一,引入:Priority Queue
A priority queue is a data structure that stores elements with priority values and processes them in an order based on these values, rather than the order in which they were inserted.
◦ The priority value of an element determine its order of service
① Priority queue property:
◦ For any two elements in the queue, x and y, if x has a lower priority value than y, then x will be deleted before y

二,Priority queue operations
◦ Insert: insert a new element into a priority queue
◦ DeleteMin: delete the element with minimum priority value from
a priority queue
◦ Build: given a set of elements with their priority values, build a
priority queue
◦ IsFull: test whether a priority queue is full or not
◦ IsEmpty: test whether a priority queue is empty or not
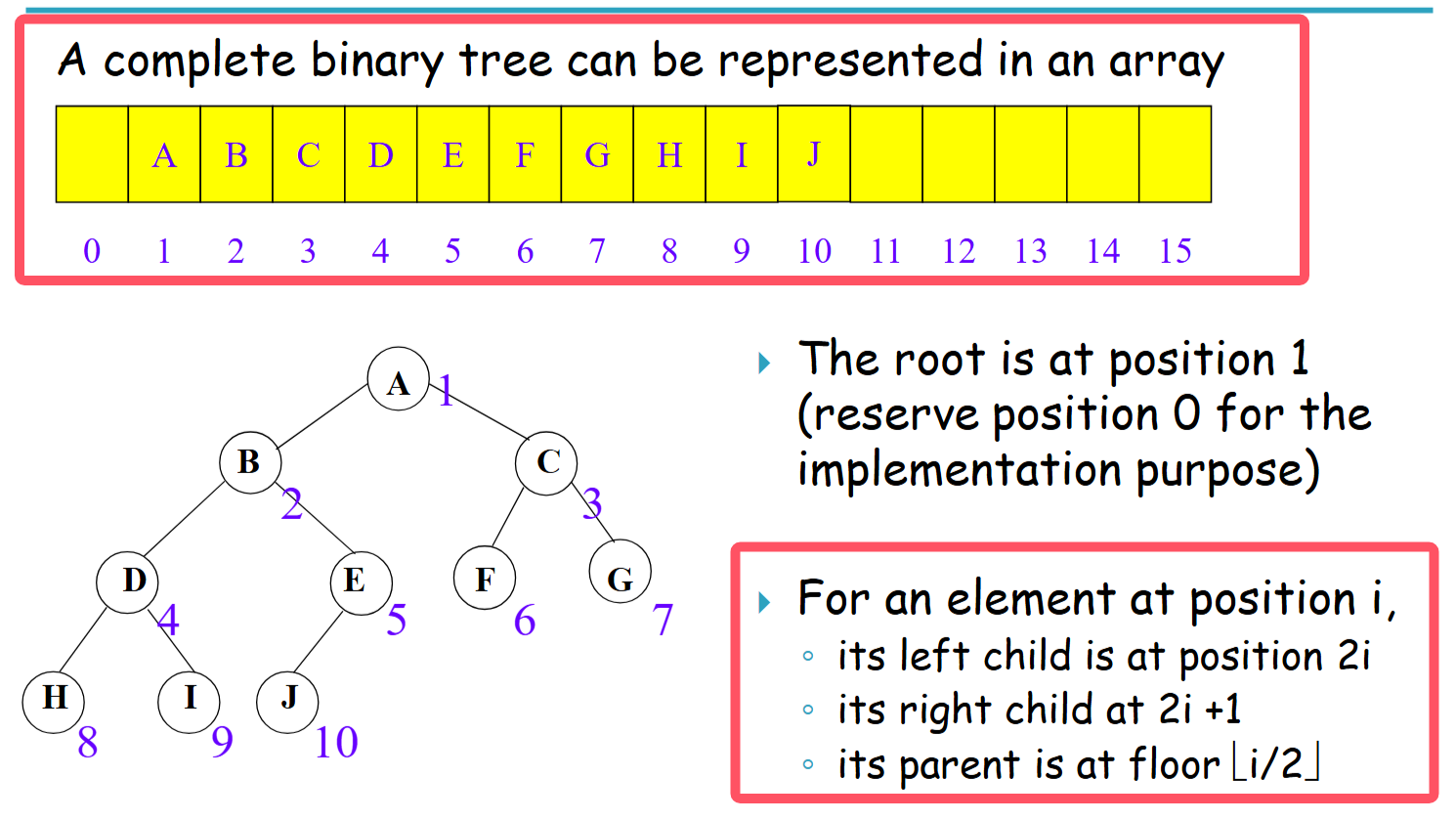
三,binary heap特点&分类
(A) Structure property
A heap is a complete binary tree. A binary tree that is completely filled, except at the bottom level,which is filled from left to right.
(B) Heap order property
◦ The value at any node should be smaller than (or equal to)all of its descendants (guarantee that the node with the minimum value is at the root)
◦ It is a recursive requirement
分类:
Min-heap ,Max-heap
四,The differences between BST和heap
| 特性 | 二叉搜索树(BST) | 二叉堆(Binary Heap) |
|---|---|---|
| 结构 | 二叉树,可能不完全 | 完全二叉树 |
| 节点值的关系 | 左子树 < 根 < 右子树 | 父节点与子节点满足堆性质(最大堆或最小堆) |
| 用途 | 快速查找、插入和删除 | 实现优先队列,快速获取最大值或最小值 |
| 时间复杂度 | 查找、插入、删除:O(log n)(平衡时) | 插入、删除:O(log n) |
| 存储方式 | 通常用指针实现 | 通常用数组实现 |
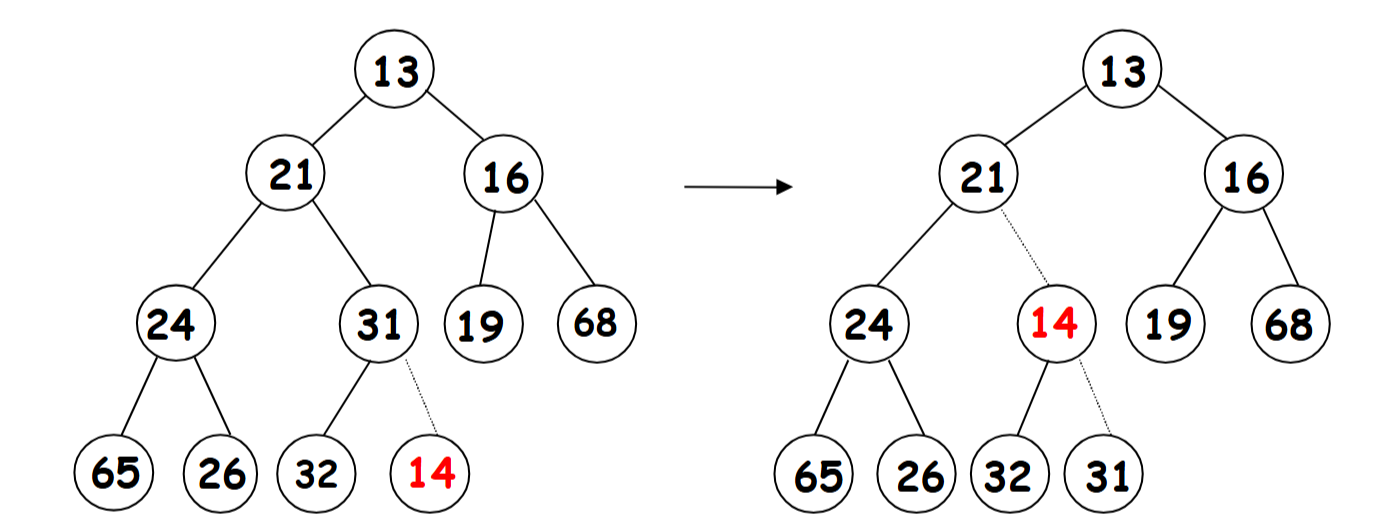
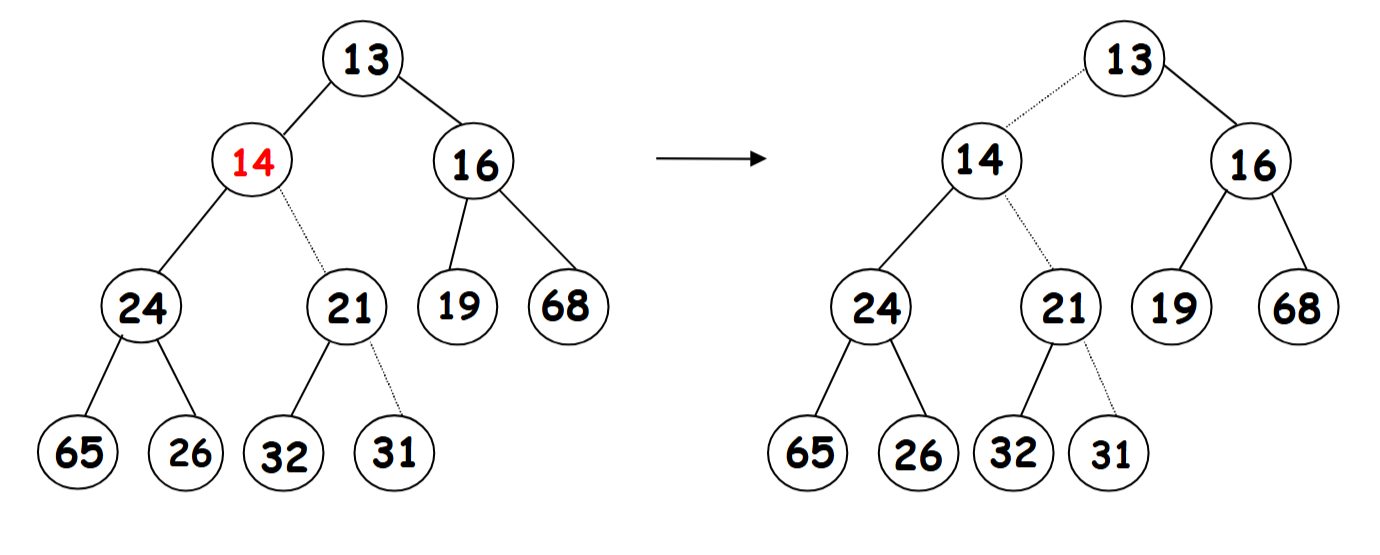
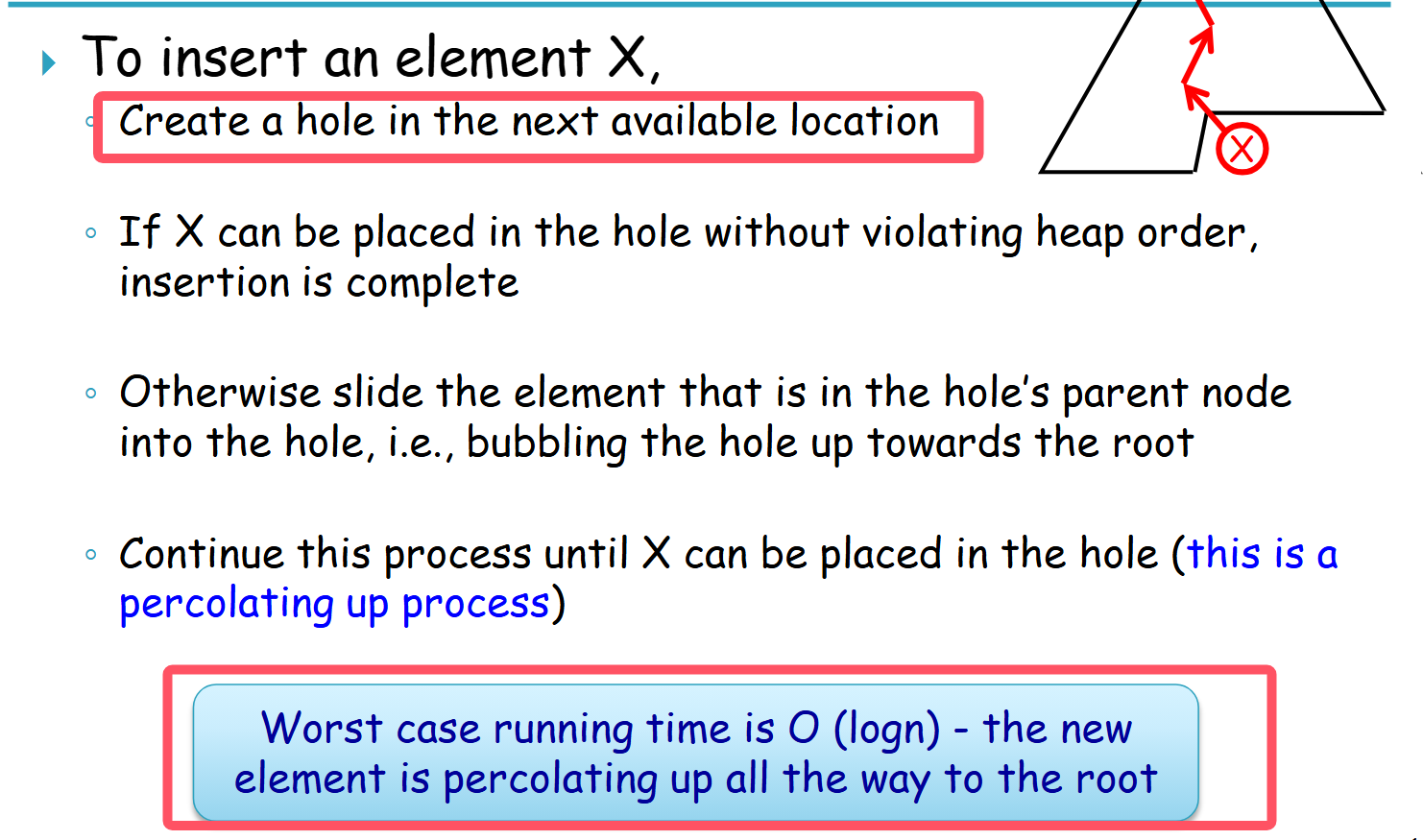
五,insertion
(如何insert?先插入最新的位置,然后在慢慢modify。将数字和parent比较,如果数字更小,那么就和parent交换位置。)
#include <iostream>
#include <stdexcept>
using namespace std;
class ElementType {
public:
int priority;
string data;
ElementType(int priority, string data) {
this->priority = priority;
this->data = data;
}
bool isHigherPriorityThan(const ElementType& e) const {
return priority < e.priority; // Assuming lower priority value means higher priority
}
};
class BinaryHeap {
private:
int currentSize;
int capacity;
ElementType** arr; // Array of pointers to ElementType
public:
BinaryHeap(int capacity) {
this->capacity = capacity;
currentSize = 0;
arr = new ElementType*[capacity + 1]; // Allocate memory for the heap array
}
~BinaryHeap() {
for (int i = 1; i <= currentSize; ++i) {
delete arr[i]; // Free memory for each element
}
delete[] arr; // Free memory for the array
}
bool isFull() const {
return currentSize == capacity;
}
void insert(const ElementType& x) {
if (isFull()) {
throw overflow_error("Overflow");
}
// Percolate up
int hole = ++currentSize;
while (hole > 1 && x.isHigherPriorityThan(*arr[hole / 2])) {
arr[hole] = arr[hole / 2];
hole /= 2;
}
arr[hole] = new ElementType(x.priority, x.data); // Insert the new element
}
void printHeap() const {
for (int i = 1; i <= currentSize; ++i) {
cout << "(" << arr[i]->priority << ", " << arr[i]->data << ") ";
}
cout << endl;
}
};
void insert(const ElementType& x) {
if (isFull()) {
throw overflow_error("Overflow");
}
int hole = ++currentSize;
while (hole > 1 && x.isHigherPriorityThan(*arr[hole / 2])) {
arr[hole] = arr[hole / 2]; //如果说x有更高的优先级那么就将父节点的值改成当前节点
hole /= 2;//并且把hole的位置更新(相当于更新要insert的值的index)
}
arr[hole] = new ElementType(x.priority, x.data); //通过while循环找到index之后,将数值放进去
}
六,DeleteMin
(delete min的思路:删除root,将最新的元素放到root,将root和两个孩子比较,交换:和最小的孩子。直到root小于两个孩子。)、
#include <iostream>
#include <stdexcept>
using namespace std;
class ElementType {
public:
int priority;
string data;
ElementType(int priority, string data) {
this->priority = priority;
this->data = data;
}
bool isHigherPriorityThan(const ElementType& e) const {
return priority < e.priority; // Assuming lower priority value means higher priority
}
};
class BinaryHeap {
private:
int currentSize;
int capacity;
ElementType** arr; // Array of pointers to ElementType
public:
BinaryHeap(int capacity) {
this->capacity = capacity;
currentSize = 0;
arr = new ElementType*[capacity + 1]; // Allocate memory for the heap array
}
~BinaryHeap() {
for (int i = 1; i <= currentSize; ++i) {
delete arr[i]; // Free memory for each element
}
delete[] arr; // Free memory for the array
}
bool isEmpty() const {
return currentSize == 0;
}
string deleteMin() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return ""; // Return empty string if the heap is empty
}
string data = arr[1]->data; // Get the data of the root (minimum element)
delete arr[1]; // Free memory for the root element
arr[1] = arr[currentSize--]; // Replace root with the last element
percolateDown(1); // Restore heap property
return data;
}
private:
void percolateDown(int hole) {
int child;
ElementType* tmp = arr[hole]; // Store the element to be moved down
while (hole * 2 <= currentSize) {
child = hole * 2; // Left child index
// Check if right child exists and has higher priority than left child
if (child != currentSize && arr[child + 1]->isHigherPriorityThan(*arr[child])) {
child++;
}
// If the child has higher priority than the current element, move the child up
if (arr[child]->isHigherPriorityThan(*tmp)) {
arr[hole] = arr[child];
} else {
break; // Stop if the heap property is satisfied
}
hole = child; // Move down to the child's position
}
arr[hole] = tmp; // Place the element in its correct position
}
};
string deleteMin() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return ""; // Return empty string if the heap is empty
}
string data = arr[1]->data; // 获取root的数据
delete arr[1]; // 释放root的内存
arr[1] = arr[currentSize--]; // 将最后一个数据填到root里面
percolateDown(1); // Restore heap property
return data;
}
void percolateDown(int hole) {
int child;
ElementType* tmp = arr[hole]; //存储位置在最后的数据
while (hole * 2 <= currentSize) { //对于hole节点来说,他的子节点位置是hole*2,检查有无左节点
child = hole * 2; //孩子指针先指向左节点。如果下述if都不成立那么,在没有右子节点或左子节点优先级更高的情况下,child 会指向左子节点。
if (child != currentSize && arr[child + 1]->isHigherPriorityThan(*arr[child])) {
child++;
} //假如左节点不是最后一个元素并且右节点优先级别比左节点高
if (arr[child]->isHigherPriorityThan(*tmp)) {//如果右节点比父母优先级别还高
arr[hole] = arr[child];//那么父母的hole(index)就直接变成孩子
} else {
break; // Stop if the heap property is satisfied
}
hole = child; // Move down to the child's position
}
arr[hole] = tmp; // Place the element in its correct position
}
};
七,Binary heap construction
①method
-
逐个插入法:
- 每次插入后通过“上浮”调整堆结构。
- 时间复杂度为
O(n log n),效率较低。
-
批量构建法:
- 先批量插入所有节点,再从底向上调整堆结构。
- 时间复杂度为
O(n),效率更高。
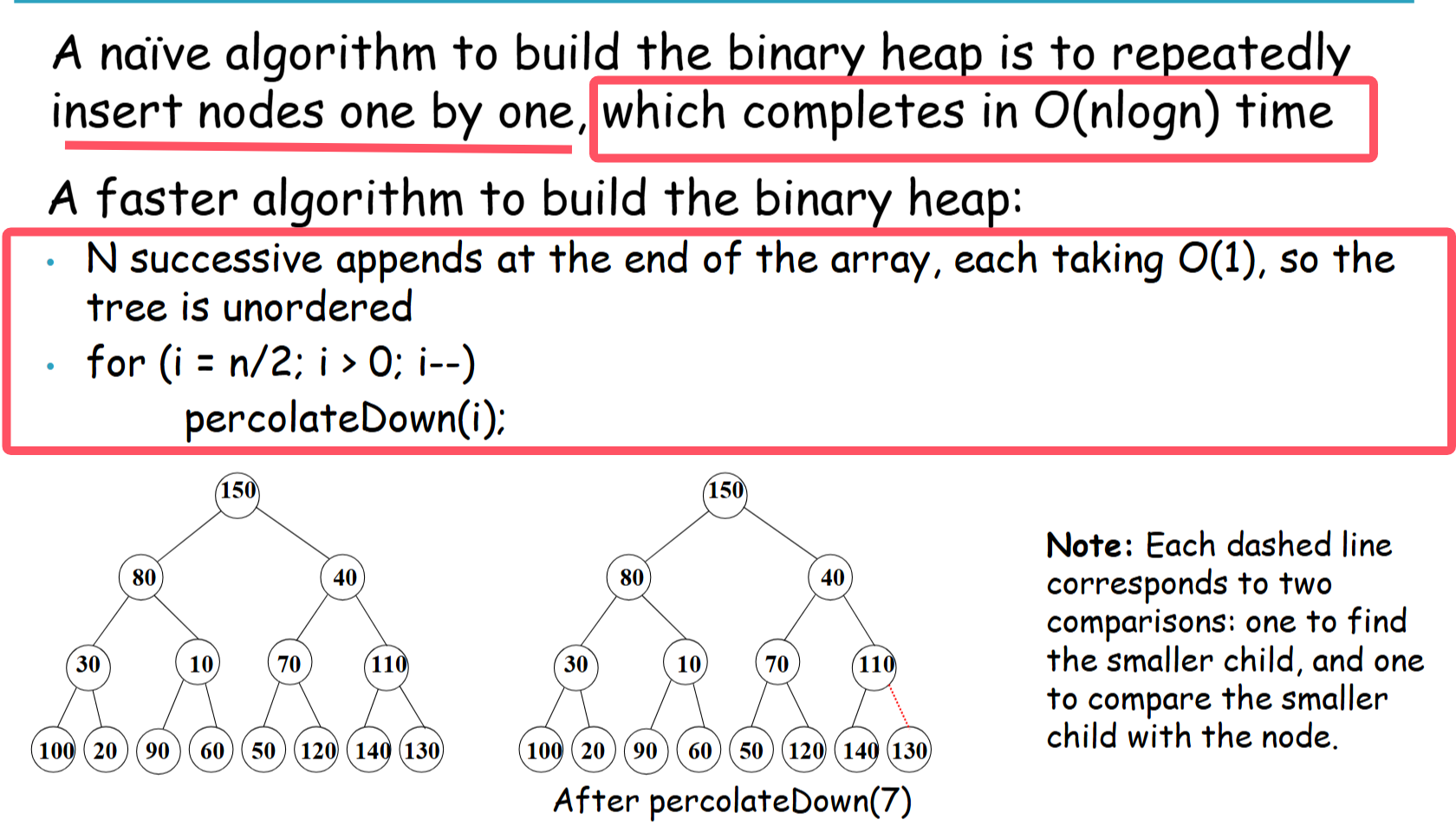
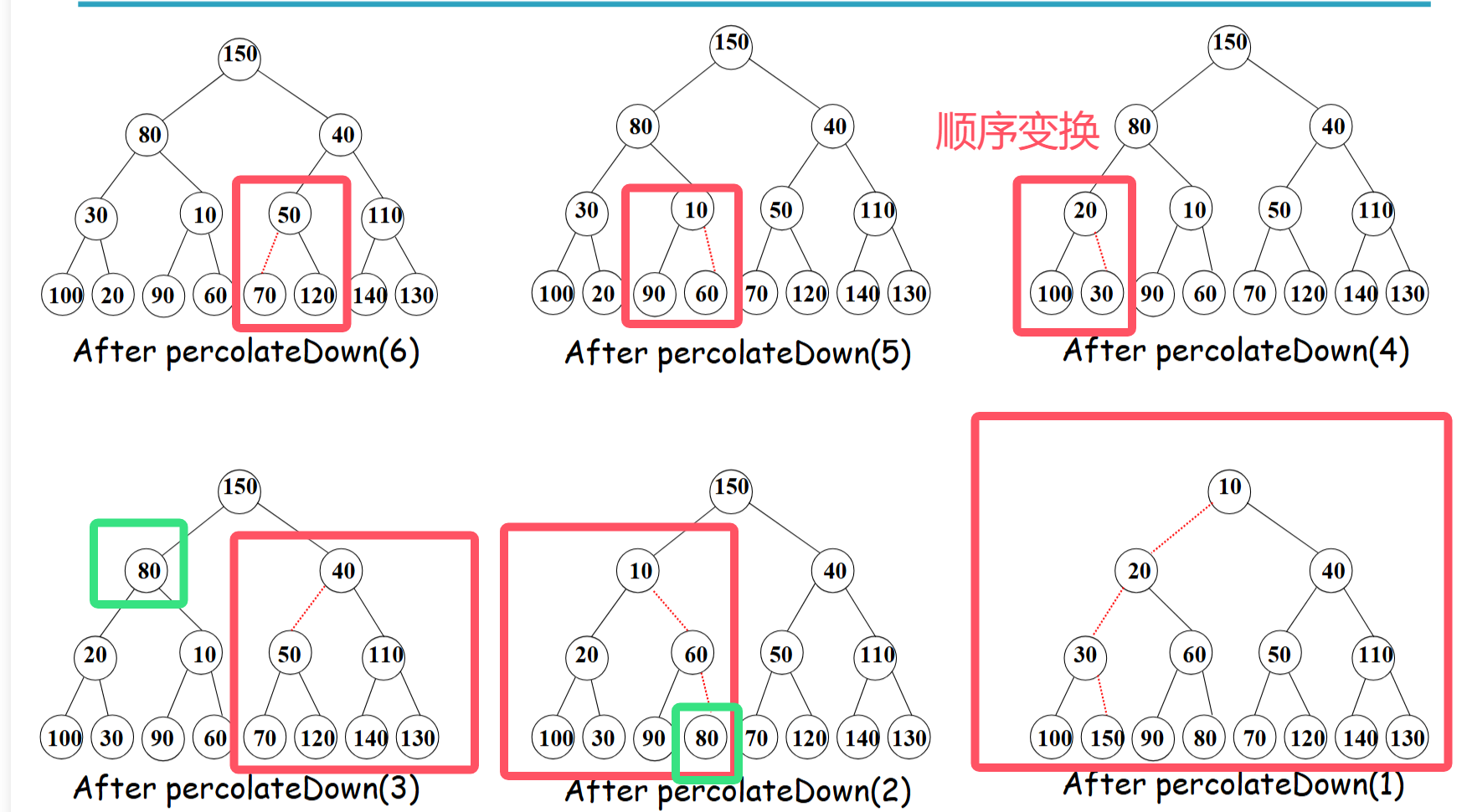
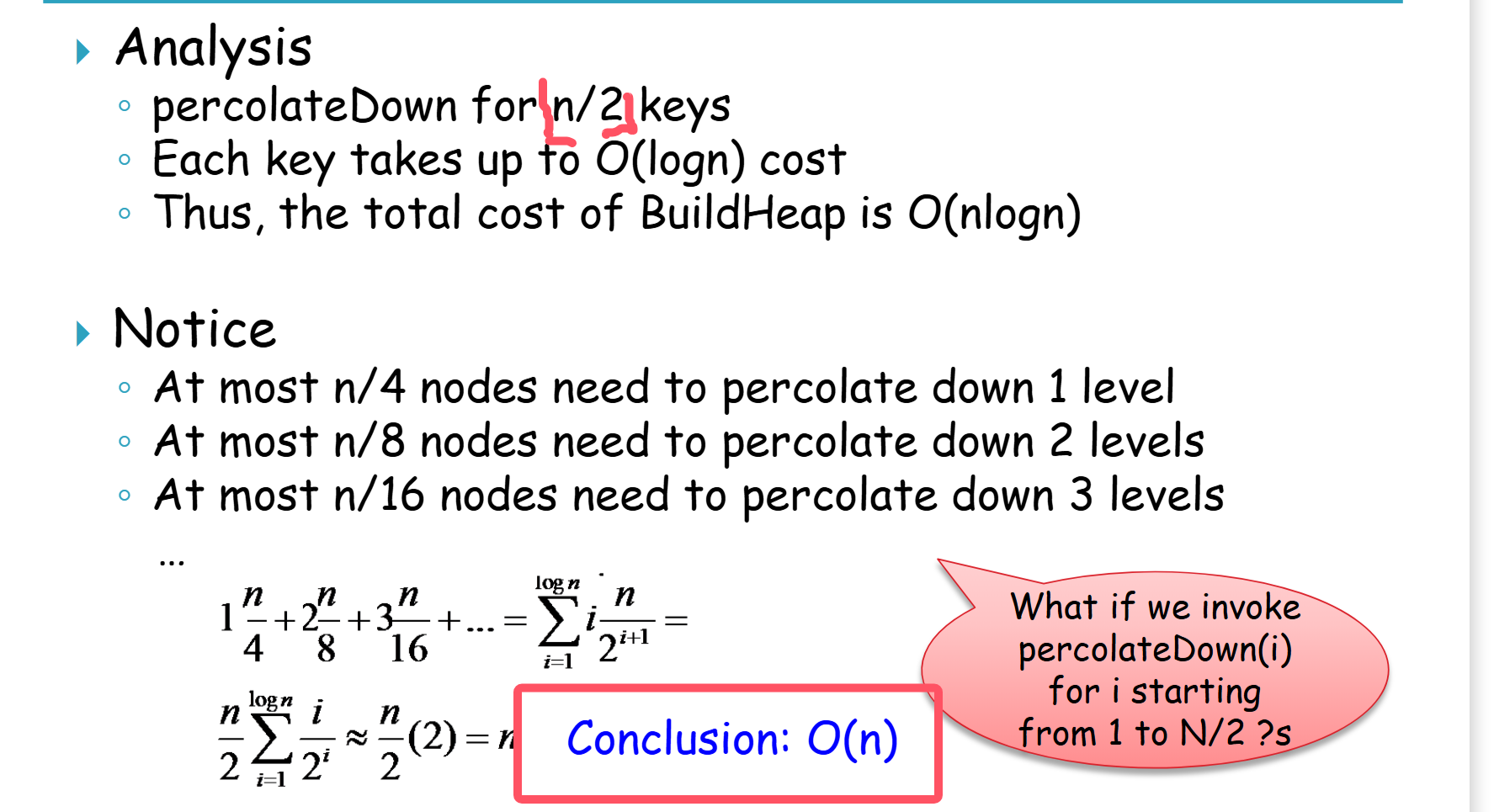
②complexity of building a heap
八,heapsort
(首先先构造一个maxheap,然后每次都删除root(root是最大值),删除root之后都把root存储到一个array里面即可。【然后调用percolate函数,重新构建maxheap,对n个元素操作,所以时间复杂度是nlogn。这个不是稳定的,因为相同的元素在sort之后位置会被改变】)
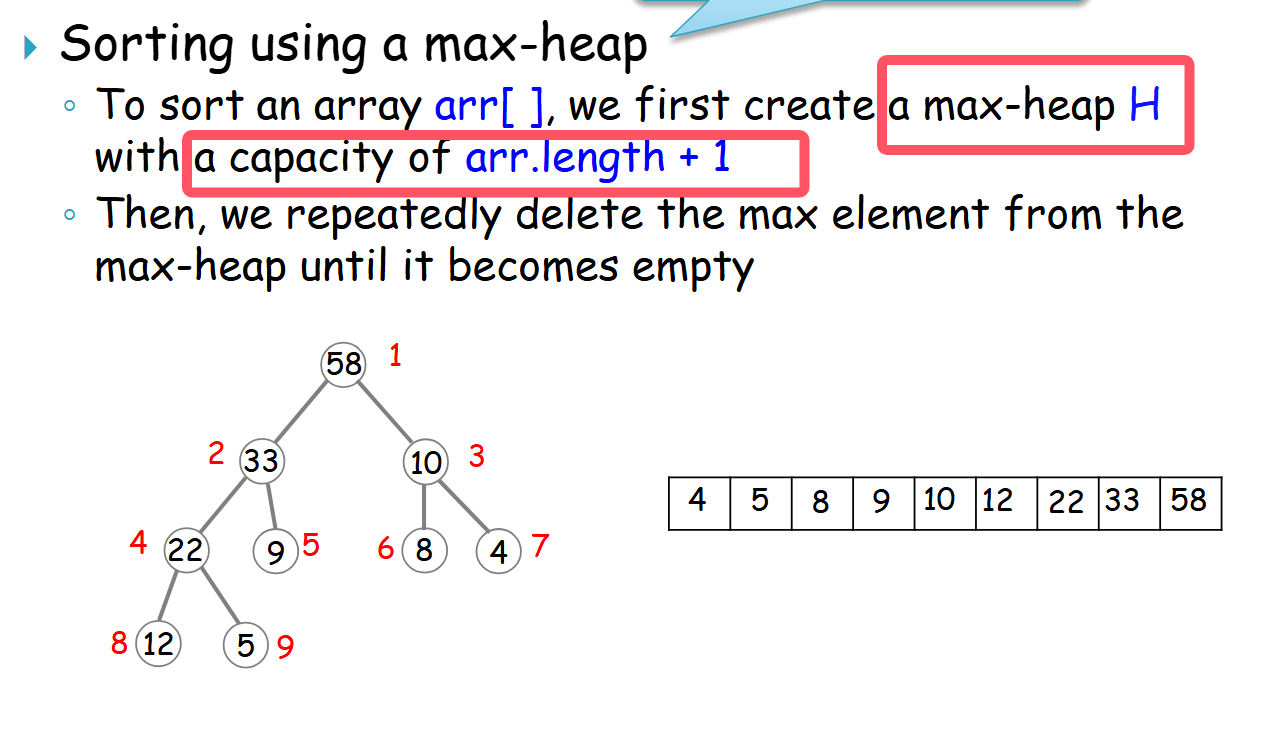
caution:注意,with a capacity of arr.length + 1
1. 初始数组
假设我们有一个数组 arr[],长度为 9,包含以下元素:
arr[] = {58, 33, 10, 22, 9, 8, 4, 12, 5}
目标是对这个数组进行排序。
2. 创建 Max-Heap
为了使用堆排序,我们需要将数组转换为一个 Max-Heap。堆通常使用数组来存储数据,并且从 索引 1 开始存储元素,而不是从索引 0 开始。
为什么从索引 1 开始存储?
- 堆的父子节点关系在索引从 1 开始时更加简单:
- 父节点索引:
i - 左子节点索引:
2 * i - 右子节点索引:
2 * i + 1
- 父节点索引:
- 如果从索引 0 开始存储,计算关系会变得复杂。
堆的容量
- 数组
arr[]的长度是 9。 - 为了从索引 1 开始存储元素,堆的容量需要是
arr.length + 1,即 10。 - 堆的数组表示为:
heap[] = [_, 58, 33, 10, 22, 9, 8, 4, 12, 5]注意:- 索引 0 的位置是空的(用
_表示)。 - 索引 1 到索引 9 存储了所有元素。
- 索引 0 的位置是空的(用
3. 堆的操作
在堆排序中,我们会对堆进行以下操作:
- 构建最大堆:从最后一个非叶子节点开始,逐个向上调整(
percolateDown),直到整个堆满足最大堆的性质。 - 删除最大值:重复删除堆顶元素(最大值),并调整堆结构,直到堆为空。





















 656
656

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








