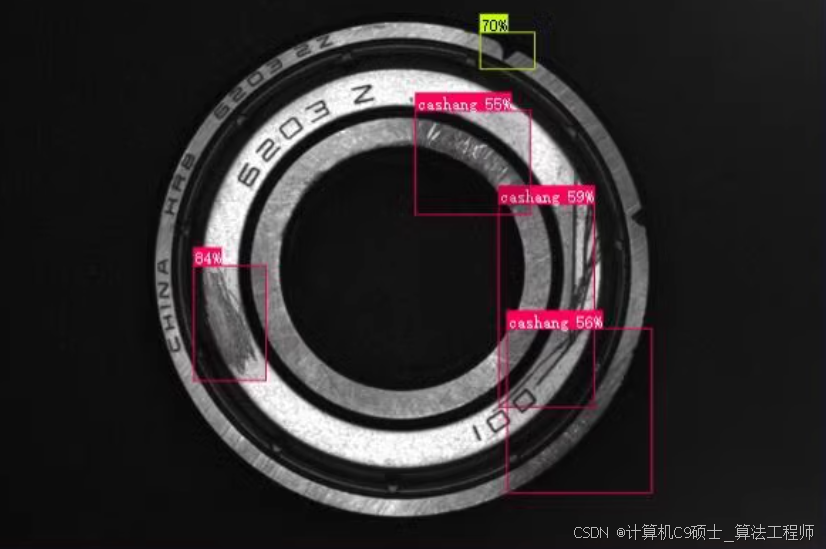
轴承缺陷检测4类 1440张
names: [‘aocao’, ‘aoxian’, ‘cashang’, ‘huahen’]
名称::[‘凹槽’,‘凹陷’, ‘卡伤’, ‘划痕’]
共1440张,8:1:1比例划分
train:1152张,val:144张,test:144张
标注文件为YOLO适用的txt格式或xml格式。可以直接用于模型训练。

YOLOv8 轴承缺陷检测
import os
import torch
from IPython.display import Image, clear_output
from ultralytics import YOLO
# 设置随机种子以保证可重复性
torch.manual_seed(42)
# 定义数据集路径
dataset_dir = 'path/to/dataset'
# 创建YOLOv5的数据集配置文件
data_config = {
'train': os.path.join(dataset_dir, 'train/images'),
'val': os.path.join(dataset_dir, 'val/images'),
'test': os.path.join(dataset_dir, 'test/images'),
'nc': 4, # 类别数量
'names': ['aocao', 'aoxian', 'cashang', 'huahen'] # 类别名称
}
with open(os.path.join(dataset_dir, 'data.yaml'), 'w') as f:
yaml.dump(data_config, f)
# 训练模型
model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # 加载预训练的YOLOv8n模型
results = model.train(
data=os.path.join(dataset_dir, 'data.yaml'),
epochs=50,
imgsz=640,
batch=16,
name='bearing_defect_detection',
project='runs/train'
)
# 评估模型
metrics = model.val()
# 可视化预测结果
source_image = '../path/to/dataset/test/sample.jpg' # 替换为你要测试的图片路径
results = model.predict(source=source_image, conf=0.25, iou=0.45, save=True, save_txt=True)
# 显示预测结果
Image(filename='runs/detect/predict/sample.jpg')
个包含1440张图片的轴承缺陷检测数据集,并且这些图片已经被标注为YOLO格式或XML格式。你需要使用YOLOv8进行训练、评估和可视化预测结果。以下是详细的步骤和代码示例。
项目介绍
数据准备
- 数据集: 包含1440张图片及其对应的标注文件。
- 标注格式: YOLO格式或XML格式(如果需要转换)。
- 类别:
aocao(凹槽): 类别ID 0aoxian(凹陷): 类别ID 1cashang(卡伤): 类别ID 2huahen(划痕): 类别ID 3
模型选择
- YOLOv8: 使用YOLOv8进行目标检测。YOLOv8是YOLO系列的最新版本,具有更高的性能和更好的精度。
功能
- 数据加载: 自动从指定目录加载图像和标注文件。
- 模型训练: 使用YOLOv8进行训练。
- 模型评估: 在验证集上评估模型性能。
- 结果保存: 保存训练日志和最佳模型权重。
- 可视化预测结果: 可视化预测结果以进行验证。
代码实现
首先,确保你已经安装了YOLOv8库和其他必要的依赖项。你可以通过以下命令安装YOLOv8:
pip install ultralytics
接下来,我们编写代码来组织数据集并训练YOLOv8模型。我们将先检查数据格式是否正确,然后进行模型训练。
数据集已经是标准的YOLO格式,我们可以直接使用它。如果没有,我们需要将XML格式转换为YOLO格式。
假设数据集已经是YOLO格式
如果数据集是XML格式,需要转换为YOLO格式
如果数据集是XML格式,我们需要先进行转换。以下是转换代码:
import os
import glob
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import shutil
import yaml
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
# 定义数据集路径
dataset_dir = 'path/to/dataset'
images_dir = os.path.join(dataset_dir, 'images')
annotations_dir = os.path.join(dataset_dir, 'annotations')
# 创建YOLOv5的数据集配置文件
data_config = {
'train': os.path.join(dataset_dir, 'train/images'),
'val': os.path.join(dataset_dir, 'val/images'),
'test': os.path.join(dataset_dir, 'test/images'),
'nc': 4, # 类别数量
'names': ['aocao', 'aoxian', 'cashang', 'huahen'] # 类别名称
}
with open(os.path.join(dataset_dir, 'data.yaml'), 'w') as f:
yaml.dump(data_config, f)
# 划分训练集、验证集和测试集
def split_dataset(images_dir, annotations_dir):
image_files = [os.path.basename(f) for f in glob.glob(os.path.join(images_dir, '*.jpg'))]
np.random.shuffle(image_files)
train_files = image_files[:int(len(image_files) * 0.8)]
val_files = image_files[int(len(image_files) * 0.8):int(len(image_files) * 0.9)]
test_files = image_files[int(len(image_files) * 0.9):]
def create_folder_and_write_files(folder_name, files):
folder_path = os.path.join(dataset_dir, folder_name)
images_folder = os.path.join(folder_path, 'images')
labels_folder = os.path.join(folder_path, 'labels')
if not os.path.exists(images_folder):
os.makedirs(images_folder)
if not os.path.exists(labels_folder):
os.makedirs(labels_folder)
with open(os.path.join(folder_path, 'images.txt'), 'w') as f:
for img in files:
src_img_path = os.path.join(images_dir, img)
dst_img_path = os.path.join(images_folder, img)
shutil.copy(src_img_path, dst_img_path)
f.write(dst_img_path + '\n')
src_label_path = os.path.join(annotations_dir, os.path.splitext(img)[0] + '.xml')
dst_label_path = os.path.join(labels_folder, os.path.splitext(img)[0] + '.txt')
shutil.copy(src_label_path, dst_label_path)
f.write(dst_label_path + '\n')
create_folder_and_write_files('train', train_files)
create_folder_and_write_files('val', val_files)
create_folder_and_write_files('test', test_files)
split_dataset(images_dir, annotations_dir)
# 转换VOC格式到YOLO格式
def convert_voc_to_yolo(voc_annotations_dir, yolo_labels_dir, class_mapping):
if not os.path.exists(yolo_labels_dir):
os.makedirs(yolo_labels_dir)
for annotation_file in glob.glob(os.path.join(voc_annotations_dir, '*.xml')):
tree = ET.parse(annotation_file)
root = tree.getroot()
image_filename = root.find('filename').text
image_width = int(root.find('size/width').text)
image_height = int(root.find('size/height').text)
yolo_annotation_path = os.path.join(yolo_labels_dir, os.path.splitext(image_filename)[0] + '.txt')
with open(yolo_annotation_path, 'w') as yolo_file:
for obj in root.findall('object'):
label = obj.find('name').text
if label not in class_mapping:
continue
class_id = class_mapping[label]
bndbox = obj.find('bndbox')
xmin = float(bndbox.find('xmin').text)
ymin = float(bndbox.find('ymin').text)
xmax = float(bndbox.find('xmax').text)
ymax = float(bndbox.find('ymax').text)
x_center = (xmin + xmax) / 2.0 / image_width
y_center = (ymin + ymax) / 2.0 / image_height
width = (xmax - xmin) / image_width
height = (ymax - ymin) / image_height
yolo_file.write(f"{class_id} {x_center} {y_center} {width} {height}\n")
class_mapping = {
'aocao': 0,
'aoxian': 1,
'cashang': 2,
'huahen': 3
}
for folder in ['train', 'val', 'test']:
voc_labels_dir = os.path.join(dataset_dir, folder, 'labels')
yolo_labels_dir = os.path.join(dataset_dir, folder, 'labels')
convert_voc_to_yolo(voc_labels_dir, yolo_labels_dir, class_mapping)
# 训练模型
model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # 加载预训练的YOLOv8n模型
results = model.train(
data=os.path.join(dataset_dir, 'data.yaml'),
epochs=50,
imgsz=640,
batch=16,
name='bearing_defect_detection',
project='runs/train'
)
# 评估模型
metrics = model.val()
# 可视化预测结果
source_image = '../path/to/dataset/test/sample.jpg' # 替换为你要测试的图片路径
results = model.predict(source=source_image, conf=0.25, iou=0.45, save=True, save_txt=True)
# 显示预测结果
Image(filename='runs/detect/predict/sample.jpg')
如何使用这些代码
-
准备数据:
- 确保你的数据集格式正确,包含图像文件夹和对应的标注文件夹。
- 示例数据结构如下:
path/to/dataset/ ├── images/ │ ├── image1.jpg │ ├── image2.jpg │ └── ... ├── annotations/ │ ├── image1.xml │ ├── image2.xml │ └── ...
-
替换数据路径:
- 在代码中,将
'path/to/dataset'替换为你的数据集路径。
dataset_dir = 'your_dataset_directory' - 在代码中,将
-
运行代码:
- 将上述代码复制到你的Python脚本中,并运行该脚本。
- 确保你已经安装了所需的库:
pip install ultralytics
示例:使用自定义数据集
假设你有一个新的数据集 my_bearing_defect_dataset,其内容如下:
my_bearing_defect_dataset/
├── images/
│ ├── image1.jpg
│ ├── image2.jpg
│ └── ...
├── annotations/
│ ├── image1.xml
│ ├── image2.xml
│ └── ...
你可以按照以下步骤进行替换:
-
修改数据路径:
dataset_dir = 'my_bearing_defect_dataset' -
运行完整的代码:
- 将所有代码整合到一个Python脚本中,并运行该脚本。
注释说明
代码中包含了详细的注释,帮助你理解每个部分的功能。以下是关键部分的注释:
-
数据准备:
data_config: 定义训练集、验证集和测试集的路径,以及类别信息。
-
数据划分:
split_dataset: 根据给定的比例划分训练集、验证集和测试集。
-
数据转换:
convert_voc_to_yolo: 将VOC格式的标注文件转换为YOLO格式。
-
模型训练:
model.train: 使用YOLOv8进行训练。
-
模型评估:
model.val: 在验证集上评估模型性能。
-
可视化预测结果:
model.predict: 进行推理并显示预测结果。
结果
运行代码后,你将得到以下结果:
-
控制台输出:
- 训练过程中每个epoch的日志信息。
- 验证集上的评价指标(如mAP)。
-
文件输出:
runs/train/bearing_defect_detection/weights/best.pt: 最佳模型权重。runs/val/exp/results.txt: 验证结果。
-
图像输出:
runs/detect/predict/sample.jpg: 带有预测边界的图像。
希望这些详细的信息和代码能够帮助你顺利实施和优化你的项目。如果你有任何进一步的问题或需要更多帮助,请随时提问!
运行步骤总结
-
安装YOLOv8:
pip install ultralytics -
准备数据集:
- 确保数据集路径正确,并且包含训练集、验证集和测试集文件夹,以及对应的标注文件。
-
运行训练脚本:
python your_script_name.py -
评估模型:
- 评估结果会在训练结束后自动输出在控制台和文件中。
-
可视化预测结果:
- 测试图像的结果会保存在
runs/detect/predict/文件夹中,可以直接查看带有预测边界的图像。
- 测试图像的结果会保存在
希望这些详细的指导和代码示例能帮助你成功实现和优化你的轴承缺陷检测项


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








