我的面试宝典:一线互联网大厂Java核心面试题库
以下是我个人的一些做法,希望可以给各位提供一些帮助:
整理了很长一段时间,拿来复习面试刷题非常合适,其中包括了Java基础、异常、集合、并发编程、JVM、Spring全家桶、MyBatis、Redis、数据库、中间件MQ、Dubbo、Linux、Tomcat、ZooKeeper、Netty等等,且还会持续的更新…可star一下!

283页的Java进阶核心pdf文档
Java部分:Java基础,集合,并发,多线程,JVM,设计模式
数据结构算法:Java算法,数据结构
开源框架部分:Spring,MyBatis,MVC,netty,tomcat
分布式部分:架构设计,Redis缓存,Zookeeper,kafka,RabbitMQ,负载均衡等
微服务部分:SpringBoot,SpringCloud,Dubbo,Docker

还有源码相关的阅读学习

// if data is available already, return it immediately
final Map<TopicPartition, List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>>> records = fetcher.fetchedRecords(); // @2
if (!records.isEmpty()) {
return records;
}
fetcher.sendFetches(); // @3
// We do not want to be stuck blocking in poll if we are missing some positions
// since the offset lookup may be backing off after a failure
// NOTE: the use of cachedSubscriptionHashAllFetchPositions means we MUST call
// updateAssignmentMetadataIfNeeded before this method.
if (!cachedSubscriptionHashAllFetchPositions && pollTimeout > retryBackoffMs) { // @4
pollTimeout = retryBackoffMs;
}
Timer pollTimer = time.timer(pollTimeout);
client.poll(pollTimer, () -> {
return !fetcher.hasCompletedFetches();
}); // @5
timer.update(pollTimer.currentTimeMs()); // @6
if (coordinator != null && coordinator.rejoinNeededOrPending()) { // @7
return Collections.emptyMap();
}
return fetcher.fetchedRecords(); // @8
}
代码@1:计算本次拉取的超时时间,其计算逻辑如下:
-
如果协调器为空,则返回当前定时器剩余时间即可。
-
如果协调器不为空,其逻辑较为复杂,为下面返回的超时间与当前定时器剩余时间相比取最小值。
-
如果不开启自动提交位移并且未加入消费组,则超时时间为Long.MAX_VALUE。
-
如果不开启自动提交位移并且已加入消费组,则返回距离下一次发送心跳包还剩多少时间。
-
如果开启自动提交位移,则返回 距离下一次自动提交位移所需时间 与 距离下一次发送心跳包所需时间 之间的最小值。
代码@2:如果数据已经拉回到本地,直接返回数据。将在下文详细介绍 Fetcher 的 fetchedRecords 方法。
代码@3:组装发送请求,并将存储在待发送请求列表中。
代码@4:如果已缓存的分区信息中存在某些分区缺少偏移量,如果拉取的超时时间大于失败重试需要阻塞的时间,则更新此次拉取的超时时间为失败重试需要的间隔时间,主要的目的是不希望在 poll 过程中被阻塞【后续会详细介绍 Kafka 拉取消息的线程模型,再来回顾一下这里】。
代码@5:通过调用NetworkClient 的 poll 方法发起消息拉取操作(触发网络读写)。
代码@6:更新本次拉取的时间。
代码@7:检查是需要重平衡。
代码@8:将从 broker 读取到的数据返回(即封装成消息)。
从上面消息拉取流程来看,有几个比较重要的方法,例如 Fetcher 类相关的方法,NetworkClient 的 poll 方法,那我们接下来来重点探讨。
我们先用一张流程图总结一下消息拉取的全过程:
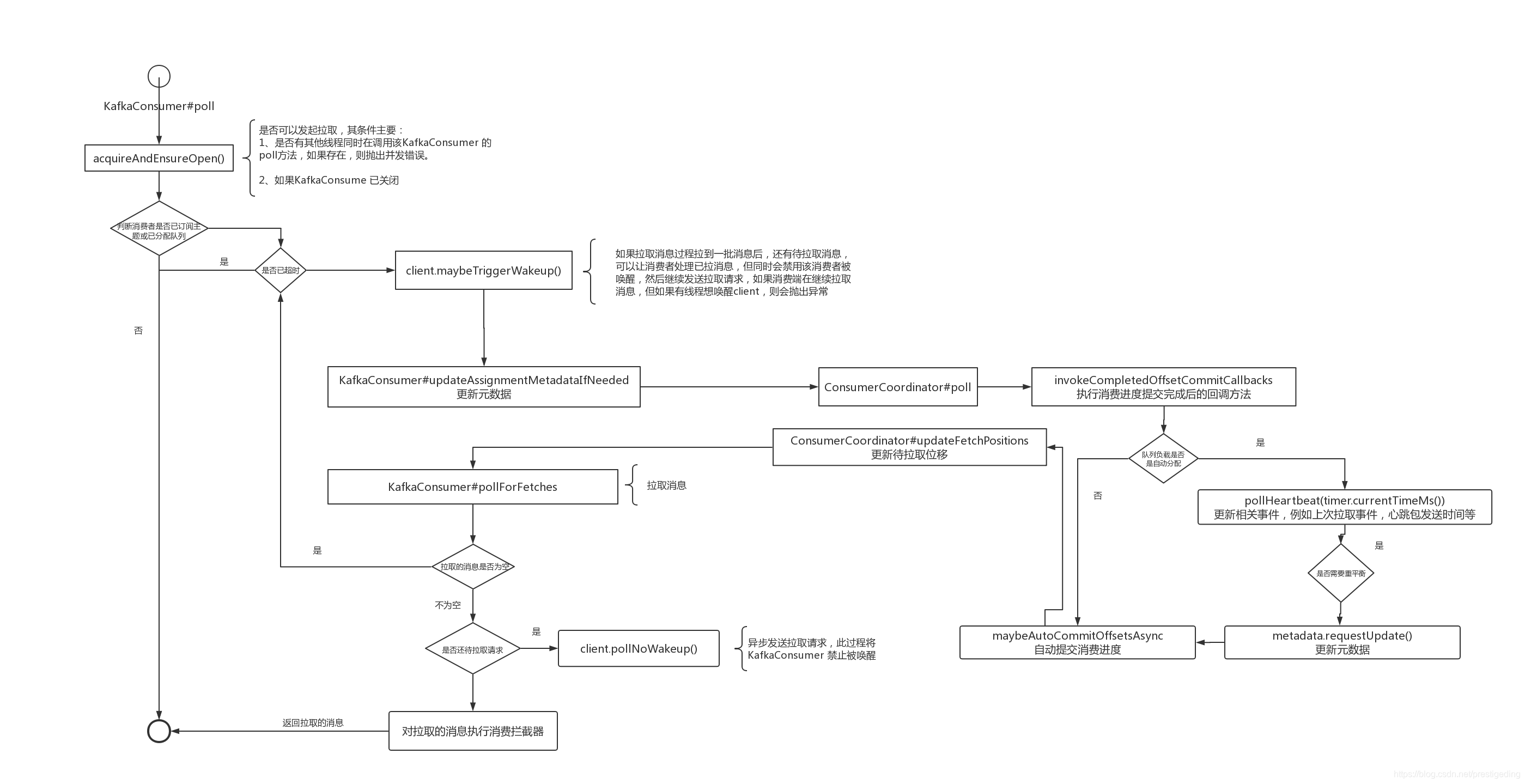
接下来我们将重点看一下 KafkaConsumer 的 pollForFetches 详细过程,也就是需要详细探究 Fetcher 类的实现细节。
Fetcher 封装消息拉取的方法,可以看成是消息拉取的门面类。
2.1 类图

我们首先一一介绍一下 Fetcher 的核心属性与核心方法。
- ConsumerNetworkClient client
消费端网络客户端,Kafka 负责网络通讯实现类。
- int minBytes
一次消息拉取需要拉取的最小字节数,如果不组,会阻塞,默认值为1字节,如果增大这个值会增大吞吐,但会增加延迟,可以通参数 fetch.min.bytes 改变其默认值。
- int maxBytes
一次消息拉取允许拉取的最大字节数,但这不是绝对的,如果一个分区的第一批记录超过了该值,也会返回。默认为50M,可通过参数 fetch.max.bytes 改变其默认值。同时不能超过 broker的配置参数(message.max.bytes) 和 主题级别的配置(max.message.bytes)。
- int maxWaitMs
在 broker 如果符合拉取条件的数据小于 minBytes 时阻塞的时间,默认为 500ms ,可通属性 fetch.max.wait.ms 进行定制。
- int fetchSize
每一个分区返回的最大消息字节数,如果分区中的第一批消息大于 fetchSize 也会返回。
- long retryBackoffMs
失败重试后需要阻塞的时间,默认为 100 ms,可通过参数 retry.backoff.ms 定制。
- long requestTimeoutMs
客户端向 broker 发送请求最大的超时时间,默认为 30s,可以通过 request.timeout.ms 参数定制。
- int maxPollRecords
单次拉取返回的最大记录数,默认值 500,可通过参数 max.poll.records 进行定制。
- boolean checkCrcs
是否检查消息的 crcs 校验和,默认为 true,可通过参数 check.crcs 进行定制。
- Metadata metadata
元数据。
- FetchManagerMetrics sensors
消息拉取的统计服务类。
- SubscriptionState subscriptions
订阅信息状态。
- ConcurrentLinkedQueue< CompletedFetch> completedFetches
已完成的 Fetch 的请求结果,待消费端从中取出数据。
- Deserializer< K> keyDeserializer
key 的反序列化器。
- Deserializer< V> valueDeserializer
value 的饭序列化器。
- IsolationLevel isolationLevel
Kafka的隔离级别(与事务消息相关),后续在研究其事务相关时再进行探讨。
- Map<Integer, FetchSessionHandler> sessionHandlers
拉取会话监听器。
接下来我们将按照消息流程,一起来看一下 Fetcher 的核心方法。
2.2 Fetcher 核心方法
2.2.1 Fetcher#fetchedRecords
Fetcher#fetchedRecords
public Map<TopicPartition, List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>>> fetchedRecords() {
Map<TopicPartition, List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>>> fetched = new HashMap<>(); // @1
int recordsRemaining = maxPollRecords;
try {
while (recordsRemaining > 0) { // @2
if (nextInLineRecords == null || nextInLineRecords.isFetched) { // @3
CompletedFetch completedFetch = completedFetches.peek();
if (completedFetch == null) break;
try {
nextInLineRecords = parseCompletedFetch(completedFetch);
} catch (Exception e) {
FetchResponse.PartitionData partition = completedFetch.partitionData;
if (fetched.isEmpty() && (partition.records == null || partition.records.sizeInBytes() == 0)) {
completedFetches.poll();
}
throw e;
}
completedFetches.poll();
} else { // @4
List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>> records = fetchRecords(nextInLineRecords, recordsRemaining);
TopicPartition partition = nextInLineRecords.partition;
if (!records.isEmpty()) {
List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>> currentRecords = fetched.get(partition);
if (currentRecords == null) {
fetched.put(partition, records);
} else {
List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>> newRecords = new ArrayList<>(records.size() + currentRecords.size());
newRecords.addAll(currentRecords);
newRecords.addAll(records);
fetched.put(partition, newRecords);
}
recordsRemaining -= records.size();
}
}
}
} catch (KafkaException e) {
if (fetched.isEmpty())
throw e;
}
return fetched;
}
代码@1:首先先解释两个局部变量的含义:
-
Map<TopicPartition, List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>>> fetched 按分区存放已拉取的消息,返回给客户端进行处理。
-
recordsRemaining:剩余可拉取的消息条数。
代码@2:循环去取已经完成了 Fetch 请求的消息,该 while 循环有两个跳出条件:
-
如果拉取的消息已经达到一次拉取的最大消息条数,则跳出循环。
-
缓存中所有拉取结果已处理。
代码@3、@4 主要完成从缓存中解析数据的两个步骤,初次运行的时候,会进入分支@3,然后从 调用 parseCompletedFetch 解析成 PartitionRecords 对象,然后代码@4的职责就是从解析 PartitionRecords ,将消息封装成 ConsumerRecord,返回给消费端线程处理。
代码@3的实现要点如下:
-
首先从 completedFetches (Fetch请求的返回结果) 列表中获取一个 Fetcher 请求,主要使用的 Queue 的 peek()方法,并不会从该队列中移除该元素。
-
然后调用 parseCompletedFetch 对处理结果进行解析返回 PartitionRecords。
-
处理成功后,调用 Queue 的方法将已处理过的 Fetcher结果移除。
从上面可知,上述方法的核心方法是:parseCompletedFetch。
代码@4的实现要点无非就是调用 fetchRecords 方法,按分区组装成 Map<TopicPartition, List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>>>,供消费者处理,例如供业务处理。
接下来将重点探讨上述两个方法的实现细节。
2.2.1.1 Fetcher#parseCompletedFetch
在尝试探讨该方法之前,我们首先对其入参进行一个梳理,特别是先认识其主要数据结构。
1、CompletedFetch 相关类图
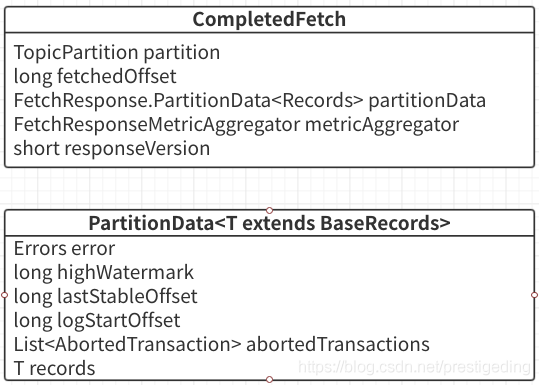
从上图可以看出,CompleteFetch 核心属性主要如下:
- TopicPartition partition
分区信息,返回结果都是以分区为纬度。
- long fetchedOffset
本次拉取的开始偏移量。
- FetchResponse.PartitionData partitionData
返回的分区数据。
- FetchResponseMetricAgregator metricAggregator
统计指标相关。
- short responseVersion
broker 端的版本号。
分区的数据是使用 PartitionData 来进行封装的。我们也来简单的了解一下其内部数据结果。
- Errors error
分区拉取的相应结果,Errors.NONE 表示请求成功。
- long highWatermark
broker 端关于该分区的高水位线,即小于该偏移量的消息对于消费端是可见的。
- long lastStableOffset
分区中小于该偏移量的消息的事务状态已得到确认,要么是已提交,要么是已回滚,与事务相关,后面会专门探讨。
- List< AbortedTransaction> abortedTransactions
已拒绝的事物。
- T records
分区数据,是 BaseRecords 的子类。
2、parseCompletedFetch 详解
private PartitionRecords parseCompletedFetch(CompletedFetch completedFetch) {
TopicPartition tp = completedFetch.partition;
FetchResponse.PartitionData partition = completedFetch.partitionData;
long fetchOffset = completedFetch.fetchedOffset;
PartitionRecords partitionRecords = null;
Errors error = partition.error;
try {
if (!subscriptions.isFetchable(tp)) { // @1
log.debug(“Ignoring fetched records for partition {} since it is no longer fetchable”, tp);
} else if (error == Errors.NONE) { // @2
Long position = subscriptions.position(tp);
if (position == null || position != fetchOffset) { // @21
log.debug("Discarding stale fetch response for partition {} since its offset {} does not match " +
“the expected offset {}”, tp, fetchOffset, position);
return null;
}
log.trace(“Preparing to read {} bytes of data for partition {} with offset {}”,
partition.records.sizeInBytes(), tp, position);
Iterator<? extends RecordBatch> batches = partition.records.batches().iterator(); // @22
partitionRecords = new PartitionRecords(tp, completedFetch, batches);
if (!batches.hasNext() && partition.records.sizeInBytes() > 0) { // @23
if (completedFetch.responseVersion < 3) {
Map<TopicPartition, Long> recordTooLargePartitions = Collections.singletonMap(tp, fetchOffset);
throw new RecordTooLargeException("There are some messages at [Partition=Offset]: " +
recordTooLargePartitions + " whose size is larger than the fetch size " + this.fetchSize +
" and hence cannot be returned. Please considering upgrading your broker to 0.10.1.0 or " +
"newer to avoid this issue. Alternately, increase the fetch size on the client (using " +
ConsumerConfig.MAX_PARTITION_FETCH_BYTES_CONFIG + “)”,
recordTooLargePartitions);
} else {
// This should not happen with brokers that support FetchRequest/Response V3 or higher (i.e. KIP-74)
throw new KafkaException("Failed to make progress reading messages at " + tp + “=” +
fetchOffset + ". Received a non-empty fetch response from the server, but no " +
“complete records were found.”);
}
}
if (partition.highWatermark >= 0) { // @24
log.trace(“Updating high watermark for partition {} to {}”, tp, partition.highWatermark);
subscriptions.updateHighWatermark(tp, partition.highWatermark);
}
if (partition.logStartOffset >= 0) { // @25
log.trace(“Updating log start offset for partition {} to {}”, tp, partition.logStartOffset);
subscriptions.updateLogStartOffset(tp, partition.logStartOffset);
}
if (partition.lastStableOffset >= 0) { // @26
log.trace(“Updating last stable offset for partition {} to {}”, tp, partition.lastStableOffset);
subscriptions.updateLastStableOffset(tp, partition.lastStableOffset);
}
} else if (error == Errors.NOT_LEADER_FOR_PARTITION ||
error == Errors.REPLICA_NOT_AVAILABLE ||
error == Errors.KAFKA_STORAGE_ERROR) { // @3
log.debug(“Error in fetch for partition {}: {}”, tp, error.exceptionName());
this.metadata.requestUpdate();
} else if (error == Errors.UNKNOWN_TOPIC_OR_PARTITION) { // @4
log.warn(“Received unknown topic or partition error in fetch for partition {}”, tp);
this.metadata.requestUpdate();
} else if (error == Errors.OFFSET_OUT_OF_RANGE) { // @5
if (fetchOffset != subscriptions.position(tp)) {
log.debug("Discarding stale fetch response for partition {} since the fetched offset {} " +
“does not match the current offset {}”, tp, fetchOffset, subscriptions.position(tp));
} else if (subscriptions.hasDefaultOffsetResetPolicy()) {
log.info(“Fetch offset {} is out of range for partition {}, resetting offset”, fetchOffset, tp);
subscriptions.requestOffsetReset(tp);
} else {
throw new OffsetOutOfRangeException(Collections.singletonMap(tp, fetchOffset));
}
} else if (error == Errors.TOPIC_AUTHORIZATION_FAILED) { // @6
log.warn(“Not authorized to read from topic {}.”, tp.topic());
throw new TopicAuthorizationException(Collections.singleton(tp.topic()));
} else if (error == Errors.UNKNOWN_SERVER_ERROR) {
log.warn(“Unknown error fetching data for topic-partition {}”, tp);
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException(“Unexpected error code " + error.code() + " while fetching data”);
}
} finally { // @7
if (partitionRecords == null)
completedFetch.metricAggregator.record(tp, 0, 0);
if (error != Errors.NONE)
// we move the partition to the end if there was an error. This way, it’s more likely that partitions for
// the same topic can remain together (allowing for more efficient serialization).
subscriptions.movePartitionToEnd(tp);
}
return partitionRecords;
}
上面的代码虽然比较长,其实整体还是比较简单,只是需要针对各种异常处理,打印对应的日志,接下来详细介绍该方法的实现关键点。
代码@1:判断该分区是否可拉取,如果不可拉取,则忽略这批拉取的消息,判断是可拉取的要点如下:
-
当前消费者负载的队列包含该分区。
-
当前消费者针对该队列并没有被用户设置为暂停(消费端限流)。
-
当前消费者针对该队列有有效的拉取偏移量。
代码@2:该分支是处理正常返回的相关逻辑。其关键点如下:
-
如果当前针对该队列的消费位移 与 发起 fetch 请求时的 偏移量不一致,则认为本次拉取非法,直接返回 null ,如代码@21。
-
从返回结构中获取本次拉取的数据,使用数据迭代器,其基本数据单位为 RecordBatch,即一个发送批次,如代码@22。
-
如果返回结果中没有包含至少一个批次的消息,但是 sizeInBytes 又大于0,则直接抛出错误,根据服务端的版本,其错误信息有所不同,但主要是建议我们如何处理,如果 broker 的版本低于 0.10.1.0,则建议升级 broker 版本,或增大客户端的 fetch size,这种错误是因为一个批次的消息已经超过了本次拉取允许的最大拉取消息大小,如代码@23。
-
依次更新消费者本地关于该队列的订阅缓存信息的 highWatermark、logStartOffset、lastStableOffset。
从代码@3到@8 是多种异常信息的处理。
代码@3:如果出现如下3种错误码,则使用 debug 打印错误日志,并且向服务端请求元数据并更新本地缓存。
- NOT_LEADER_FOR_PARTITION
请求的节点上不是该分区的 Leader 分区。
- REPLICA_NOT_AVAILABLE
该分区副本之间无法复制
- KAFKA_STORAGE_ERROR
存储异常。
Kafka 认为上述错误是可恢复的,而且对消费不会造成太大影响,故只是用 debug 打印日志,然后更新本地缓存即可。
代码@4:如果出现 UNKNOWN_TOPIC_OR_PARTITION 未知主题与分区时,则使用 warn 级别输出错误日志,并更新元数据。
代码@5:针对 OFFSET_OUT_OF_RANGE 偏移量超过范围异常的处理逻辑,其实现关键点如下:
-
如果此次拉取的开始偏移量与消费者本地缓存的偏移量不一致,则丢弃,说明该消息已过期,打印错误日志。
-
如果此次拉取的开始偏移量与消费者本地缓存的偏移量一致,说明此时的偏移量非法,如果有配置重置偏移量策略,则使用重置偏移量,否则抛出 OffsetOutOfRangeException 错误。
代码@6:如果是 TOPIC_AUTHORIZATION_FAILED 没有权限(ACL)则抛出异常。
代码@7:如果本次拉取的结果不是NONE(成功),并且是可恢复的,将该队列的订阅关系移动到消费者缓存列表的末尾。如果成功,则返回拉取到的分区数据,其封装对象为 PartitionRecords。
接下来我们再来看看 2.1.1 fetchedRecords 中的另外一个核心方法。
2.2.1.2 fetchRecords()
在介绍该方法之前同样先来看一下参数 PartitionRecords 的内部结构。
1、PartitionRecords 类图
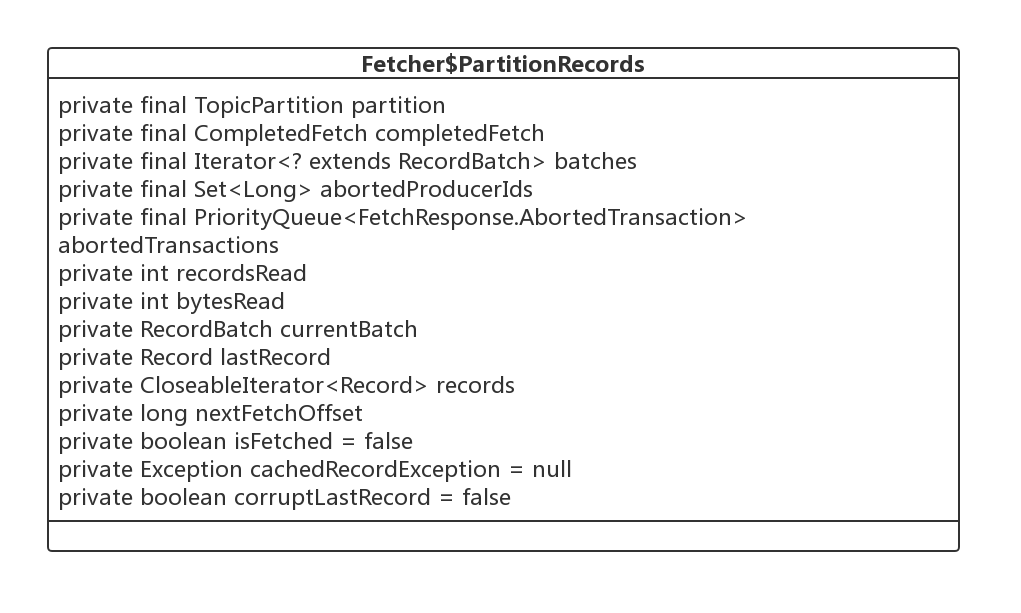
主要的核心属性如下:
- TopicPartition partition
分区信息。
- CompletedFetch completedFetch
Fetch请求完成结果
- Iterator<? extends RecordBatch> batches
本次 Fetch 操作获取的结果集。
- Set< Long> abortedProducerIds
与事物相关,后续会专门的章节详细介绍。
- PriorityQueue<FetchResponse.AbortedTransaction> abortedTransactions
与事物相关,后续会专门的章节详细介绍。
- int recordsRead
已读取的记录条数。
- int bytesRead
已读取的记录字节数。
- RecordBatch currentBatch
当前遍历的批次。
- Record lastRecord
该迭代器最后一条消息。
- long nextFetchOffset
下次待拉取的偏移量。
2、fetchRecords 详解
private List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>> fetchRecords(PartitionRecords partitionRecords, int maxRecords) {
if (!subscriptions.isAssigned(partitionRecords.partition)) { // @1
// this can happen when a rebalance happened before fetched records are returned to the consumer’s poll call
log.debug(“Not returning fetched records for partition {} since it is no longer assigned”,
partitionRecords.partition);
} else if (!subscriptions.isFetchable(partitionRecords.partition)) { // @2
// this can happen when a partition is paused before fetched records are returned to the consumer’s
// poll call or if the offset is being reset
log.debug(“Not returning fetched records for assigned partition {} since it is no longer fetchable”,
partitionRecords.partition);
} else {
long position = subscriptions.position(partitionRecords.partition); // @3
if (partitionRecords.nextFetchOffset == position) { // @4
List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>> partRecords = partitionRecords.fetchRecords(maxRecords);
long nextOffset = partitionRecords.nextFetchOffset;
log.trace("Returning fetched records at offset {} for assigned partition {} and update " +
“position to {}”, position, partitionRecords.partition, nextOffset);
subscriptions.position(partitionRecords.partition, nextOffset);
Long partitionLag = subscriptions.partitionLag(partitionRecords.partition, isolationLevel);
if (partitionLag != null)
this.sensors.recordPartitionLag(partitionRecords.partition, partitionLag);
Long lead = subscriptions.partitionLead(partitionRecords.partition);
if (lead != null) {
this.sensors.recordPartitionLead(partitionRecords.partition, lead);
}
return partRecords;
} else { // @5
// these records aren’t next in line based on the last consumed position, ignore them
// they must be from an obsolete request
log.debug(“Ignoring fetched records for {} at offset {} since the current position is {}”,
partitionRecords.partition, partitionRecords.nextFetchOffset, position);
}
}
partitionRecords.drain();
return emptyList();
}
代码@1:从 PartitionRecords 中提取消息之前,再次判断订阅消息中是否包含当前分区,如果不包含,则使用 debug 打印日志,很有可能是发生了重平衡。
代码@2:是否允许拉取,如果用户主动暂停消费,则忽略本次拉取的消息。备注:Kafka 消费端如果消费太快,可以进行限流。
代码@3:从本地消费者缓存中获取该队列已消费的偏移量,在发送拉取消息时,就是从该偏移量开始拉取的。
代码@4:如果本地缓存已消费偏移量与从服务端拉回的起始偏移量相等的话,则认为是一个有效拉取,否则则认为是一个过期的拉取,该批消息已被消费,见代码@5。如果是一个有效请求,则使用 sensors 收集统计信息,并返回拉取到的消息, 返回结果被封装在 List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>> 。
2.2.2 sendFetches
“发送” fetch 请求,注意这里并不会触发网络操作,而是组装拉取请求,将其放入网络缓存区。
Fetcher#sendFetches
public synchronized int sendFetches() {
Map<Node, FetchSessionHandler.FetchRequestData> fetchRequestMap = prepareFetchRequests(); // @1
for (Map.Entry<Node, FetchSessionHandler.FetchRequestData> entry : fetchRequestMap.entrySet()) { // @2
final Node fetchTarget = entry.getKey();
final FetchSessionHandler.FetchRequestData data = entry.getValue();
final FetchRequest.Builder request = FetchRequest.Builder
.forConsumer(this.maxWaitMs, this.minBytes, data.toSend())
.isolationLevel(isolationLevel)
.setMaxBytes(this.maxBytes)
.metadata(data.metadata())
.toForget(data.toForget()); // @3
client.send(fetchTarget, request) // @4
.addListener(new RequestFutureListener() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(ClientResponse resp) { // @5
synchronized (Fetcher.this) {
@SuppressWarnings(“unchecked”)
FetchResponse response = (FetchResponse) resp.responseBody();
FetchSessionHandler handler = sessionHandler(fetchTarget.id());
if (handler == null) {
log.error(“Unable to find FetchSessionHandler for node {}. Ignoring fetch response.”,
fetchTarget.id());
return;
}
if (!handler.handleResponse(response)) {
return;
}
Set partitions = new HashSet<>(response.responseData().keySet());
FetchResponseMetricAggregator metricAggregator = new FetchResponseMetricAggregator(sensors, partitions);
for (Map.Entry<TopicPartition, FetchResponse.PartitionData> entry :
response.responseData().entrySet()) {
TopicPartition partition = entry.getKey();
long fetchOffset = data.sessionPartitions().get(partition).fetchOffset;
FetchResponse.PartitionData fetchData = entry.getValue();
completedFetches.add(new CompletedFetch(partition, fetchOffset, fetchData, metricAggregator,
resp.requestHeader().apiVersion()));
} // @6
sensors.fetchLatency.record(resp.requestLatencyMs());
}
}
public void onFailure(RuntimeException e) { // @7
总结
在清楚了各个大厂的面试重点之后,就能很好的提高你刷题以及面试准备的效率,接下来小编也为大家准备了最新的互联网大厂资料。




ata> entry :
response.responseData().entrySet()) {
TopicPartition partition = entry.getKey();
long fetchOffset = data.sessionPartitions().get(partition).fetchOffset;
FetchResponse.PartitionData fetchData = entry.getValue();
completedFetches.add(new CompletedFetch(partition, fetchOffset, fetchData, metricAggregator,
resp.requestHeader().apiVersion()));
} // @6
sensors.fetchLatency.record(resp.requestLatencyMs());
}
}
public void onFailure(RuntimeException e) { // @7
总结
在清楚了各个大厂的面试重点之后,就能很好的提高你刷题以及面试准备的效率,接下来小编也为大家准备了最新的互联网大厂资料。
[外链图片转存中…(img-erKPtXPQ-1715677077259)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-mEHBUF7G-1715677077259)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-iKSEIhUO-1715677077259)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-5PI0nZVJ-1715677077260)]






















 620
620











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








