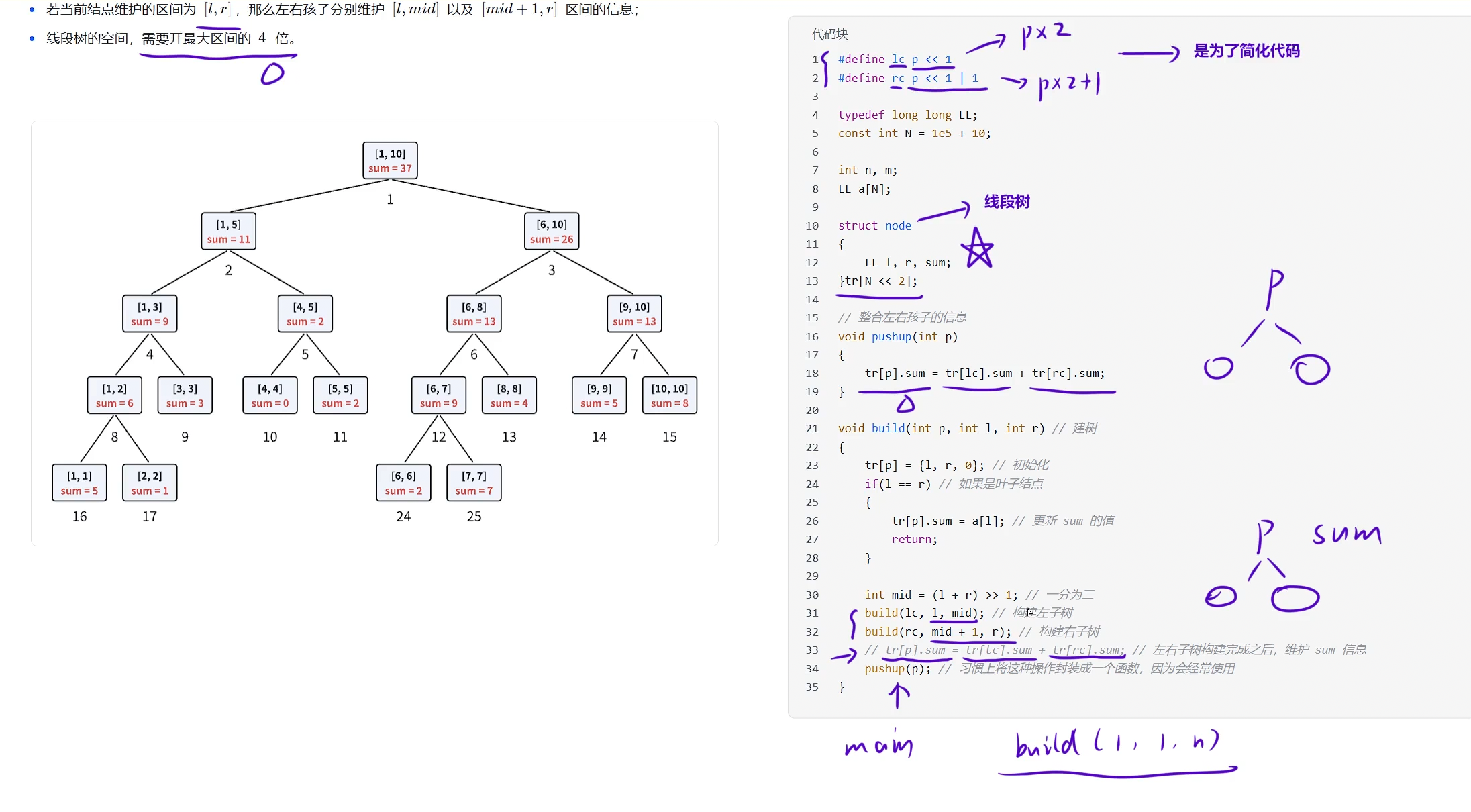
线段树常见场景

节点最大个数为区间长度4倍
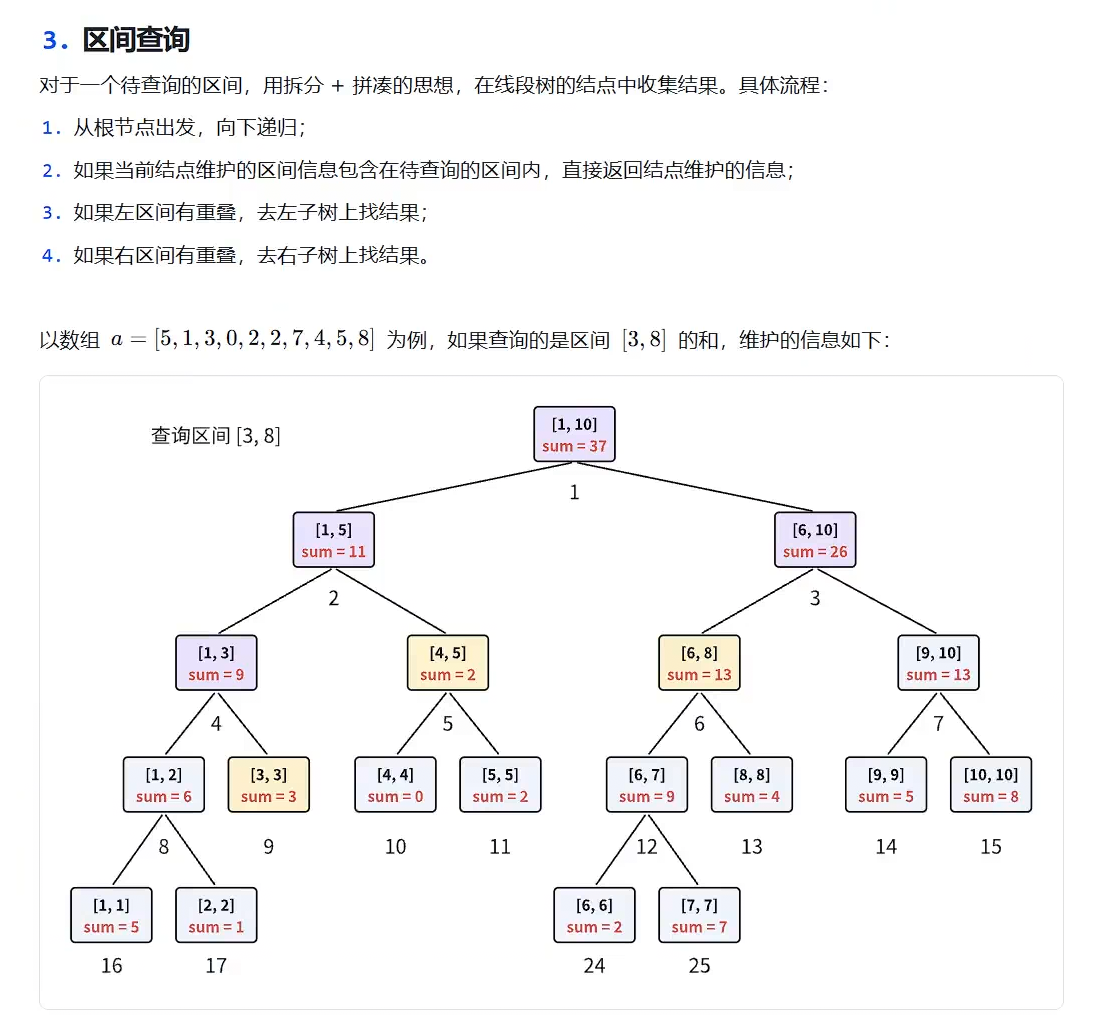
单点修改模版P3374 【模板】树状数组 1 - 洛谷
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define lc p<<1
#define rc p<<1|1
const int N = 5e5 + 10;
int n, m;
int a[N];
struct node
{
int l, r, sum;
}tr[4*N];
void pushup(int p)
{
tr[p].sum = tr[lc].sum + tr[rc].sum;
}
void build(int p, int l, int r)
{
tr[p] = { l,r,0 };
if (l == r)
{
tr[p].sum = a[l]; return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
build(lc, l, mid);
build(rc, mid + 1, r);
pushup(p);
}
int query(int p,int x,int y)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (x <= l && y >= r)return tr[p].sum;
int ret = 0; int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (x <= mid)ret += query(lc, x, y);
if (y >= mid + 1)ret += query(rc, x, y);
return ret;
}
void modify(int p, int x, int k)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (l == r)
{
tr[p].sum += k; return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (x <= mid)modify(lc, x, k);
else modify(rc, x, k);
pushup(p);
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> a[i];
build(1, 1, n);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int a; cin >> a;
if (a == 1)
{
int x, k; cin >> x >> k;
modify(1, x, k);
}
else
{
int x, y; cin >> x >> y;
cout<<query(1, x, y)<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
区间修改及查询操作案例:P3372 【模板】线段树 1 - 洛谷
经常不注意会踩的坑:(以区间+操作为例)
1.sum,add操作时均为+=
2.modify在修改左右子树前也要pushdown下放懒标记(modify中的最后操作会pushup)
3.query操作中记得pushdown
4.pushdown操作中记得判断add
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
#define lc p<<1
#define rc p<<1|1
typedef long long LL;
LL a[N]; int n, m;
struct node
{
int l, r;
LL sum, add;
}tr[4*N];
void pushup(int p)
{
tr[p].sum = tr[lc].sum + tr[rc].sum;
}
void build(int p, int l, int r)
{
tr[p] = { l,r,0,0 };
if (l == r)
{
tr[p].sum = a[l];
return;
}
int mid = (l + r)/2;
build(lc, l, mid); build(rc, mid + 1, r);
pushup(p);
}
void lazy(int p, LL add)
{
//已在pushdown检查是否有懒标记了,此处记得均为+=
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
tr[p].sum += (r - l + 1) *add;
tr[p].add += add;
}
void pushdown(int p)
{
if(tr[p].add)//先看是否有懒标记
{
lazy(lc, tr[p].add);
lazy(rc, tr[p].add);
tr[p].add = 0;
}
}
void modify(int p, int x, int y, int k)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (x <= l && y >= r)
{
/*tr[p].sum += (r - l + 1) * k;
tr[p].add += k;*/
lazy(p, k);
return;
}
pushdown(p);//因为modify最后的操作是pushup,多次modify时为防止原值pushup导致算错,要pushdown更新
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (x <= mid)modify(lc, x, y, k);
if (y> mid)modify(rc, x, y, k);
pushup(p);
}
LL query(int p, int x, int y)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (x <= l && y >= r)return tr[p].sum;
pushdown(p); //懒标记下放
int mid = (l + r) / 2; LL ret = 0;
if (x <= mid)ret+=query(lc, x, y);
if (y > mid)ret += query(rc, x, y);
return ret;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> a[i];
build(1, 1, n);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int a; cin >> a;
if (a == 1)
{
int x, y, k; cin >> x >> y >> k;
modify(1, x, y, k);
}
else
{
int x, y; cin >> x >> y;
cout << query(1, x, y) << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}重难点:线段树多个区间修改操作
1.P3373 【模板】线段树 2 - 洛谷
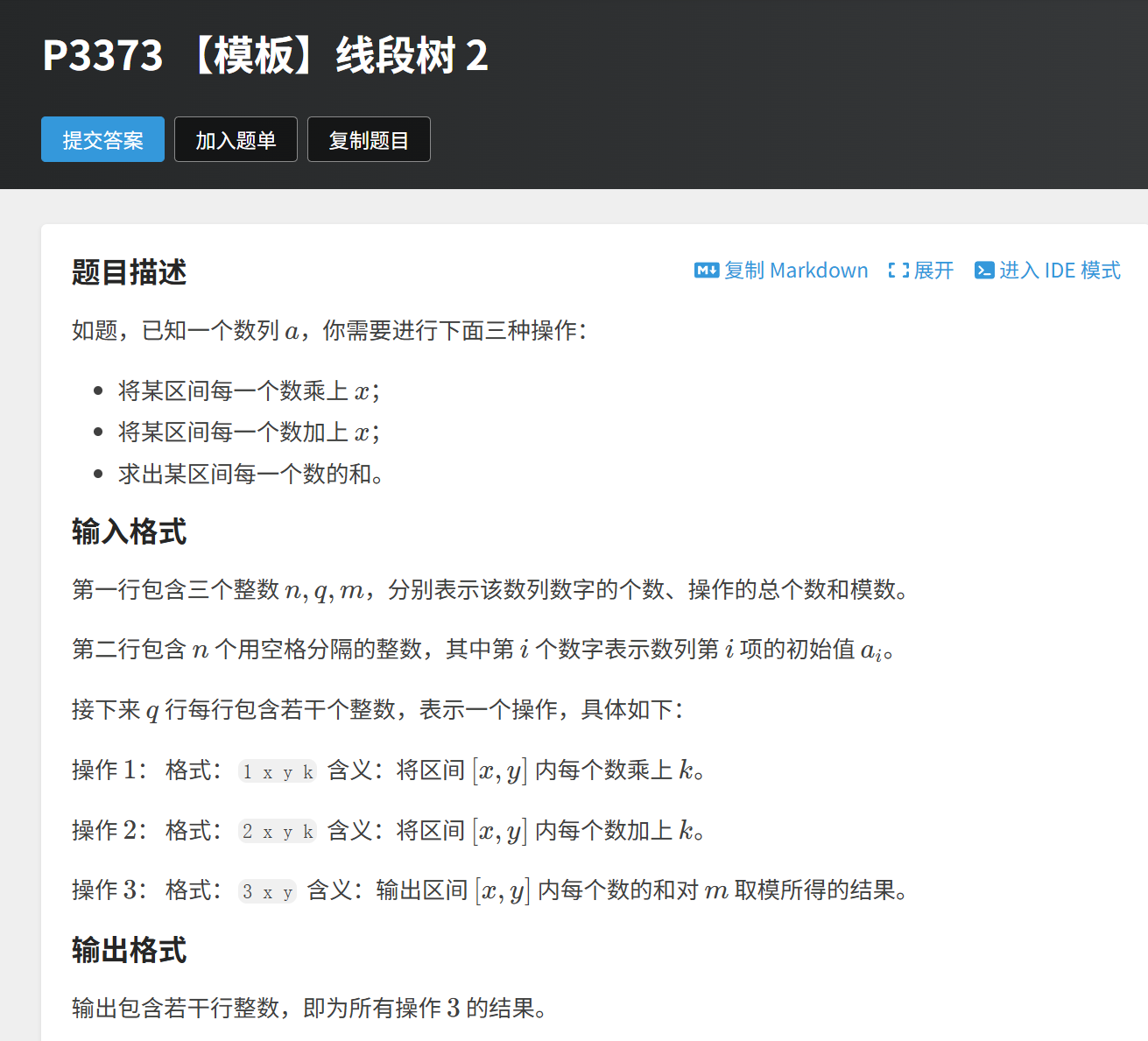
既有+又有*,无法判断谁先操作,那就假设规定(推导数学公式来保证正确性)
在懒标记下放时我们规定:每一步都是
先加后乘,推导数学式如下图,我们发现更新add时(a'=a+A/m)可能会导致精度丢失
而先乘后加我们发现不存在此问题,故而使用它

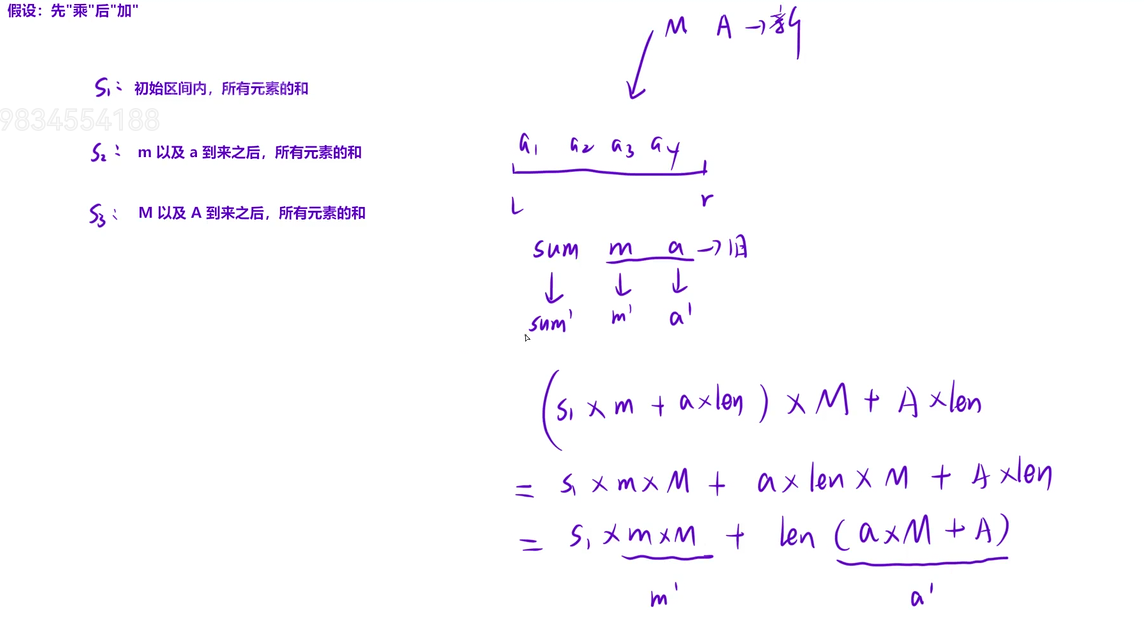
s1表示的是该区间原来之和,最后将其拆出是为了延续公式的一般性
s2表示的是该区间现在之和
s3表示的是懒标记传递至此处时该区间更新后之和
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
//此题数据范围极大,LL也会越界,必须在不断更新区间时就对其进行摸操作,
//只在query是取模仍会出现负数
#define lc p<<1
#define rc p<<1|1
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
struct node
{
int l, r;
LL sum, add, mul;
}tr[N<<2];
int n, q, mod;
int a[N];
void pushup(int p)
{
tr[p].sum = tr[lc].sum + tr[rc].sum;
}
void build(int p, int l, int r)
{
tr[p] = { l,r,a[l],0,1 };
if (l == r)return;
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
build(lc, l, mid); build(rc, mid + 1, r);
pushup(p);
}
void lazy(int p, LL add, LL mul)
{
tr[p].sum = (tr[p].sum * mul + (tr[p].r - tr[p].l + 1) * add)%mod;
tr[p].add = (tr[p].add * mul + add)%mod;
tr[p].mul = (tr[p].mul * mul)%mod;
}
// void lazy(int p, LL add, LL mul)
// {
// int len = tr[p].r - tr[p].l + 1;
// tr[p].sum = tr[p].sum * mul + add * len;
// tr[p].mul *= mul;
// tr[p].add = tr[p].add * mul + add;
// }
void pushdown(int p)
{
if (tr[p].add != 0 || tr[p].mul != 1)
{
lazy(lc, tr[p].add, tr[p].mul);
lazy(rc, tr[p].add, tr[p].mul);
tr[p].add = 0;
tr[p].mul = 1;
}
}
void modify(int p, int x, int y, LL add, LL mul)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (x <= l && y >= r)
{
lazy(p, add, mul);
return;
}
pushdown(p);
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (x <= mid)modify(lc, x, y, add, mul);
if (y > mid)modify(rc, x, y, add, mul);
pushup(p);
}
LL query(int p, int x, int y)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (x <= l && y >= r)return tr[p].sum;
pushdown(p);
int mid = (l + r) / 2; LL ret = 0;
if (x <= mid)ret += query(lc, x, y);
if (y > mid)ret += query(rc, x, y);
return ret%mod;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> q >> mod;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> a[i];
build(1, 1, n);
while (q--)
{
int op, x, y, k;
cin >> op;
if (op == 1)
{
cin >> x >> y >> k;
modify(1, x, y, 0, k);
}
else if (op == 2)
{
cin >> x >> y >> k;
modify(1, x, y, k, 1);
}
else
{
cin >> x >> y;
cout << query(1, x, y) << endl;;
}
}
}2.P1253 扶苏的问题 - 洛谷
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
#define lc p<<1
#define rc p<<1|1
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int a[N];
int n, m;
struct node
{
int l, r;
LL max, add, update;
bool st;
}tr[N<<2];
void pushup(int p)
{
tr[p].max = max(tr[lc].max, tr[rc].max);
}
void build(int p,int l,int r)
{
tr[p] = { l,r,a[l],0,0,false };
if (l == r)return;
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
build(lc, l, mid); build(rc, mid + 1, r);
pushup(p);
}
void lazy(int p, LL add, LL update, bool st)
{
if (st)
{
tr[p].max = update;
tr[p].add = 0;
tr[p].update = update;
tr[p].st = true;
}
tr[p].max += add;
tr[p].add += add;
}
void pushdown(int p)
{
lazy(lc, tr[p].add, tr[p].update, tr[p].st);
lazy(rc, tr[p].add, tr[p].update, tr[p].st);
tr[p].add = tr[p].update = tr[p].st = 0;
}
void modify(int p, int x, int y, LL add, LL update,bool st)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (x <= l && y >= r)
{
lazy(p, add, update,st);
return;
}
pushdown(p);
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (x <= mid)modify(lc, x, y, add, update,st);
if (y > mid)modify(rc, x, y, add, update,st);
pushup(p);
}
LL query(int p, int x, int y)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (x <= l && y >= r)return tr[p].max;
pushdown(p);
int mid = (l + r) / 2;LL ret = -1e18;
if (x <= mid)ret = max(ret, query(lc, x, y));
if (y > mid)ret = max(ret, query(rc, x, y));
return ret;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)scanf("%d", &a[i]);
build(1, 1, n);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int op; scanf("%d",&op);
if (op == 1)
{
int x, y, k; scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &k);
modify(1, x, y, 0, k, true);
}
else if (op == 2)
{
int x, y, k; scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &k);
modify(1, x, y, k, 0, false);
}
else
{
int x, y; scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
printf("%ld\n",query(1,x,y));
}
}
return 0;
}练习部分
P3368 【模板】树状数组 2 - 洛谷
typedef long long LL;
#define lc p<<1
#define rc p<<1|1
const int N = 5e5 + 10;
int a[N];
int n, m;
struct node
{
int l, r;
LL sum, add;
}tr[N << 2];
void pushup(int p)
{
tr[p].sum = tr[lc].sum + tr[rc].sum;
}
void build(int p, int l, int r)
{
tr[p] = { l,r,a[l],0 };
if (l == r)return;
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
build(lc, l, mid); build(rc, mid + 1, r);
pushup(p);
}
void lazy(int p, int k)
{
tr[p].sum += (tr[p].r - tr[p].l + 1) * k;
tr[p].add += k;
}
void pushdown(int p)
{
if (tr[p].add)
{
lazy(lc, tr[p].add);
lazy(rc, tr[p].add);
tr[p].add = 0;
}
}
void modify(int p, int x, int y, int k)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (x <= l && y >= r)
{
lazy(p, k);
return;
}
pushdown(p);
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (x <= mid)modify(lc, x, y, k);
if (y > mid)modify(rc, x, y, k);
pushup(p);
}
int query(int p, int x)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (l == r)return tr[p].sum;
pushdown(p);
int mid = (l + r) / 2; int ret = 0;
if (x <= mid)ret += query(lc, x);
else ret += query(rc, x);
return ret;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)scanf("%d", &a[i]);
build(1, 1, n);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int a; cin >> a;
if (a == 1)
{
int x, y, k; cin >> x >> y >> k;
modify(1, x, y, k);
}
else
{
int x; cin >> x;
printf("%d\n", query(1, x));
}
}
}P3870 [TJOI2009] 开关 - 洛谷
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define lc p<<1
#define rc p<<1|1
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
struct node
{
int l, r, ret, cnt;
}tr[N<<2];
int n, m;
void pushup(int p)
{
tr[p].ret = tr[lc].ret + tr[rc].ret;
}
void build(int p, int l, int r)
{
tr[p] = { l,r,0,0 };
if (l == r)return;
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
build(lc, l, mid);
build(rc, mid + 1, r);
}
void lazy(int p)
{
tr[p].ret = (tr[p].r - tr[p].l + 1) - tr[p].ret;
tr[p].cnt += 1;
}
void pushdown(int p)
{
if (tr[p].cnt % 2)
{
lazy(lc);
lazy(rc);
}
tr[p].cnt = 0;
}
void modify(int p,int x,int y)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (x <= l && y >= r)
{
lazy(p);
return;
}
pushdown(p);
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (x <= mid)modify(lc, x, y);
if (y > mid)modify(rc, x, y);
pushup(p);
}
int query(int p, int x, int y)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (x <= l && y >= r)return tr[p].ret;
pushdown(p);
int mid = (l + r) / 2; int ret = 0;
if (x <= mid)ret += query(lc, x, y);
if (y > mid)ret += query(rc, x, y);
return ret;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
build(1, 1, n);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int a,x,y; cin >> a>>x>>y;
if (!a)
{
modify(1, x, y);
}
else
{
cout << query(1, x, y) << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
P1438 无聊的数列 - 洛谷
本题是区间等差修改+单点查询操作,故而可用线段树+差分数组。可减少代码细节错误率
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
#define lc p<<1
#define rc p<<1|1
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int a[N], n, m;
struct node
{
LL l, r, sum, A, D;
}tr[N<<2];
void pushup(int p)
{
tr[p].sum = tr[lc].sum + tr[rc].sum;
}
void build(int p, int l, int r)
{
tr[p] = { l,r,a[l],0,0 };
if (l == r)return;
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
build(lc, l, mid); build(rc, mid + 1, r);
pushup(p);
}
void lazy(int p, LL a, LL d)
{
int len = tr[p].r - tr[p].l + 1;
tr[p].sum += len * a + len * (len - 1) * d / 2;
tr[p].A += a;
tr[p].D += d;
}
void pushdown(int p)
{
if (tr[p].A||tr[p].D)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
int mid = (r+l) / 2;
lazy(lc, tr[p].A, tr[p].D);
lazy(rc, tr[p].A+(mid+1-l)*tr[p].D, tr[p].D);//虽然能pushdown说明此范围全是可修改区域,但不能用mid*d,而是(mid+1-l)*d,要的是区间长度
tr[p].A = 0;
tr[p].D = 0;
}
}
void modify(int p, int x, int y, LL a, LL k)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (x <= l && y >= r)
{
lazy(p, a+(l-x)*k, k);
return;
}
pushdown(p);
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (x <= mid)modify(lc, x, y, a, k);
if (y > mid)modify(rc, x, y, a, k);
pushup(p);
}
LL query(int p, int x)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (l == r)return tr[p].sum;
pushdown(p);
int mid = (l + r) / 2; LL ret = 0;
if (x <= mid)ret+=query(lc, x);
else ret+=query(rc, x);
return ret;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> a[i];
build(1, 1, n);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int a; cin >> a;
if (a == 1)
{
int x, y, a, k; cin >> x >> y >> a >> k;
modify(1, x, y, a, k);
}
else
{
int x; cin >> x;
cout << query(1, x) << endl;
}
}
}重难点:线段树+分治
1.P4513 小白逛公园 - 洛谷
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define lc p<<1
#define rc p<<1|1
const int N = 5e5 + 10;
int n, m, a[N];
struct node
{
int l, r, max, lmax, rmax, sum;
}tr[N<<2];
void pushup(node& p,node& l,node&r)
{
p.max = max(max(r.max, l.max), l.rmax+r.lmax);
p.lmax = max(l.lmax, l.sum + r.lmax);
p.rmax = max(r.rmax, r.sum + l.rmax);
p.sum = l.sum + r.sum;
}
void build(int p, int l, int r)
{
tr[p] = { l,r,a[l],a[l],a[l],a[l]};
if (l == r)return;
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
build(lc, l, mid); build(rc, mid + 1, r);
pushup(tr[p],tr[lc],tr[rc]);
}
void modify(int p, int x, int k)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (l == r)
{
tr[p].max = tr[p].lmax = tr[p].rmax = tr[p].sum = k;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (x <= mid)modify(lc, x, k);
else modify(rc, x, k);
pushup(tr[p], tr[lc], tr[rc]);
}
node query(int p, int x, int y)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (x <= l && y >= r)return tr[p];
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (y <= mid)return query(lc, x, y);
if (x > mid)return query(rc, x, y);
node ret, L = query(lc, x, y), R = query(rc, x, y);
pushup(ret, L, R);
return ret;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> a[i];
build(1, 1, n);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int op; cin >> op;
if (op == 1)
{
int x, y; cin >> x >> y;
if (x > y)swap(x, y);
cout<<query(1, x, y).max<<endl;
}
else
{
int x, k; cin >> x >> k;
modify(1, x, k);
}
}
}线段树+剪枝
P4145 上帝造题的七分钟 2 / 花神游历各国 - 洛谷
区间修改+区间查询 但我们发现区间无法直接修改,即无法正常使用懒标记(正常使用懒标记是指:当前节点可以直接修改,并不依赖子节点)。
此题意味着修改时我们需要每次都遍历子节点,时间复杂度为m*n*logn,还不如直接使用数组(复杂度为n*m),那我们看看能否使用剪枝操作来降低时间复杂度。
思路:
我们又发现10^12最多开根6次变成了1,到了1时就没必要开根了(1开根仍为1)
那我们在node节点中存储一个max(区间最大值)不就能监视到区间当前还有无必要开根了吗
即当前区间中的最大值为1时就可以返回了
总结:
遍历一次线段树时间复杂度为n*logn,而最多开根6次就无需开根,即最多遍历6次完整的线段树就可以使得其区间最大值为1,故而使用剪枝后的时间复杂度为6*n*logn(与修改次数m无关了,6次之后进来即返回)
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
#define lc p<<1
#define rc p<<1|1
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m;
LL a[N];
struct node
{
int l, r;
LL max, sum;
}tr[N<<2];
void pushup(int p)
{
tr[p].sum = tr[lc].sum + tr[rc].sum;
tr[p].max = max(tr[lc].max, tr[rc].max);
}
void build(int p, int l, int r)
{
tr[p] = { l,r,a[l],a[l] };
if (l == r)return;
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
build(lc, l, mid); build(rc, mid + 1, r);
pushup(p);
}
void modify(int p, int x, int y)
{
if (tr[p].max == 1)return;
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (l == r)
{
tr[p].sum = sqrt(tr[p].sum);
tr[p].max = sqrt(tr[p].max);
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (x <= mid)modify(lc, x, y);
if (y > mid)modify(rc, x, y);
pushup(p);
}
LL query(int p, int x, int y)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (x <= l && y >= r)return tr[p].sum;
int mid = (l + r) / 2; LL ret = 0;
if (x <= mid)ret += query(lc,x,y);
if (y > mid)ret += query(rc, x, y);
return ret;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> a[i];
build(1, 1, n);
cin >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int op, x, y; cin >> op >> x >> y;
if (x > y)swap(x, y);
if (op == 0)
{
modify(1, x, y);
}
else
{
cout<<query(1, x, y)<<endl;
}
}
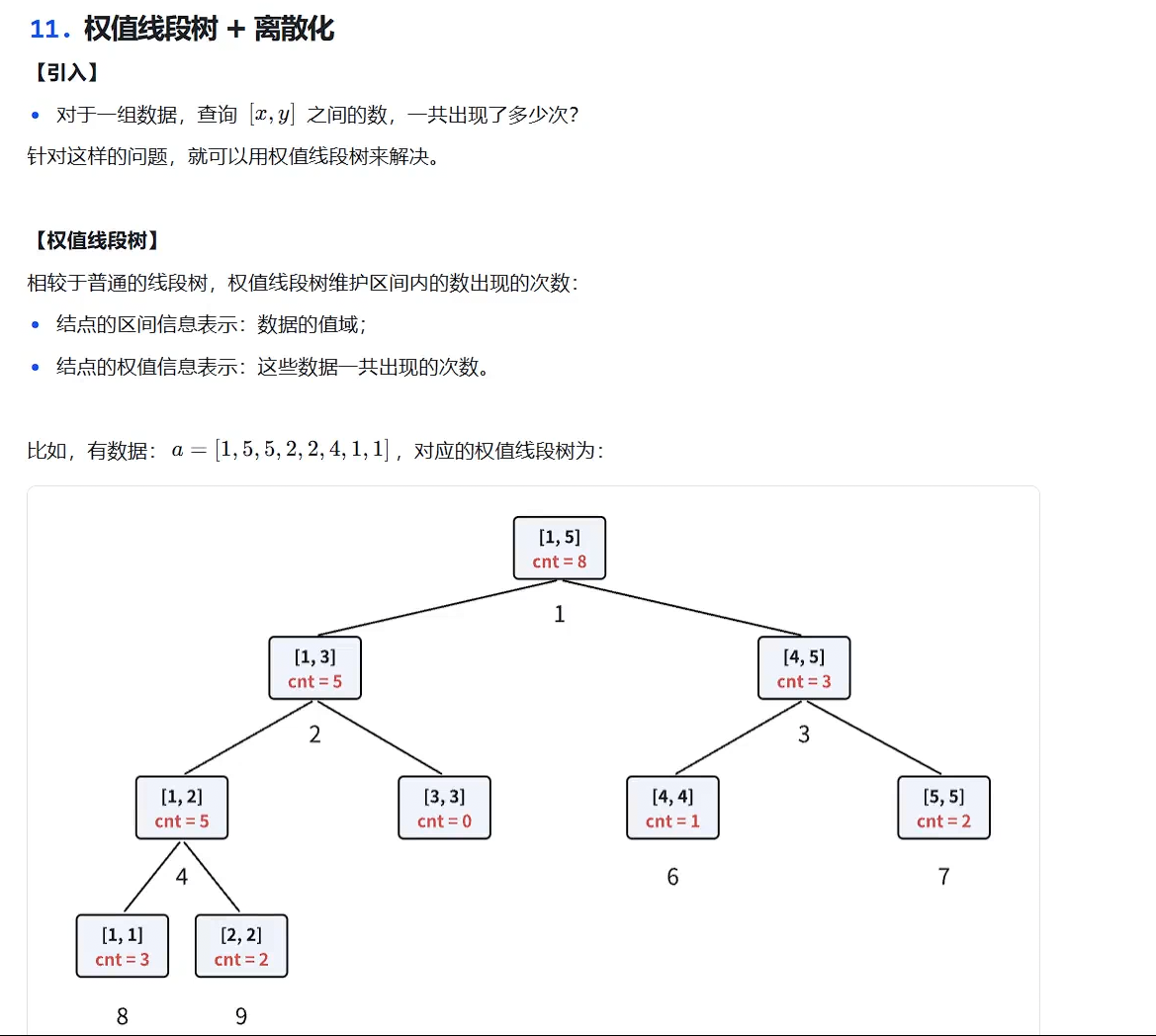
}权值线段树+离散化
P1908 逆序对 - 洛谷
上面注释掉的两种方法是分治思想实现的:全队是基于归并排序
而今天讲的线段树方法是一遍查询区间,一边更新线段树
#include<iostream>//时间复杂度为n*logn^2(sort的缘故)
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
// const int N = 5e5 + 10;
// int a[N];
// int tmp[N];
// long long ret;
//void dfs(int left, int right)
//{
// if (left == right)return;
// if (right - left == 1)
// {
// if (a[left] > a[right])ret += 1;
// return;
// }
// int mid = (left + right) / 2;
// dfs(left, mid);
// dfs(mid + 1, right);
//
// sort(a + left, a + mid + 1);
// sort(a + mid + 1, a + right + 1);
// int start1 = left, end1 = mid;
// int start2 = mid + 1, end2 = right;
// while (start1 <= end1 && start2 <= end2)
// {
// if (a[start1] > a[start2])
// {
// ret += end1 - start1 + 1;
// start2++;
// }
// else
// {
// start1++;
// }
// }
//}
//int main()
//{
// int n; cin >> n;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> a[i];
//
// dfs(1, n);
// cout << ret << endl;
//}
// void merge(int left, int right)
// {
// if (left >= right)return;
// int mid = (left + right) / 2;
// merge(left, mid);
// merge(mid + 1, right);
// int start1 = left, end1 = mid;
// int start2 = mid + 1, end2 = right;
// int i = left;
// while (start1 <= end1 && start2 <= end2)
// {
// if (a[start1] > a[start2])
// {
// ret += end1 - start1 + 1;
// tmp[i++] = a[start2];
// start2++;
// }
// else
// {
// tmp[i++] = a[start1];
// start1++;
// }
// }
// while (start1 <= end1)tmp[i++] = a[start1++];
// while (start2 <= end2)tmp[i++] = a[start2++];
// for (int j = left; j <= right; j++)a[j] = tmp[j];
// }
// int main()
// {
// int n; cin >> n;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> a[i];
// merge(1, n);
// cout << ret << endl;
// }
typedef long long LL;
#include<unordered_map>
#define lc p<<1
#define rc p<<1|1
const int N = 5e5 + 10;
int a[N], t[N];
int n, pos;//pos来表示离散化后的最大的数
unordered_map<int, int>mp;
struct node
{
int l, r;
LL cnt;
}tr[N<<2];
void pushup(int p)
{
tr[p].cnt = tr[lc].cnt + tr[rc].cnt;
}
void build(int p,int l,int r)
{
tr[p] = { l,r,0 };
if (l == r)return;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(lc, l, mid); build(rc, mid + 1, r);
//pushup(p); 此题此处不用
}
LL query(int p, int x, int y)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (x <= l && y >= r)return tr[p].cnt;
int mid = (l + r) / 2; LL ret = 0;
if (x <= mid)ret += query(lc, x, y);
if (y > mid)ret += query(rc, x, y);
return ret;
}
void modify(int p, int x)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (l==r)
{
tr[p].cnt++;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (x <= mid)modify(lc, x);
else modify(rc, x);
pushup(p);
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i]; t[i] = a[i];
}
//离散化
sort(t + 1, t + n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (mp.count(t[i]))continue;
mp[t[i]] = ++pos;
}
build(1, 1, pos);
LL ret = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int x = mp[a[i]];
ret+=query(1, x + 1, pos);
modify(1, x);
}
cout << ret << endl;
}线段树+数学
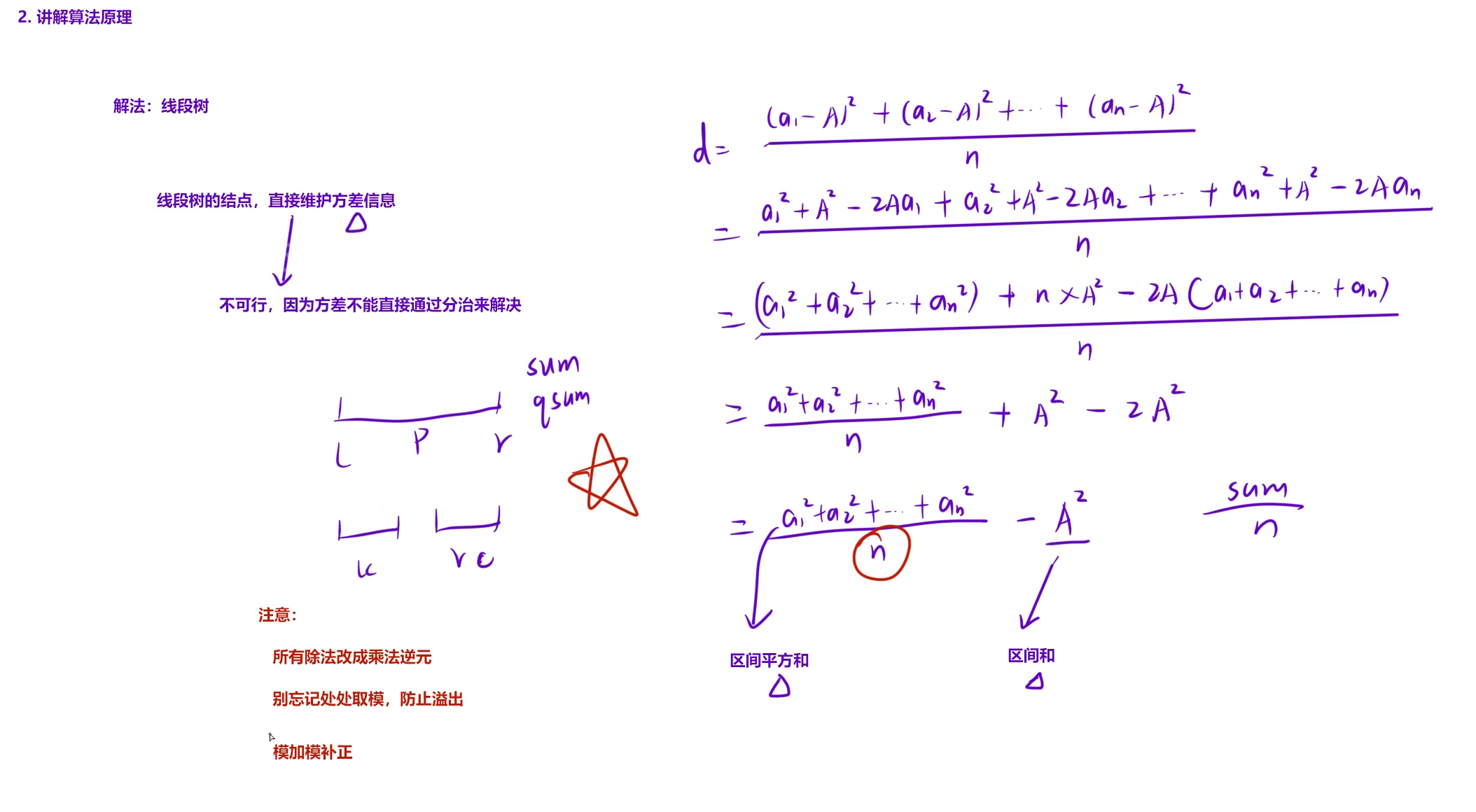
P5142 区间方差 - 洛谷
#define lc p<<1
#define rc p<<1|1
const int N = 1e5 + 10, mod = 1e9 + 7;
int n, m;
LL a[N];//很扯淡,这儿必须用LL
struct node
{
int l, r;
LL sum, qsum;
}tr[N<<2];
LL qpow(LL a, LL b, LL p)
{
LL ret = 1;
while (b)
{
if (b & 1) ret = ret * a % p;
a = a * a % p;
b >>= 1;
}
return ret;
}
void pushup(node& p, node& l, node& r)
{
//p.l = l.l, p.r = r.r;
p.qsum = (l.qsum + r.qsum) % mod;
p.sum = (l.sum + r.sum) % mod;
}
void build(int p, int l, int r)
{
tr[p] = { l,r,a[l],a[l] * a[l] % mod };
if (l == r)return;
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
build(lc, l, mid); build(rc, mid + 1, r);
pushup(tr[p], tr[lc], tr[rc]);
}
void modify(int p, int x, LL y)//将第x个节点的值改为y
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (l == r)
{
tr[p].sum = y;
tr[p].qsum = y * y % mod;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (x <= mid)modify(lc, x, y);
else modify(rc, x, y);
pushup(tr[p], tr[lc], tr[rc]);
}
node query(int p, int x, int y)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (x <= l && y >= r)return tr[p];
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (y <= mid)return query(lc, x, y);
else if (x > mid)return query(rc, x, y);
node t, L = query(lc, x, y), R = query(rc, x, y);
pushup(t, L, R);
return t;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> a[i];
build(1, 1, n);
while (m--)
{
int op, x, y; cin >> op >> x >> y;
if (op == 1)
{
modify(1, x, y);
}
else
{
node t = query(1, x, y);
LL sum = t.sum, qsum = t.qsum, len = (y-x+1);
LL inv = qpow(len, mod - 2, mod);
LL A = sum * inv % mod;
LL D = qsum * inv % mod - A * A % mod;
D = (D % mod + mod) % mod;
cout << D << endl;
}
}
}
P10463 Interval GCD - 洛谷(区间修改(无法懒标记以及剪枝)--利用差分改为单点修改)
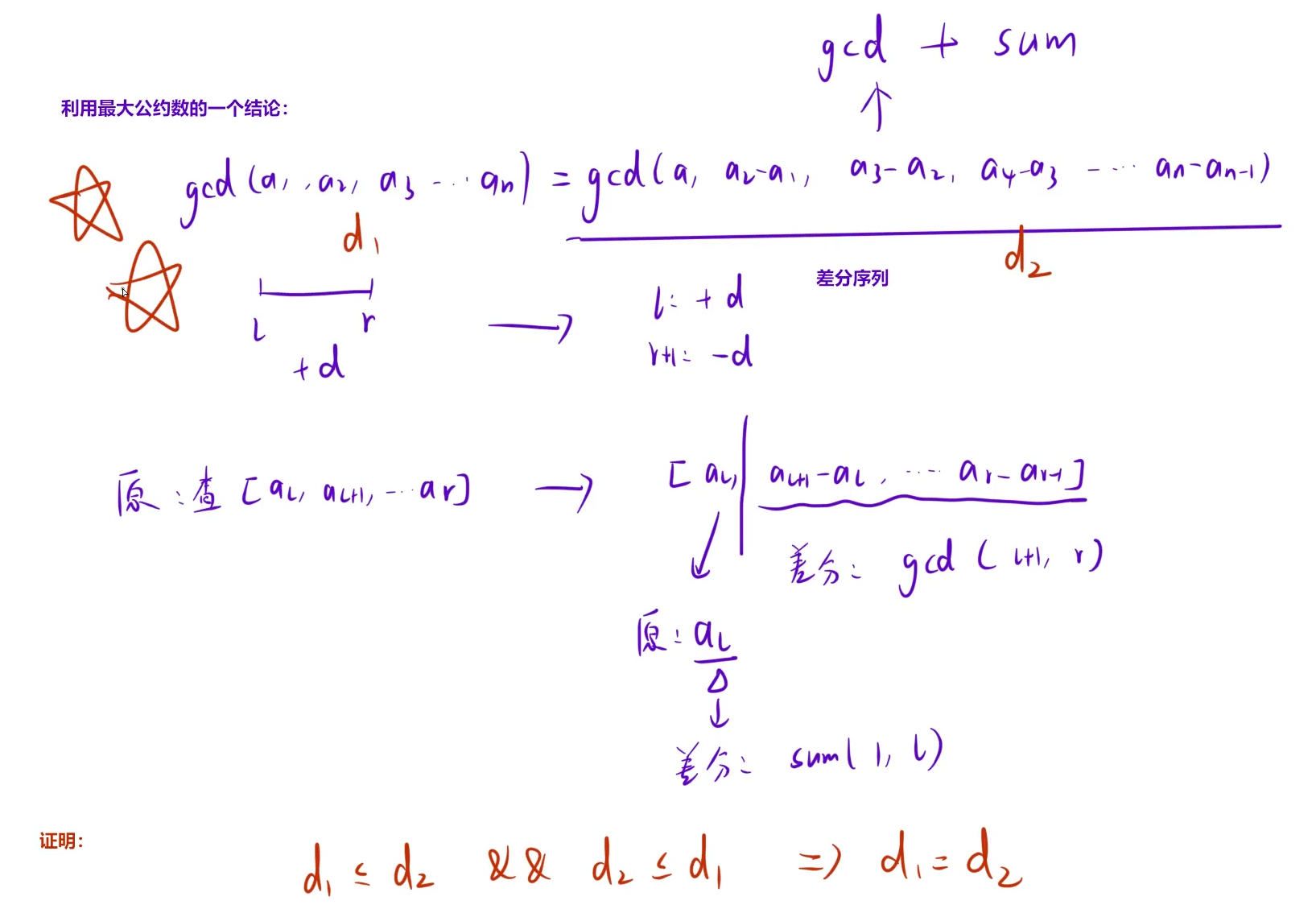
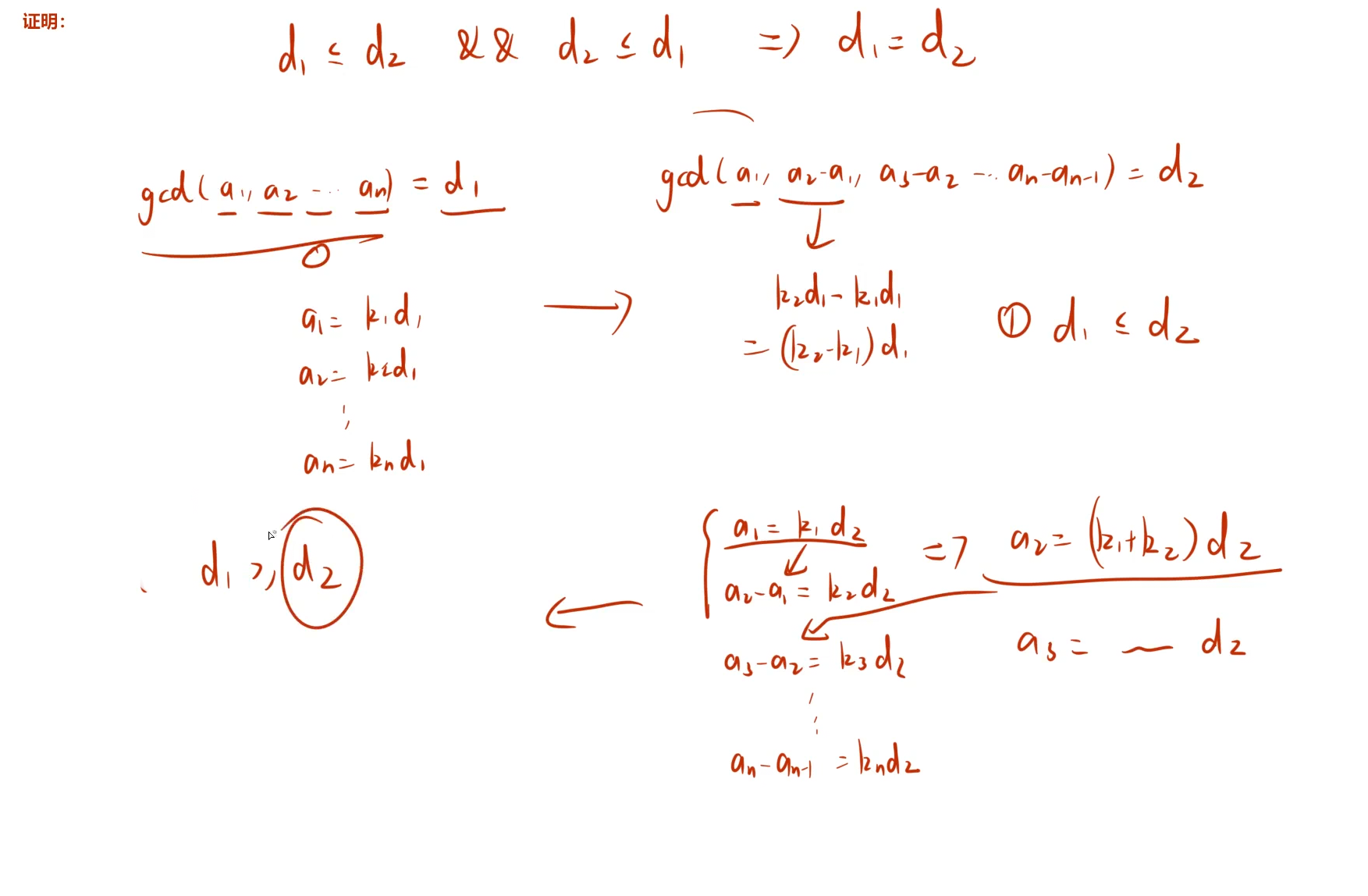
有这个结论,我们就可以维护原序列差分序列中的最大公约数,此时区间修改就变成的两次单点修改.
但是,在求差分序列 的最⼤公约数时除了区间的gcd值,还需要知道原数列的值。(可以在差分序列中维护⼀个区间和query1,此时原数列的值就是差分序列中区间的和。因为gcd区间【l+1,r】和差分和区间【1,l】不同,所以写了两个query,省的返回结构体
注意⽤差分解决问题时,最⼤公约数会出现负数的情况。注意取绝对值
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
#define lc p<<1
#define rc p<<1|1
const int N = 5e5 + 10;
LL n, m;
struct node
{
int l, r;
LL sum, gcd;
}tr[N<<2];
LL gcd(LL a, LL b)
{
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b);
}
LL a[N];//差分数组 注意越界情况
void pushup(int p)
{
tr[p].sum = tr[lc].sum + tr[rc].sum;
tr[p].gcd = gcd(tr[lc].gcd, tr[rc].gcd);
}
void build(int p, int l, int r)
{
tr[p] = { l,r,a[l],a[l] };
if (l == r)return;
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
build(lc, l, mid); build(rc, mid + 1, r);
pushup(p);
}
void modify(int p, int x, LL k)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (l == r)
{
tr[p].sum += k;
tr[p].gcd += k;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (x <= mid)modify(lc, x, k);
else modify(rc, x, k);
pushup(p);
}
LL query1(int p, int x, int y)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (x <= l && y >= r)return tr[p].sum;
int mid = (l + r) / 2; LL ret = 0;
if (x <= mid)ret += query1(lc, x, y);
if (y > mid)ret += query1(rc, x, y);
return ret;
}
LL query2(int p,int x,int y)
{
int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;
if (x <= l && y >= r)return tr[p].gcd;
int mid = (l + r) / 2; LL g = 0;
if (x <= mid)g = gcd(query2(lc, x, y),g);
if (y > mid)g = gcd(query2(rc, x, y), g);
return g;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
LL x; cin >> x;
a[i] += x; a[i + 1] -= x;
}
build(1, 1, n);
while (m--)
{
char ch; cin >> ch;
if (ch == 'C')
{
int l, r; LL d; cin >> l >> r >> d;
modify(1, l, d);
if(r+1<=n)modify(1, r + 1, -d);
}
else
{
int x, y; cin >> x >> y;
LL sum = query1(1, 1, x);//sum表示第x个元素的值(差分累加值)
LL g = 0;
if(x+1<=y) g = query2(1, x + 1, y);
LL ret = gcd(sum, g);
cout << abs(ret) << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}




















 5万+
5万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








