fgRequired, String callingPackage, final int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
…
ComponentName cmp = startServiceInnerLocked(smap, service, r, callerFg, addToStarting);
return cmp;
}
ComponentName startServiceInnerLocked(ServiceMap smap, Intent service, ServiceRecord r,
boolean callerFg, boolean addToStarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
…
String error = bringUpServiceLocked(r, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false, false);
if (error != null) {
return new ComponentName(“!!”, error);
}
…
return r.name;
}
private String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting, boolean permissionsReviewRequired)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
// 发送Service参数
if (r.app != null && r.app.thread != null) {
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, false);
return null;
}
…
final boolean isolated = (r.serviceInfo.flags&ServiceInfo.FLAG_ISOLATED_PROCESS) != 0;
final String procName = r.processName;
String hostingType = “service”;
ProcessRecord app;
if (!isolated) {
app = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(procName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
if (DEBUG_MU) Slog.v(TAG_MU, “bringUpServiceLocked: appInfo.uid=” + r.appInfo.uid
- " app=" + app);
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.versionCode, mAm.mProcessStats);
// 启动Service
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
return null;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting service " + r.shortName, e);
}
// If a dead object exception was thrown – fall through to
// restart the application.
}
} else {
// If this service runs in an isolated process, then each time
…
}
// 如果Service进程不存在则创建
if (app == null && !permissionsReviewRequired) {
if ((app=mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true, intentFlags,
hostingType, r.name, false, isolated, false)) == null) {
String msg = "Unable to launch app "
- r.appInfo.packageName + “/”
- r.appInfo.uid + " for service "
- r.intent.getIntent() + “: process is bad”;
Slog.w(TAG, msg);
bringDownServiceLocked®;
return msg;
}
if (isolated) {
r.isolatedProc = app;
}
}
…
return null;
}
bringUpServiceLocked方法会获取Service所在的进程,如果存在则通过realStartServiceLocked启动Service,否则先创建进程再启动Service
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
…
boolean created = false;
try {
…
app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
r.postNotification();
created = true;
} catch (DeadObjectException e) {
…
} finally {
…
}
…
}
这里的app.thread指的是IApplicationThread,它的实现是ActivityThread的内部类ApplicationThread, 其中ApplicationThread继承了IApplicationThread.Stub
ActivityThread启动Service
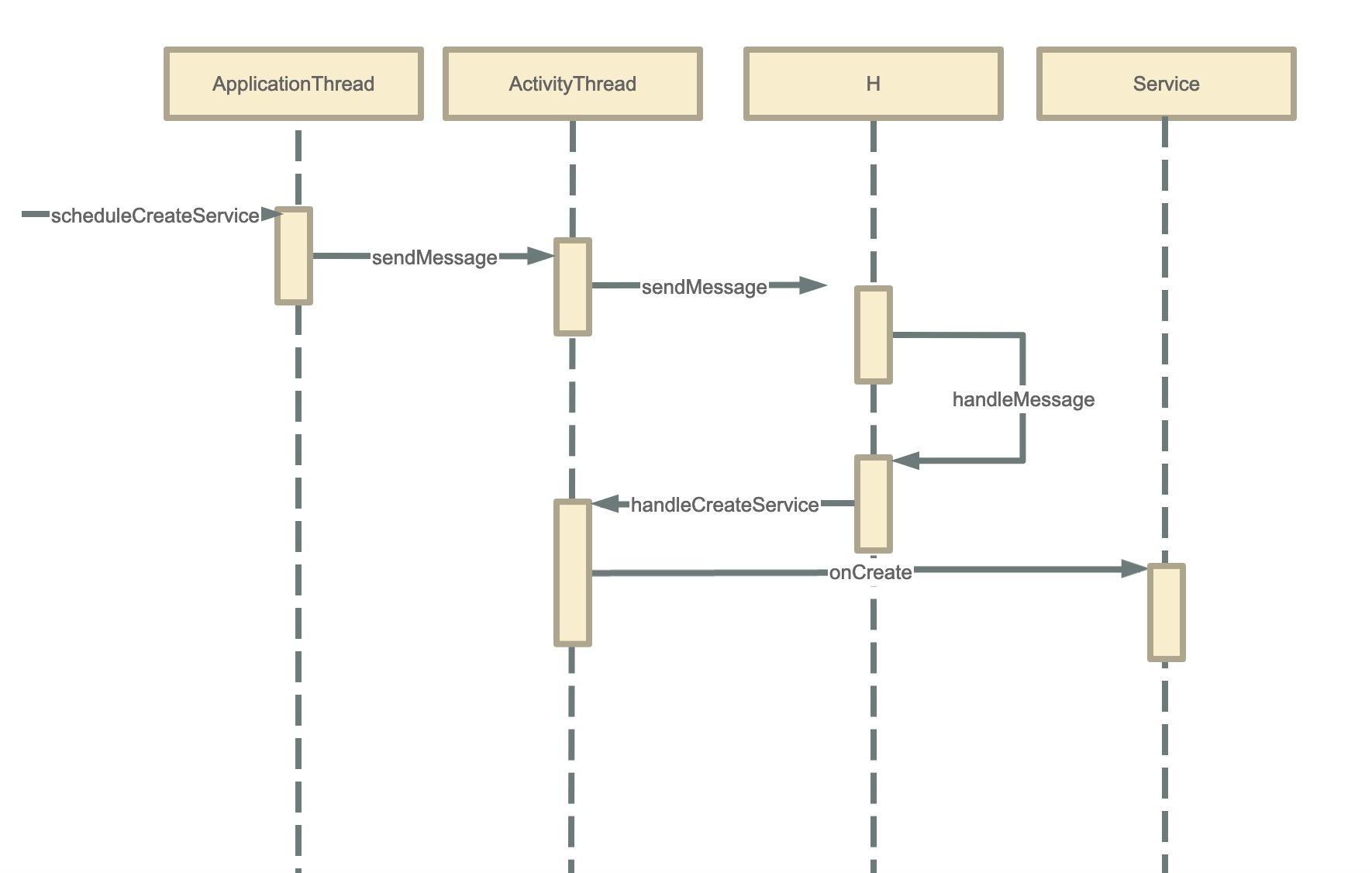
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java#ApplicationThread
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token,
ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.info = info;
s.compatInfo = compatInfo;
sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s);
}
然后就是向mH发送CREATE_SERVICE命令,在H的handleMessage里面接收
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(TAG, ">>> handling: " + codeToString(msg.what));
switch (msg.what) {
case CREATE_SERVICE: {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, ("serviceCreate: " + String.valueOf(msg.obj)));
handleCreateService((CreateServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
} break;
}
}
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
// 获取包信息
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
Service service = null;
try {
// 获取类加载器
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
// 创建Service实例
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate service " + data.info.name
- ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name);
//创建上下文
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
context.setOuterContext(service);
// 创建或获取Application
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
// 初始化Service
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManager.getService());
// 回调通知开发者service创建完成
service.onCreate();
mServices.put(data.token, service);
try {
//通知AMS
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create service " + data.info.name
- ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
这一步主要做了以下事情:
- 获取包信息
- 获取类加载器
- 创建Service实例
- 创建上下文
- 创建或获取Application
- 初始化Service
- 回调通知开发者service创建完成
- 通知AMS
Service 的绑定
ContextImpl到AMS的调用过程
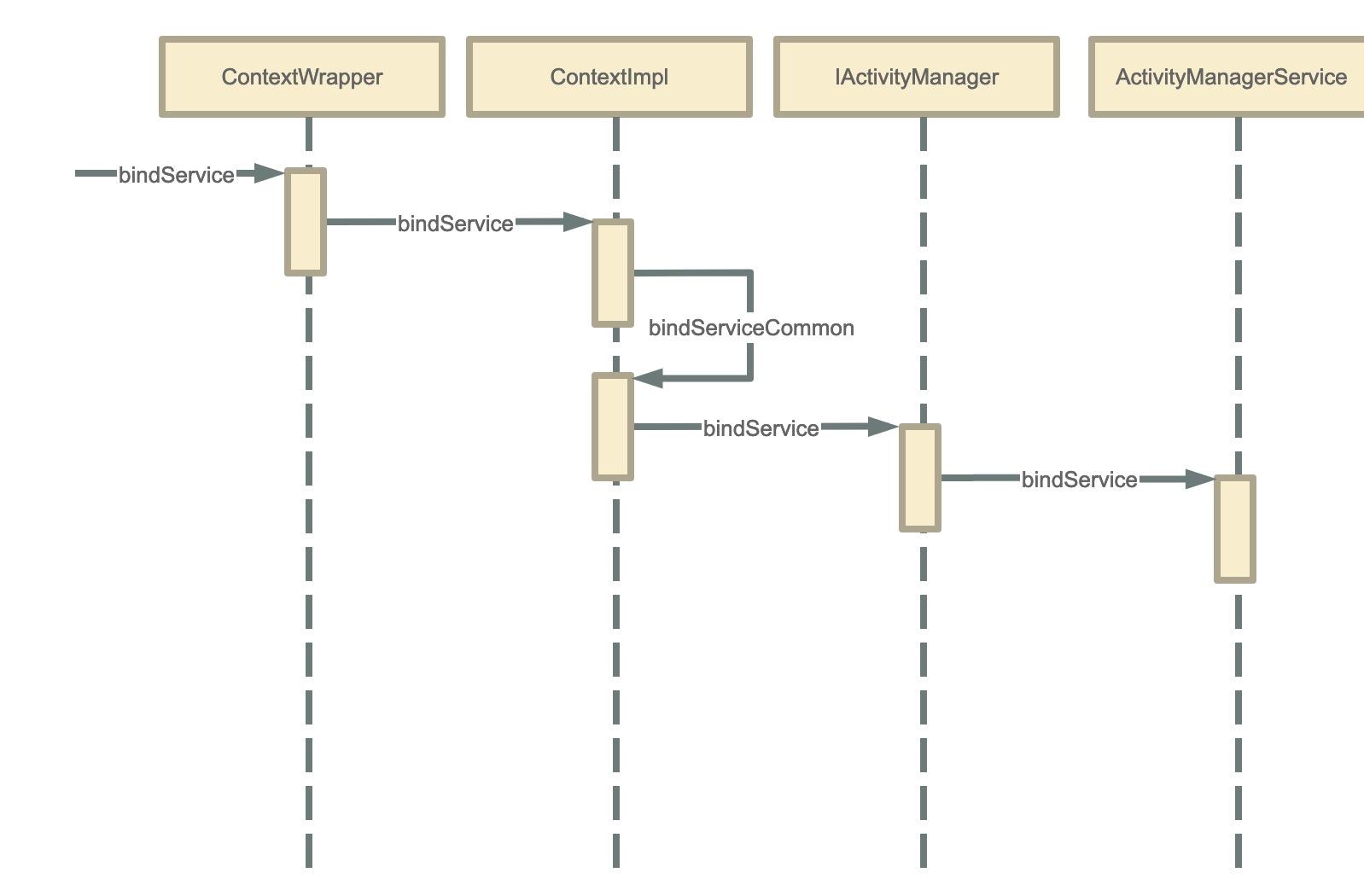
我们调用startService其实调的是ContextWrapper的startService方法
frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/ContextWrapper.java
Context mBase;
@Override
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
return mBase.bindService(service, conn, flags);
}
Context的具体实现是ContextImpl
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ContextImpl.java
@Override
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return bindServiceCommon(service, conn, flags, mMainThread.getHandler(),
Process.myUserHandle());
}
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags, Handler
handler, UserHandle user) {
IServiceConnection sd;
…
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(), handler, flags);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException(“Not supported in system context”);
}
…
validateServiceIntent(service);
try {
…
int res = ActivityManager.getService().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
if (res < 0) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Not allowed to bind to service " + service);
}
return res != 0;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
AMS通知ActivityThread
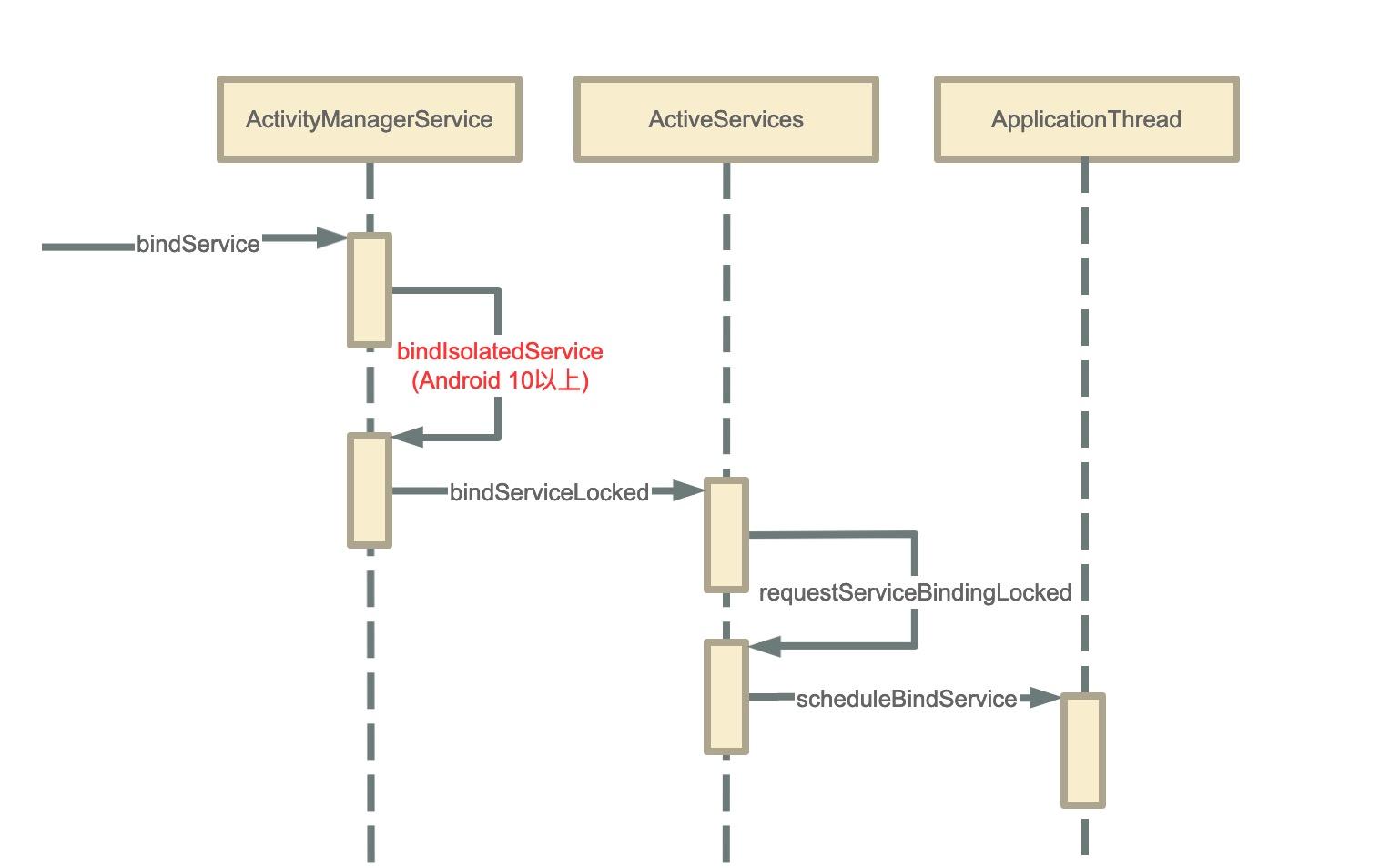
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
final ActiveServices mServices;
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String callingPackage,
int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
…
synchronized(this) {
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service,
resolvedType, connection, flags, callingPackage, userId);
}
}
(Android 10 之后会跳转bindIsolatedService方法先)
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags,
String callingPackage, int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
return bindIsolatedService(caller, token, service, resolvedType, connection, flags,
null, callingPackage, userId);
}
public int bindIsolatedService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String instanceName,
String callingPackage, int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
…
synchronized(this) {
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service,
resolvedType, connection, flags, instanceName, callingPackage, userId);
}
}
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
int bindServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, final IServiceConnection connection, int flags,
String callingPackage, final int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
…
// 记录进程信息
final ProcessRecord callerApp = mAm.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
…
// Activity信息
ActivityRecord activity = null;
if (token != null) {
activity = ActivityRecord.isInStackLocked(token);
if (activity == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Binding with unknown activity: " + token);
return 0;
}
}
…
try {
…
// Service与应用程序的关系
AppBindRecord b = s.retrieveAppBindingLocked(service, callerApp);
ConnectionRecord c = new ConnectionRecord(b, activity,
connection, flags, clientLabel, clientIntent);
IBinder binder = connection.asBinder();
ArrayList clist = s.connections.get(binder);
…
// 如果设置了BIND_AUTO_CREATE标志,则启动bringUpServiceLocked方法,后面参考Service启动
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
s.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (bringUpServiceLocked(s, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false,
permissionsReviewRequired) != null) {
return 0;
}
}
…
if (s.app != null && b.intent.received) {
try {
c.conn.connected(s.name, b.intent.binder, false);
} catch (Exception e) {
…
}
if (b.intent.apps.size() == 1 && b.intent.doRebind) {
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, true);
}
} else if (!b.intent.requested) {
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, false);
}
getServiceMapLocked(s.userId).ensureNotStartingBackgroundLocked(s);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
return 1;
}
这个方法会先获取进程与Activity等信息,然后获取Service与应用程序的关系,
(注意的是,如果存在设置了BIND_AUTO_CREATE的连接,就不销毁服务直接返回,启动bringUpServiceLocked方法,后面参考Service启动)
后面调用requestServiceBindingLocked方法
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r, IntentBindRecord i,
boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
…
if ((!i.requested || rebind) && i.apps.size() > 0) {
try {
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, “bind”);
r.app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.repProcState);
if (!rebind) {
i.requested = true;
}
i.hasBound = true;
i.doRebind = false;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
…
} catch (RemoteException e) {
…
}
}
return true;
}
这里的app.thread指的是IApplicationThread,它的实现是ActivityThread的内部类ApplicationThread, 其中ApplicationThread继承了IApplicationThread.Stub
ActivityThread绑定Service
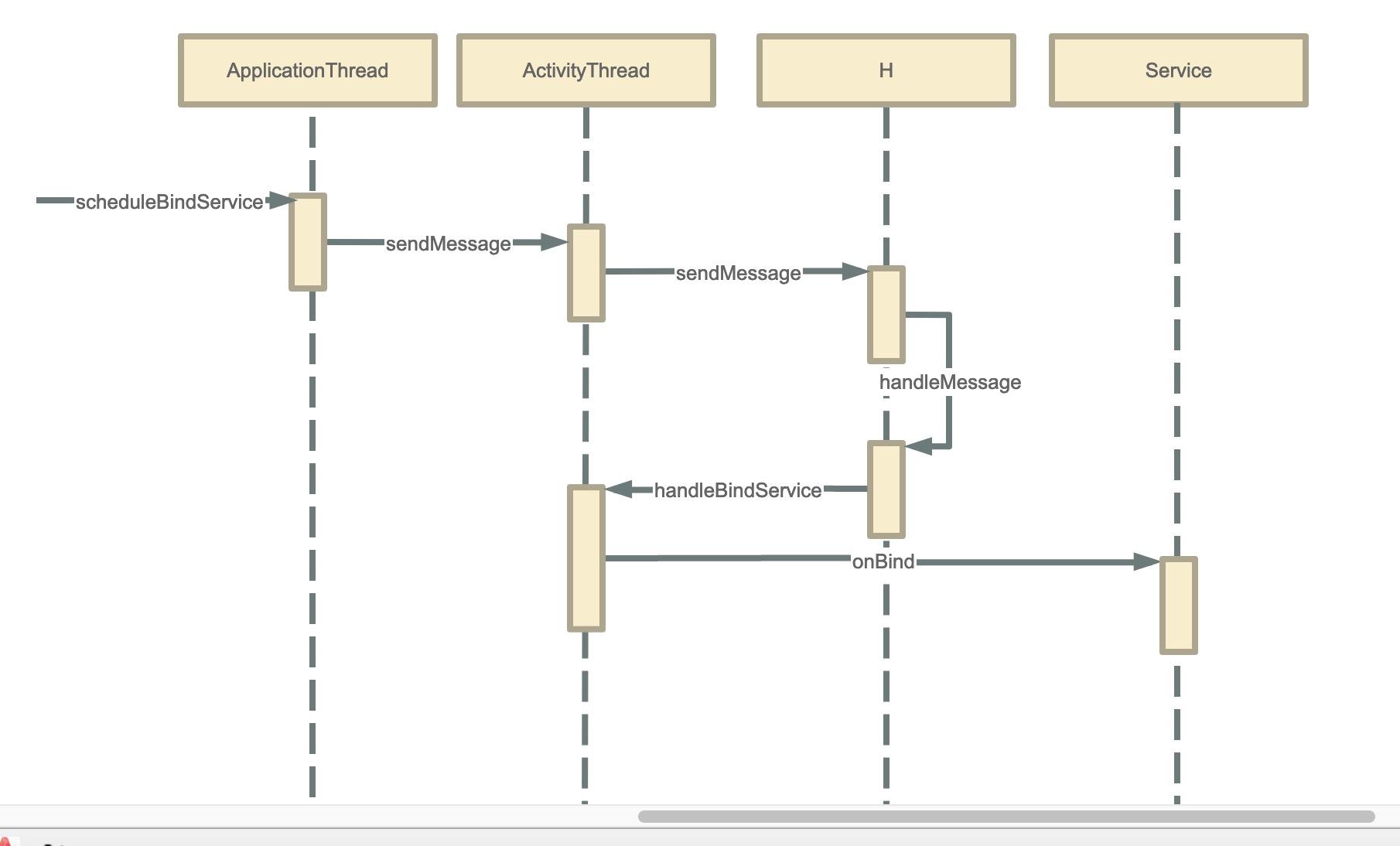
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java#ApplicationThread
public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent,
boolean rebind, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
BindServiceData s = new BindServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.intent = intent;
s.rebind = rebind;
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, “scheduleBindService token=” + token + " intent=" + intent + " uid="
- Binder.getCallingUid() + " pid=" + Binder.getCallingPid());
sendMessage(H.BIND_SERVICE, s);
}
然后就是向mH发送BIND_SERVICE命令,在H的handleMessage里面接收
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(TAG, ">>> handling: " + codeToString(msg.what));
switch (msg.what) {
case BIND_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, “serviceBind”);
handleBindService((BindServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
} break;
}
}
final ArrayMap<IBinder, Service> mServices = new ArrayMap<>();
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
总结
Android架构学习进阶是一条漫长而艰苦的道路,不能靠一时激情,更不是熬几天几夜就能学好的,必须养成平时努力学习的习惯。所以:贵在坚持!
上面分享的字节跳动公司2021年的面试真题解析大全,笔者还把一线互联网企业主流面试技术要点整理成了视频和PDF(实际上比预期多花了不少精力),包含知识脉络 + 诸多细节。

【Android高级架构视频学习资源】
Android部分精讲视频领取学习后更加是如虎添翼!进军BATJ大厂等(备战)!现在都说互联网寒冬,其实无非就是你上错了车,且穿的少(技能),要是你上对车,自身技术能力够强,公司换掉的代价大,怎么可能会被裁掉,都是淘汰末端的业务Curd而已!现如今市场上初级程序员泛滥,这套教程针对Android开发工程师1-6年的人员、正处于瓶颈期,想要年后突破自己涨薪的,进阶Android中高级、架构师对你更是如鱼得水,赶快领取吧!
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
mg-ADIQY9w0-1714211774441)]
【Android高级架构视频学习资源】
Android部分精讲视频领取学习后更加是如虎添翼!进军BATJ大厂等(备战)!现在都说互联网寒冬,其实无非就是你上错了车,且穿的少(技能),要是你上对车,自身技术能力够强,公司换掉的代价大,怎么可能会被裁掉,都是淘汰末端的业务Curd而已!现如今市场上初级程序员泛滥,这套教程针对Android开发工程师1-6年的人员、正处于瓶颈期,想要年后突破自己涨薪的,进阶Android中高级、架构师对你更是如鱼得水,赶快领取吧!
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!





















 3400
3400

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








