1. 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。 OJ链接

public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head==null) {
return null;
}
ListNode cur=head.next;
ListNode pre=head;
while(cur!=null) {
if(cur.val==val) {
pre.next=cur.next;
cur=cur.next;
}
else {
pre=cur;
cur=cur.next;
}
}
if(head.val==val)
head=head.next;
return head;
}
}

2. 反转一个单链表。 OJ链接

class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode cur = head.next;
head.next = null;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode C = cur.next;
cur.next = head;
head = cur;
cur = pre;
}
return head;
}
}
3. 给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结
点。OJ链接

class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(slow!=null&&slow.next!=null) {
fast=fast.next;
slow=slow.next.next;
}
return fast;
}
}
4. 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。 OJ链接

方法1
public int kthToLast2( int k) {
if(k <= 0 ) {
return -1;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
int count = 0;
while (count != k-1) {
fast = fast.next;
if(fast == null) {
return -1;
}
count++;
}
while (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow.val;
}
方法2
class Solution {
public int kthToLast(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode cur=head;
while(k!=0) {
if (cur==null) {
return -1;
}
cur=cur.next;
k--;
}
if (k==0) {
while(cur!=null) {
cur=cur.next;
head=head.next;
}
return head.val;
}
return -1;
}
}
5. 将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。OJ

class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1==null) {
return list2;
}
if (list2==null) {
return list1;
}
ListNode temp;
if(list1.val>list2.val) {
temp=list2;
list2=list2.next;
}
else {
temp=list1;
list1=list1.next;
}
ListNode head=temp;
while(list1!=null&&list2!=null) {
if(list1.val>list2.val) {
temp.next=list2;
list2=list2.next;
temp=temp.next;
}
else {
temp.next=list1;
list1=list1.next;
temp=temp.next;
}
}
if(list1!=null) {
temp.next=list1;
}
if(list2!=null) {
temp.next=list2;
}
return head;
}
}
6. 编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前 。OJ链接

public class Partition {
public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) {
ListNode cur = pHead;
ListNode be = null;
ListNode bs = null;
ListNode as = null;
ListNode ae = null;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val < x) {
if (bs == null) {
bs = be = cur;
} else {
be.next = cur;
be=be.next;
}
} else {
if (as == null) {
as = ae = cur;
} else {
ae.next = cur;
ae=ae.next;
}
}
cur=cur.next;
}
if(be==null) {
return as;
}
if(ae!=null) {
ae.next=null;
}
be.next = as;
return bs;
}
}
7. 链表的回文结构。OJ链接

public class PalindromeList {
public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null) {
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
}
ListNode cur=slow.next;
ListNode curN=cur;
while(curN!=null) {
curN=curN.next;
cur.next=slow;
slow=cur;
cur=curN;
}
while(slow!=head) {
if(head.val!=slow.val) {
return false;
}
if (head.next==slow) {
return true;
}
head=head.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return true;
}
}
8. 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。OJ链接

public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode pl=headA;
ListNode ps=headB;
int len1=size(pl);
int len2=size(ps);
int leng=Math.abs(len1-len2);
if(len1>len2) {
while(leng!=0) {
pl=pl.next;
leng--;
}
}else {
while (leng !=0) {
ps=ps.next;
leng--;
}
}
while(ps!=null&&pl!=null) {
if(ps==pl) {
return ps;
}
ps=ps.next;
pl=pl.next;
}
return null;
}
public int size(ListNode head) {
int count=0;
while (head!=null) {
head=head.next;
count++;
}
return count;
}
}
9. 给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。 OJ链接

public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null) {
return false;
}
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null) {
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if(fast==slow) {
return true;
}
} return false;
}
}
【思路】
快慢指针,即慢指针一次走一步,快指针一次走两步,两个指针从链表起始位置开始运行,如果链表
带环则一定会在环中相遇,否则快指针率先走到链表的末尾。比如:陪女朋友到操作跑步减肥。
【扩展问题】
为什么快指针每次走两步,慢指针走一步可以?
假设链表带环,两个指针最后都会进入环,快指针先进环,慢指针后进环。当慢指针刚进环时,可能就和快
指针相遇了,最差情况下两个指针之间的距离刚好就是环的长度。此时,两个指针每移动一次,之间的距离
就缩小一步,不会出现每次刚好是套圈的情况,因此:在慢指针走到一圈之前,快指针肯定是可以追上慢指
针的,即相遇。
快指针一次走3步,走4步,…n步行吗?

按上面的方法,每次快指针走三步,慢指针走一步,永远不会相遇,因为快指针把慢指针套圈了。
因此只有快指针走2步,慢指针走一步,即使慢指针被套圈,slow和fast也是同一位置。
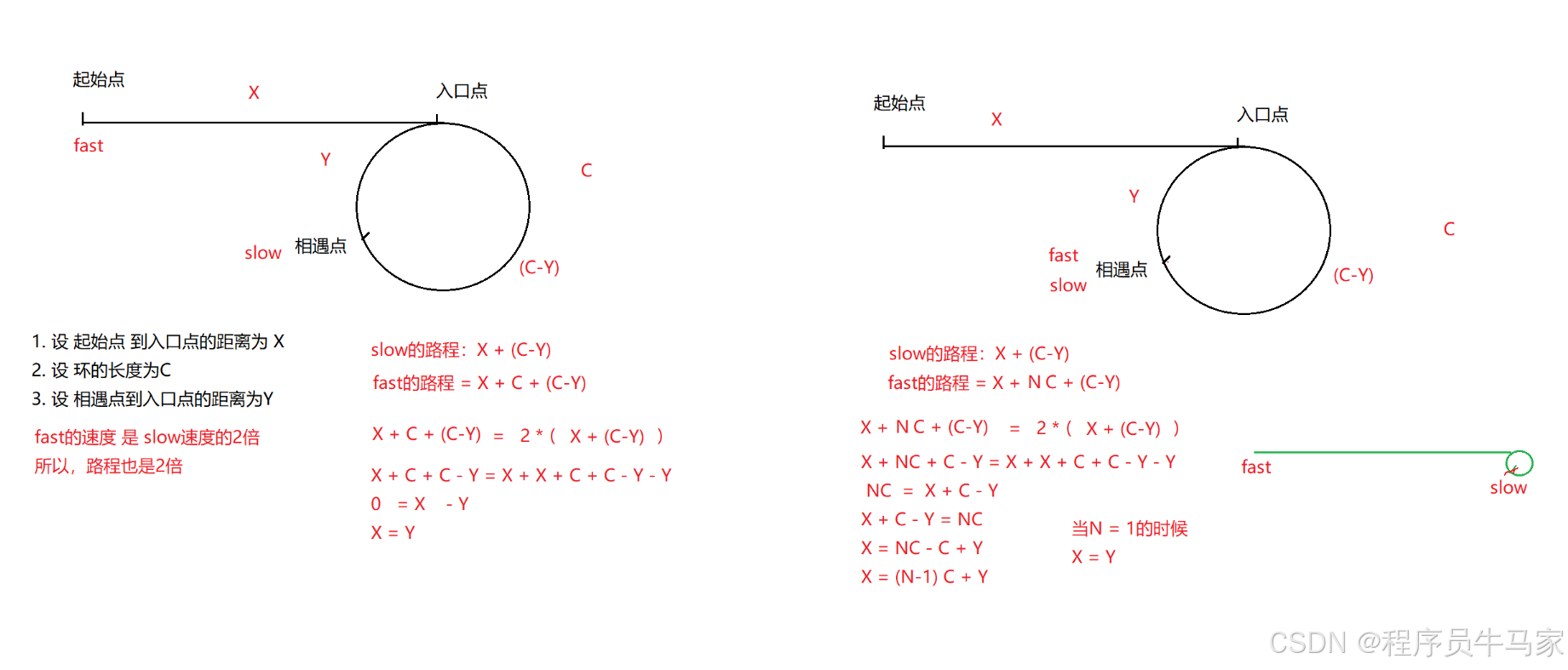
10. 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 NULL OJ链接

public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null) {
return null;
}
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while (fast!=null&&fast.next!=null) {
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if(slow==fast) {
break;
}
}
if(fast==null||fast.next==null) {
return null;
}
fast=head;
while (fast!=slow) {
fast=fast.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return fast;
}
}






















 2386
2386

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








