题目描述
在一个标准8×8的国际象棋棋盘上,棋盘中有些格子是可能有障碍物的。已知骑士的初始位置和目标位置,你的任务是计算出骑士最少需要多少步可以从初始位置到达目标位置。有障碍物的格子当然不可能到达。
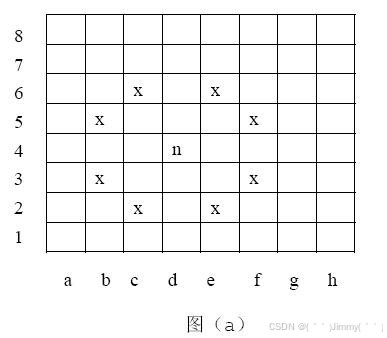
标准的8×8的国际象棋棋盘中每一个格子可以用唯一的编号确定。行用1~8这8个数字依次表示,列用“a”~“h”这8个字母依次表示。例如下图(a)的骑士所在位置(图中有n的格子)的编号为“d4”(注意“d”和“4”之间没有空格)。 我们知道国际象棋中的骑士可以按“L”路线移动(一个方向走2个格子,接着垂直方向走一个格子)。因此,如图(a)所示的骑士(位于d4),可以到达位置c2,b3,b5,c6,e6,f5,f3和e2(图中有“x”标记的格子)。此外,骑士不能移出棋盘。
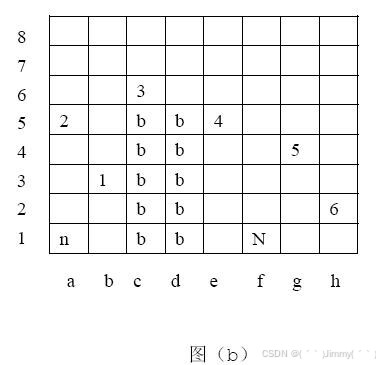
骑士可以按照移动规则自由地在棋盘上没有障碍物的格子中移动。图(b)给出了一个骑士移动的例子,也就是输入样例中第一组数据对应的例子。初始格子用“n”标记,目标格子用“N”标记,有障碍物的格子用“b”标记。一个可行的移动序列在图中用数字标记出来(a1,b3,a5,c6,e5,g4,h2,f1)。 总共需要7步才能完成。事实上,这也是最少的步数了。
输入
输入包含1个或多个测试数据。
每一个测试数据的第一行是一个整数b(-1 <= b <= 62),表示棋盘中有障碍物的格子数目。当b=-1时,输入结束。
第二行含b个不同的障碍物的格子编号,用空格隔开。当b=0时,此行为空行。
第三行是骑士的初始格子和目标格子的编号,也是用空格隔开。初始格子和目标格子是不同的,且都没有障碍物。
输出
对于每个数据,输出一行。格式:
Board i: m moves
其中i表示数据的组序号(从1开始),m表示骑士所用的最小步数。
如果骑士无法到达目标格子,输出:
Board i: not reachable
样例输入
10 c1 d1 d5 c2 c3 c4 d2 d3 d4 c5 a1 f1 0 c1 b3 2 b3 c2 a1 b2 -1
样例输出
Board 1: 7 moves Board 2: 1 moves Board 3: not reachable
AC代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int Map[10][10], vis[10][10];
int queue[1001][3]; // 队列
int dx[] = {1, 1, -1, -1, 2, -2, 2, -2};
int dy[] = {2, -2, 2, -2, 1, -1, -1, 1};
inline void Getval(int& x, int& y, const char* str)
{
x = str[0] - 'a' + 1;
y = str[1] - '0';
}
char str[128] = {0}, buf[128] = {0};
int sx, sy, lx, ly;
int bfs(void)
{
int head = 1, tail = 2;
queue[1][0] = sx, queue[1][1] = sy, queue[1][2] = 1;
vis[sx][sy] = 1;
while (head != tail)
{
int fx = queue[head][0], fy = queue[head][1], fstep = queue[head][2];
head ++;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
int tx = fx + dx[i], ty = fy + dy[i];
if (tx == lx && ty == ly) return fstep;
if (tx >= 1 && ty >= 1 && tx <= 8 && ty <= 8 && vis[tx][ty] == 0 && Map[tx][ty] == 0)
{
vis[tx][ty] = 1;
queue[tail][0] = tx, queue[tail][1] = ty, queue[tail][2] = fstep + 1;
tail++;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int b, cnt=0;
while (scanf("%d", &b) == 1 && b != -1)
{
memset(Map, 0, sizeof(Map)), memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)), memset(queue, 0, sizeof(queue));
int tx, ty;
if (b != 0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < b; i++)
{
scanf("%s", str);
Getval(tx, ty, str);
Map[tx][ty] = 1;
// printf("%s\n", str);
}
}
scanf("%s %s", str, buf);
// puts(str); puts(buf);
Getval(sx, sy, str), Getval(lx, ly, buf);
// printf("sx=%d sy=%d lx=%d ly=%d\n", sx, sy, lx, ly);
// printf("%d %d %d %d\n", sx, sy, lx, ly);
int ret = bfs();
if (ret == -1) printf("Board %d: not reachable\n", ++cnt);
else printf("Board %d: %d moves\n", ++cnt, ret);
}
return 0;
}



























 2726
2726

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








