文末
从转行到现在,差不多两年的时间,虽不能和大佬相比,但也是学了很多东西。我个人在学习的过程中,习惯简单做做笔记,方便自己复习的时候能够快速理解,现在将自己的笔记分享出来,和大家共同学习。
个人将这段时间所学的知识,分为三个阶段:
第一阶段:HTML&CSS&JavaScript基础
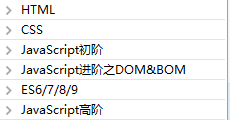
第二阶段:移动端开发技术
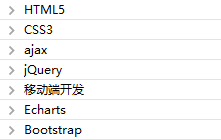
第三阶段:前端常用框架
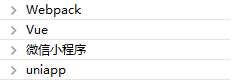
开源分享:【大厂前端面试题解析+核心总结学习笔记+真实项目实战+最新讲解视频】
-
推荐学习方式:针对某个知识点,可以先简单过一下我的笔记,如果理解,那是最好,可以帮助快速解决问题;
-
大厂的面试难在,针对一个基础知识点,比如JS的事件循环机制,不会上来就问概念,而是换个角度,从题目入手,看你是否真正掌握。所以对于概念的理解真的很重要。
this.history = new HashHistory(this, options.base, this.fallback)
break
case ‘abstract’:
this.history = new AbstractHistory(this, options.base)
break
default:
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== ‘production’) {
assert(false, invalid mode: ${mode})
}
}
}
首先在初始化 vueRouter 整个对象时定义了许多变量,app 代表 Vue 实例,options 代表传入的配置参数,然后就是路由拦截有用的 hooks 和重要的 matcher (后文会写到)。构造函数其实在做两件事情: 1. 确定当前路由使用的 mode;2. 实例化对应的 history 对象。
init
接着完成实例化 vueRouter 之后,如果这个实例传入后,也就是刚开始说的将 vueRouter 实例在初始化 Vue 时传入,它会在执行 beforeCreate 时执行 init 方法
init (app: any) {
…
this.apps.push(app)
// 确保后面的逻辑只走一次
if (this.app) {
return
}
// 保存 Vue 实例
this.app = app
const history = this.history
// 拿到 history 实例之后,调用 transitionTo 进行路由过渡
if (history instanceof HTML5History) {
history.transitionTo(history.getCurrentLocation())
} else if (history instanceof HashHistory) {
const setupHashListener = () => {
history.setupListeners()
}
history.transitionTo(
history.getCurrentLocation(),
setupHashListener,
setupHashListener
)
}
}
init 方法传入 Vue 实例,保存到 this.apps 当中。Vue实例 会取出当前的 this.history,如果是哈希路由,先走 setupHashListener 函数,然后调一个关键的函数 transitionTo 路由过渡,这个函数其实调用了 this.matcher.match 去匹配。
小结
首先在 vueRouter 构造函数执行完会完成路由模式的选择,生成 matcher ,然后初始化路由需要传入 vueRouter 实例对象,在组件初始化阶段执行 beforeCreate 钩子,调用 init 方法,接着拿到 this.history 去调用 transitionTo 进行路由过渡。
Matcher
之前在 vueRouter 的构造函数中初始化了 macther,本节将详细分析下面这句代码到底在做什么事情,以及 match 方法在做什么 源码地址 (https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router/blob/dev/src/create-matcher.js)。
this.matcher = createMatcher(options.routes || [], this)
首先将代码定位到create-matcher.js
export function createMatcher (
routes: Array,
router: VueRouter
): Matcher {
// 创建映射表
const { pathList, pathMap, nameMap } = createRouteMap(routes)
// 添加动态路由
function addRoutes(routes){…}
// 计算新路径
function match (
raw: RawLocation,
currentRoute?: Route,
redirectedFrom?: Location
): Route {…}
// … 后面的一些方法暂不展开
return {
match,
addRoutes
}
}
createMatcher 接受俩参数,分别是 routes,这个就是我们平时在 router.js 定义的路由表配置,然后还有一个参数是 router 他是 new vueRouter 返回的实例。
createRouteMap
下面这句代码是在创建一张 path-record,name-record 的映射表,我们将代码定位到 create-route-map.js 源码地址 (https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router/blob/dev/src/create-route-map.js)
export function createRouteMap (
routes: Array,
oldPathList?: Array,
oldPathMap?: Dictionary,
oldNameMap?: Dictionary
): {
pathList: Array,
pathMap: Dictionary,
nameMap: Dictionary
} {
// 记录所有的 path
const pathList: Array = oldPathList || []
// 记录 path-RouteRecord 的 Map
const pathMap: Dictionary = oldPathMap || Object.create(null)
// 记录 name-RouteRecord 的 Map
const nameMap: Dictionary = oldNameMap || Object.create(null)
// 遍历所有的 route 生成对应映射表
routes.forEach(route => {
addRouteRecord(pathList, pathMap, nameMap, route)
})
// 调整优先级
for (let i = 0, l = pathList.length; i < l; i++) {
if (pathList[i] === ‘*’) {
pathList.push(pathList.splice(i, 1)[0])
l–
i–
}
}
return {
pathList,
pathMap,
nameMap
}
}
createRouteMap 需要传入路由配置,支持传入旧路径数组和旧的 Map 这一步是为后面递归和 addRoutes 做好准备。首先用三个变量记录 path,pathMap,nameMap,接着我们来看 addRouteRecord 这个核心方法。这一块代码太多了,列举几个重要的步骤
// 解析路径
const pathToRegexpOptions: PathToRegexpOptions =
route.pathToRegexpOptions || {}
// 拼接路径
const normalizedPath = normalizePath(path, parent, pathToRegexpOptions.strict)
// 记录路由信息的关键对象,后续会依此建立映射表
const record: RouteRecord = {
path: normalizedPath,
regex: compileRouteRegex(normalizedPath, pathToRegexpOptions),
// route 对应的组件
components: route.components || { default: route.component },
// 组件实例
instances: {},
name,
parent,
matchAs,
redirect: route.redirect,
beforeEnter: route.beforeEnter,
meta: route.meta || {},
props: route.props == null
? {}
: route.components
? route.props
: { default: route.props }
}
使用 recod 对象 记录路由配置有利于后续路径切换时计算出新路径,这里的 path 其实是通过传入父级 record 对象的path和当前 path 拼接出来的 。然后 regex 使用一个库将 path 解析为正则表达式。如果 route 有子节点就递归调用 addRouteRecord
// 如果有 children 递归调用 addRouteRecord
route.children.forEach(child => {
const childMatchAs = matchAs
? cleanPath(${matchAs}/${child.path})
: undefined
addRouteRecord(pathList, pathMap, nameMap, child, record, childMatchAs)
})
最后映射两张表,并将 record·path 保存进 pathList,nameMap 逻辑相似就不列举了
if (!pathMap[record.path]) {
pathList.push(record.path)
pathMap[record.path] = record
}
废了这么大劲将 pathList 和 pathMap 和 nameMap 抽出来是为啥呢? 首先 pathList 是记录路由配置所有的 path,然后 pathMap 和 nameMap 方便我们传入 path 或者 name 快速定位到一个 record,然后辅助后续路径切换计算路由的。
addRoutes
这是在 vue2.2.0 之后新添加的 api ,或许很多情况路由并不是写死的,需要动态添加路由。有了前面的 createRouteMap 的基础上我们只需要传入 routes 即可,他就能在原基础上修改
function addRoutes (routes) {
createRouteMap(routes, pathList, pathMap, nameMap)
}
并且看到在 createMathcer 最后返回了这个方法,所以我们就可以使用这个方法
return {
match,
addRoutes
}
match
function match (
raw: RawLocation,
currentRoute?: Route,
redirectedFrom?: Location
): Route {
…
}
接下来就是 match 方法,它接收 3 个参数,其中 raw 是 RawLocation 类型,它可以是一个 url 字符串,也可以是一个 Location 对象;currentRoute 是 Route 类型,它表示当前的路径;redirectedFrom 和重定向相关。match 方法返回的是一个路径,它的作用是根据传入的 raw 和当前的路径 currentRoute 计算出一个新的路径并返回。至于他是如何计算出这条路径的,可以详细看一下如何计算出location的 normalizeLocation 方法和 _createRoute 方法。
小结
-
createMatcher: 根据路由的配置描述建立映射表,包括路径、名称到路由record的映射关系, 最重要的就是createRouteMap这个方法,这里也是动态路由匹配和嵌套路由的原理。 -
addRoutes: 动态添加路由配置 -
match: 根据传入的raw和当前的路径currentRoute计算出一个新的路径并返回。
路由模式
vue-router 支持三种路由模式(mode):hash、history、abstract,其中 abstract 是在非浏览器环境下使用的路由模式 源码地址 (https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router/blob/dev/src/index.js)。
这一部分在前面初始化 vueRouter 对象时提到过,首先拿到配置项的模式,然后根据当前传入的配置判断当前浏览器是否支持这种模式,默认 IE9 以下会降级为 hash。然后根据不同的模式去初始化不同的 history 实例。
// 一般分两种模式 hash 和 history 路由 第三种是抽象模式不常用
let mode = options.mode || ‘hash’
// 判断当前传入的配置是否能使用 history 模式
this.fallback = mode === ‘history’ && !supportsPushState && options.fallback !== false
// 降级处理
if (this.fallback) {
mode = ‘hash’
}
if (!inBrowser) {
mode = ‘abstract’
}
this.mode = mode
// 根据模式实例化不同的 history history 对象会对路由进行管理 继承于 history class
switch (mode) {
case ‘history’:
this.history = new HTML5History(this, options.base)
break
case ‘hash’:
this.history = new HashHistory(this, options.base, this.fallback)
break
case ‘abstract’:
this.history = new AbstractHistory(this, options.base)
break
default:
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== ‘production’) {
assert(false, invalid mode: ${mode})
}
}
小结
vue-router 支持三种路由模式,hash、history和 abstract。默认为 hash,如果当前浏览器不支持 history则会做降级处理,然后完成 history 的初始化。
路由切换
切换 url 主要是调用了
push 方法,下面以哈希模式为例,分析push方法实现的原理 。push 方法切换路由的实现原理 源码地址 (https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router/blob/dev/src/history/hash.js)
首先在 src/index.js 下找到 vueRouter 定义的 push 方法
push (location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) {
// $flow-disable-line
if (!onComplete && !onAbort && typeof Promise !== ‘undefined’) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
this.history.push(location, resolve, reject)
})
} else {
this.history.push(location, onComplete, onAbort)
}
}
接着我们需要定位到 history/hash.js。这里首先获取到当前路径然后调用了 transitionTo 做路径切换,在回调函数当中执行 pushHash 这个核心方法。
push (location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) {
const { current: fromRoute } = this
// 路径切换的回调函数中调用 pushHash
this.transitionTo(
location,
route => {
pushHash(route.fullPath)
handleScroll(this.router, route, fromRoute, false)
onComplete && onComplete(route)
},
onAbort
)
}
而 pushHash 方法在做完浏览器兼容判断后调用的 pushState 方法,将 url 传入
export function pushState (url?: string, replace?: boolean) {
const history = window.history
try {
// 调用浏览器原生的 history 的 pushState 接口或者 replaceState 接口,pushState 方法会将 url 入栈
if (replace) {
history.replaceState({ key: _key }, ‘’, url)
} else {
_key = genKey()
history.pushState({ key: _key }, ‘’, url)
}
} catch (e) {
window.locationreplace ? ‘replace’ : ‘assign’
}
}
可以发现,push 底层调用了浏览器原生的 history 的 pushState 和 replaceState 方法,不是 replace 模式 会将 url 推历史栈当中。
另外提一嘴拼接哈希的原理
源码位置 (https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router/blob/dev/src/history/hash.js)
初始化 HashHistory 时,构造函数会执行 ensureSlash 这个方法
export class HashHistory extends History {
constructor (router: Router, base: ?string, fallback: boolean) {
…
ensureSlash()
}
…
}
这个方法首先调用 getHash,然后执行 replaceHash()
function ensureSlash (): boolean {
const path = getHash()
if (path.charAt(0) === ‘/’) {
return true
}
replaceHash(‘/’ + path)
return false
}
下面是这几个方法
export function getHash (): string {
const href = window.location.href
const index = href.indexOf(‘#’)
return index === -1 ? ‘’ : href.slice(index + 1)
}
// 真正拼接哈希的方法
function getUrl (path) {
const href = window.location.href
const i = href.indexOf(‘#’)
const base = i >= 0 ? href.slice(0, i) : href
return ${base}#${path}
}
function replaceHash (path) {
if (supportsPushState) {
replaceState(getUrl(path))
} else {
window.location.replace(getUrl(path))
}
}
export function replaceState (url?: string) {
pushState(url, true)
}
举个例子来说: 假设当前URL是 http://localhost:8080,path 为空,执行 replcaeHash('/' + path),然后内部执行 getUrl 计算出 url 为http://localhost:8080/#/,最后执行 pushState(url,true),就大功告成了!
小结
hash 模式的 push 方法会调用路径切换方法 transitionTo,接着在回调函数中调用pushHash方法,这个方法调用的 pushState 方法底层是调用了浏览器原生 history 的方法。push 和 replace 的区别就在于一个将 url 推入了历史栈,一个没有,最直观的体现就是 replace 模式下浏览器点击后退不会回到上一个路由去 ,另一个则可以。
router-view & router-link
vue-router 在 install 时全局注册了两个组件一个是 router-view 一个是 router-link,这两个组件都是典型的函数式组件。源码地址 (https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router/tree/dev/src/components)
router-view
首先在 router 组件执行 beforeCreate 这个钩子时,把 this._route 转为了响应式的一个对象
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, ‘_route’, this._router.history.current)
所以说每次路由切换都会触发 router-view 重新 render 从而渲染出新的视图。
核心的 render 函数作用请看代码注释
render (_, { props, children, parent, data }) {
…
// 通过 depth 由 router-view 组件向上遍历直到根组件,遇到其他的 router-view 组件则路由深度+1 这里的 depth 最直接的作用就是帮助找到对应的 record
let depth = 0
let inactive = false
while (parent && parent._routerRoot !== parent) {
// parent.$vnode.data.routerView 为 true 则代表向上寻找的组件也存在嵌套的 router-view
if (parent.KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '&' at position 7: vnode &̲& parent.vnode.data.routerView) {
depth++
}
if (parent._inactive) {
inactive = true
}
parent = parent.$parent
}
data.routerViewDepth = depth
if (inactive) {
return h(cache[name], data, children)
}
// 通过 matched 记录寻找出对应的 RouteRecord
const matched = route.matched[depth]
if (!matched) {
cache[name] = null
return h()
}
// 通过 RouteRecord 找到 component
const component = cache[name] = matched.components[name]
// 往父组件注册 registerRouteInstance 方法
data.registerRouteInstance = (vm, val) => {
const current = matched.instances[name]
if (
(val && current !== vm) ||
(!val && current === vm)
) {
matched.instances[name] = val
}
}
// 渲染组件
return h(component, data, children)
}
触发更新也就是 setter 的调用,位于 src/index.js,当修改 _route 就会触发更新。
history.listen(route => {
this.apps.forEach((app) => {
// 触发 setter
app._route = route
})
})
router-link
分析几个重要的部分:
- 设置
active路由样式
router-link 之所以可以添加 router-link-active 和 router-link-exact-active 这两个 class 去修改样式,是因为在执行 render 函数时,会根据当前的路由状态,给渲染出来的 active 元素添加 class
render (h: Function) {
…
const globalActiveClass = router.options.linkActiveClass
const globalExactActiveClass = router.options.linkExactActiveClass
// Support global empty active class
const activeClassFallback = globalActiveClass == null
? ‘router-link-active’
: globalActiveClass
const exactActiveClassFallback = globalExactActiveClass == null
? ‘router-link-exact-active’
: globalExactActiveClass
…
}
router-link默认渲染为a标签,如果不是会去向上查找出第一个a标签
if (this.tag === ‘a’) {
data.on = on
data.attrs = { href }
} else {
// find the first child and apply listener and href
const a = findAnchor(this.$slots.default)
if (a) {
// in case the is a static node
a.isStatic = false
const aData = (a.data = extend({}, a.data))
aData.on = on
const aAttrs = (a.data.attrs = extend({}, a.data.attrs))
aAttrs.href = href
} else {
// 不存在则渲染本身元素
data.on = on
}
}
- 切换路由,触发相应事件
const handler = e => {
if (guardEvent(e)) {
if (this.replace) {
// replace路由
router.replace(location)
} else {
// push 路由
router.push(location)
}
}
}
权限控制动态路由原理分析
我相信,开发过后台项目的同学经常会碰到以下的场景: 一个系统分为不同的角色,然后不同的角色对应不同的操作菜单和操作权限。例如: 教师可以查询教师自己的个人信息查询然后还可以查询操作学生的信息和学生的成绩系统、学生用户只允许查询个人成绩和信息,不允许更改。在 vue2.2.0 之前还没有加入 addRoutes 这个 API 是十分困难的的。
目前主流的路由权限控制的方式是:
-
登录时获取
token保存到本地,接着前端会携带token再调用获取用户信息的接口获取当前用户的角色信息。 -
前端再根据当前的角色计算出相应的路由表拼接到常规路由表后面。
登录生成动态路由全过程
了解 如何控制动态路由之后,下面是一张全过程流程图
前端在 beforeEach 中判断:
-
缓存中存在 JWT 令牌
-
- 访问
/login: 重定向到首页/
- 访问
-
访问
/login以外的路由: 首次访问,获取用户角色信息,然后生成动态路由,然后访问以replace模式访问/xxx路由。这种模式用户在登录之后不会在history存放记录 -
不存在 JWT 令牌
-
- 路由在白名单中: 正常访问
/xxx路由
- 路由在白名单中: 正常访问
-
不在白名单中: 重定向到
/login页面
结合框架源码分析
下面结合 vue-element-admin 的源码分析该框架中如何处理路由逻辑的。
路由访问逻辑分析
首先可以定位到和入口文件 main.js 同级的 permission.js, 全局路由守卫处理就在此。源码地址 (https://github.com/251205668/student-admin-template/blob/master/src/permission.js)
const whiteList = [‘/login’, ‘/register’] // 路由白名单,不会重定向
// 全局路由守卫
router.beforeEach(async(to, from, next) => {
NProgress.start() //路由加载进度条
// 设置 meta 标题
document.title = getPageTitle(to.meta.title)
// 判断 token 是否存在
const hasToken = getToken()
if (hasToken) {
if (to.path === ‘/login’) {
// 有 token 跳转首页
next({ path: ‘/’ })
NProgress.done()
} else {
const hasRoles = store.getters.roles && store.getters.roles.length > 0
if (hasRoles) {
next()
} else {
try {
// 获取动态路由,添加到路由表中
const { roles } = await store.dispatch(‘user/getInfo’)
const accessRoutes = await store.dispatch(‘permission/generateRoutes’, roles)
router.addRoutes(accessRoutes)
// 使用 replace 访问路由,不会在 history 中留下记录,登录到 dashbord 时回退空白页面
next({ …to, replace: true })
} catch (error) {
next(‘/login’)
文末
技术是没有终点的,也是学不完的,最重要的是活着、不秃。
零基础入门的时候看书还是看视频,我觉得成年人,何必做选择题呢,两个都要。喜欢看书就看书,喜欢看视频就看视频。
最重要的是在自学的过程中,一定不要眼高手低,要实战,把学到的技术投入到项目当中,解决问题,之后进一步锤炼自己的技术。
自学最怕的就是缺乏自驱力,一定要自律,杜绝“三天打鱼两天晒网”,到最后白忙活一场。
高度自律的同时,要保持耐心,不抛弃不放弃,切勿自怨自艾,每天给自己一点点鼓励,学习的劲头就会很足,不容易犯困。
技术学到手后,找工作的时候一定要好好准备一份简历,不要无头苍蝇一样去海投简历,容易“竹篮打水一场空”。好好的准备一下简历,毕竟是找工作的敲门砖。
拿到面试邀请后,在面试的过程中一定要大大方方,尽力把自己学到的知识舒适地表达出来,不要因为是自学就不够自信,给面试官一个好的印象,面试成功的几率就会大很多,加油吧,骚年!






















 6万+
6万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








