install,
version: ‘VERSION’,
mapState,
mapMutations,
mapGetters,
mapActions,
createNamespacedHelpers
}
- 其次是定义store,并且实现vue的Install方法
// src/store.js
let Vue // bind on install
export class Store {
…
}
// 实现的Install方法
export function install (_Vue) {
if (Vue && _Vue === Vue) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== ‘production’) {
console.error(
‘[vuex] already installed. Vue.use(Vuex) should be called only once.’
)
}
return
}
Vue = _Vue
applyMixin(Vue)
}
问题2:state的数据响应式
看懂了Vuex的入口定义,下面我们就针对store的定义来一探究竟,先看看state的实现
// src/store.js
export class Store {
constructor(options = {}) {
…
// strict mode
this.strict = strict
const state = this._modules.root.state
// initialize the store vm, which is responsible for the reactivity
// (also registers _wrappedGetters as computed properties)
// 看上面的注释可以得知,resetStoreVM就是初始化store中负责响应式的vm的方法,而且还注册所有的gettersz作为vm的计算属性
resetStoreVM(this, state)
}
}
我们来看看resetStoreVM的具体实现
// src/store.js
function resetStoreVM (store, state, hot) {
const oldVm = store._vm
// bind store public getters
store.getters = {}
// reset local getters cache
store._makeLocalGettersCache = Object.create(null)
const wrappedGetters = store._wrappedGetters
const computed = {}
// 这里是实现getters的派生
forEachValue(wrappedGetters, (fn, key) => {
// use computed to leverage its lazy-caching mechanism
// direct inline function use will lead to closure preserving oldVm.
// using partial to return function with only arguments preserved in closure environment.
computed[key] = partial(fn, store)
Object.defineProperty(store.getters, key, {
get: () => store._vm[key],
enumerable: true // for local getters
})
})
// use a Vue instance to store the state tree
// suppress warnings just in case the user has added
// some funky global mixins
// 这是是通过new一个Vue实例,并将state作为实例的datas属性,那他自然而然就具有了响应式
const silent = Vue.config.silent
Vue.config.silent = true
store._vm = new Vue({
data: {
$$state: state
},
computed
})
Vue.config.silent = silent
// enable strict mode for new vm
if (store.strict) {
enableStrictMode(store)
}
if (oldVm) {
if (hot) {
// dispatch changes in all subscribed watchers
// to force getter re-evaluation for hot reloading.
store._withCommit(() => {
oldVm._data.$$state = null
})
}
Vue.nextTick(() => oldVm.$destroy())
}
}
问题3:getters实现state中的数据的派生
关于getters的实现,我们在上面也做了相应的解释,实际上就是将getters的方法包装一层后,收集到computed对象中,并使用Object.defineProperty注册store.getters,使得每次取值时,从store._vm中取。
关键的步骤就是创建一个Vue的实例
store._vm = new Vue({
data: {
$$state: state // 这是store中的所有state
},
computed // 这是store中的所有getters
})
问题4:mutations中同步commit
// src/store.js
// store的构造函数
constructor(options = {}) {
// 首先在构造方法中,把store中的commit和dispatch绑定到自己的实例上,
// 为什么要这么做呢?
// 是因为在commit或者dispatch时,尤其是dispatch,执行function时会调用实例this,而方法体内的this是具有作用域属性的,所以如果要保证每次this都代表store实例,就需要重新绑定一下。
const store = this
const { dispatch, commit } = this
this.dispatch = function boundDispatch (type, payload) {
return dispatch.call(store, type, payload)
}
this.commit = function boundCommit (type, payload, options) {
return commit.call(store, type, payload, options)
}
}
// commit 的实现
commit (_type, _payload, _options) {
// check object-style commit
const {
type,
payload,
options
} = unifyObjectStyle(_type, _payload, _options)
const mutation = { type, payload }
// 通过传入的类型,查找到mutations中的对应的入口函数
const entry = this._mutations[type]
…
// 这里是执行的主方法,通过遍历入口函数,并传参执行
this._withCommit(() => {
entry.forEach(function commitIterator (handler) {
handler(payload)
})
})
…
}
问题5:actions中的异步dispatch
上面说了在构造store时绑定dispatch的原因,下面我们就继续看看dispatch的具体实现。
// src/store.js
// dispatch 的实现
dispatch (_type, _payload) {
// check object-style dispatch
const {
type,
payload
} = unifyObjectStyle(_type, _payload)
const action = { type, payload }
// 同样的道理,通过type获取actions中的入口函数
const entry = this._actions[type]
······
// 由于action是异步函数的集合,这里就用到了Promise.all,来合并多个promise方法并执行
const result = entry.length > 1
-
? Promise.all(entry.map(handler => handler(payload)))
- entry 0
return result.then(res => {
try {
this._actionSubscribers
.filter(sub => sub.after)
.forEach(sub => sub.after(action, this.state))
} catch (e) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== ‘production’) {
console.warn([vuex] error in after action subscribers: )
console.error(e)
}
}
return res
})
}
到这里,我们就把整个store中状态存储和状态变更的流程系统的串联了一遍,让我们对Vuex内部的机智有个简单的认识,最后我们根据我们对Vuex的理解来实现一个简单的Vuex。
// store.js
let Vue
// 定义store类
class Store{
constructor(options = {}) {
this.$options = options
this._mutations = options.mutations
this._actions = options.actions
this._wrappedGetters = options.getters
// 定义computed
const computed = {}
this.getters = {}
const store = this
Object.keys(this._wrappedGetters).forEach(key => {
// 获取用户定义的getters
const fn = store._wrappedGetters[key]
// 转换为computed可以使用无参数形式
computed[key] = function() {
return fn(store.state)
}
// 为getters定义只读属性
Object.defineProperty(store.getters, key {
get:() => store._vm[key]
})
})
// state的响应式实现
this._vm = new Vue({
data: {
// 加两个$,Vue不做代理
$$state: options.state
},
computed // 添加计算属性
})
this.commit = this.commit.bind(this)
this.dispatch = this.dispatch.bind(this)
}
// 存取器,获取store.state ,只通过get形式获取,而不是直接this.xxx, 达到对state
get state() {
return this._vm._data.$$state
}
set state(v) {
// 如果用户不通过commit方式来改变state,就可以在这里做一控制
}
// commit的实现
commit(type, payload) {
const entry = this._mutations[type]
if (entry) {
entry(this.state, payload)
}
}
// dispatch的实现
dispatch(type, payload) {
const entry = this._actions[type]
if (entry) {
entry(this, payload)
}
}
}
// 实现install
function install(_Vue) {
Vue = _Vue
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
if (this.$options.store) {
Vue.prototype. S t o r e = t h i s . Store = this. Store=this.options.store // 这样就可以使用 this.$store
文末
js前端的重头戏,值得花大部分时间学习。
推荐通过书籍学习,《 JavaScript 高级程序设计(第 4 版)》你值得拥有。整本书内容质量都很高,尤其是前十章语言基础部分,建议多读几遍。
另外,大推一个网上教程 现代 JavaScript 教程 ,文章深入浅出,很容易理解,上面的内容几乎都是重点,而且充分发挥了网上教程的时效性和资料链接。
学习资料在精不在多,二者结合,定能构建你的 JavaScript 知识体系。
面试本质也是考试,面试题就起到很好的考纲作用。想要取得优秀的面试成绩,刷面试题是必须的,除非你样样精通。
这是288页的前端面试题
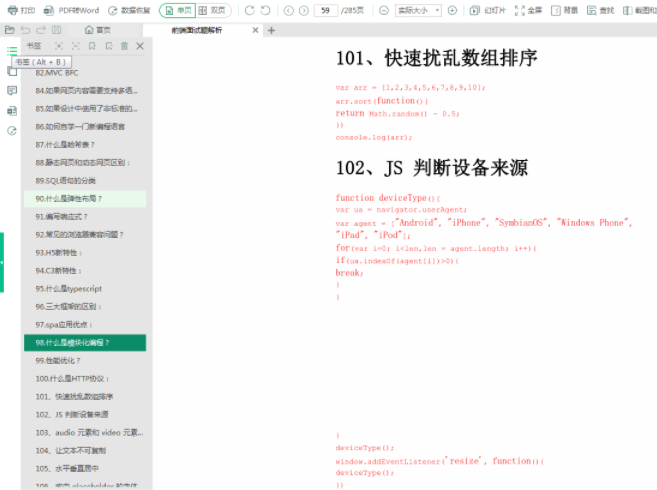





















 269
269

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








