目录
1、WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
一、权限管理简介
1、什么是权限管理
基本上涉及到用户参与的系统都要进行权限管理,权限管理属于系统安全的范畴,权限管理实现对用户访问系统的控制,按照安全规则或者安全策略控制用户可以访问而且只能访问自己被授权的资源。
权限管理包括用户身份认证鉴权(授权)两部分,简称认证授权。对于需要访问控制的资源用户首先经过身份认证,认证通过后用户具有该资源的访问权限方可访问。
2、认证
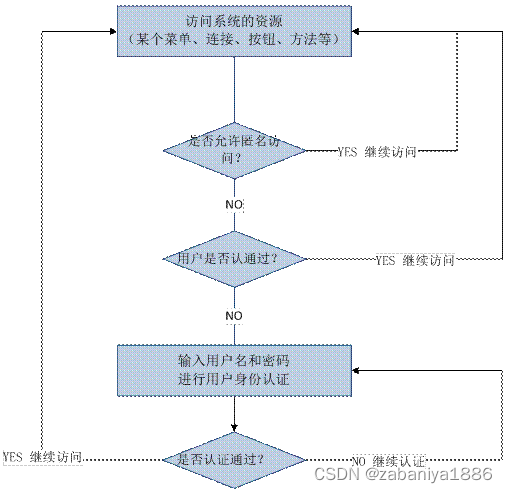
身份认证,就是判断一个用户是否为合法用户的处理过程。最常用的简单身份认证方式是系统通过核对用户输入的用户名和口令,看其是否与系统中存储的该用户的用户名和口令一致,来判断用户身份是否正确。对于采用指纹等系统,则出示指纹;对于硬件Key等刷卡系统,则需要刷卡。
3、授权
授权,即访问控制,控制谁能访问哪些资源。主体进行身份认证后需要分配权限方可访问系统的资源,对于某些资源没有权限是无法访问的。
下图中橙色为授权流程。

二、权限管理解决方案
1、基于角色的访问控制
RBAC基于角色的访问控制(Role-Based Access Control)是以角色为中心进行访问控制,比如:主体的角色为总经理可以查询企业运营报表,查询员工工资信息等,访问控制流程如下:

上图中的判断逻辑代码可以理解为:
if(主体.hasRole("总经理角色id")){
查询工资
}缺点:以角色进行访问控制粒度较粗,如果上图中查询工资所需要的角色变化为总经理和部门经理,此时就需要修改判断逻辑为“判断主体的角色是否是总经理或部门经理”,系统可扩展性差。
修改代码如下:
if(主体.hasRole("总经理角色id") || 主体.hasRole("部门经理角色id")){
查询工资
}2、基于资源的访问控制
RBAC基于资源的访问控制(Resource-Based Access Control)是以资源为中心进行访问控制,比如:主体必须具有查询工资权限才可以查询员工工资信息等,访问控制流程如下:
上图中的判断逻辑代码可以理解为:
if(主体.hasPermission("查询工资权限标识")){
查询工资
}优点:系统设计时定义好查询工资的权限标识,即使查询工资所需要的角色变化为总经理和部门经理也只需要将“查询工资信息权限”添加到“部门经理角色”的权限列表中,判断逻辑不用修改,系统可扩展性强。
三、Spring Security概述
1,Spring Security简介
Spring Security 是一个能够为基于 Spring 的企业应用系统提供声明式的安全访问控制解决方案的安全框架。它提供了一组可以在 Spring 应用上下文中配置的 Bean,充分利用了 Spring IoC(Inversion of Control 控制反转),DI(Dependency Injection 依赖注入)和 AOP(面向切面编程)功能,为应用系统提供声明式的安全访问控制功能,减少了为企业系统安全控制编写大量重复代码的工作。
Spring Security 拥有以下特性:
-
对身份验证和授权的全面且可扩展的支持
-
防御会话固定、点击劫持,跨站请求伪造等攻击
-
支持 Servlet API 集成
-
支持与 Spring Web MVC 集成
Spring、Spring Boot 和 Spring Security 三者的关系如下图所示:

2、Spring Security快速入门
2.1、引入依赖
<!--springboot整合security坐标-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>2.2、创建一个控制器
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("hello")
public String hello(){
return "Hello Spring security";
}
}2.3、启动项目
访问:http://localhost:8080/hello 结果打开的是一个登录页面,其实这时候我们的请求已经被保护起来了,要想访问,需要先登录。

Spring Security 默认提供了一个用户名为 user 的用户,其密码在控制台可以找到
四、Spring Security 认证配置
1、WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
当然还可以通过配置类的方式进行配置,创建一个配置类去继承,实现自定义用户名密码登录
/**
* Spring Security配置类
* 在springboot2.7 后WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter弃用了,用2.5.4
*/
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
// 对密码进行加密。123 是密码明文,现在 Spring Security 强制性要求『不允许明文存储密码』。
BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
String password = passwordEncoder.encode("123");
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("tom").password(password).roles("admin");
}
}springsecurity强制性要求必须使用密码加密器(PasswordEncoder)对原始密码(注册密码)进行加密。因此,如果忘记指定 PasswordEncoder 会导致执行时会出现 There is no PasswordEncoder mapped for the id "null" 异常。
这是因为我们在对密码加密的时候使用到了 BCryptPasswordEncoder 对象,而 Spring Security 在对密码比对的过程中不会『自己创建』加密器,因此,需要我们在 Spring IoC 容器中配置、创建好加密器的单例对象,以供它直接使用。
所以,我们还需要在容器中配置、创建加密器的单例对象(上面那个 new 理论上可以改造成注入),修改Spring securitry配置类
/**
* Spring Security配置类
* 在springboot2.7后WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter弃用了,用2.5.4
*/
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
// 对密码进行加密。123 是密码明文,现在 Spring Security 强制性要求『不允许明文存储密码』。
BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
String password = passwordEncoder.encode("123");
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("tom").password(password).roles("admin");
}
/**
* 将PasswordEncoder注入到ioc容器
* @return
*/
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}Spring Security 内置的 Password Encoder 有:
| 加密算法名称 | PasswordEncoder |
|---|---|
| NOOP | NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance() |
| SHA256 | new StandardPasswordEncoder() |
| BCRYPT(官方推荐) | new BCryptPasswordEncoder() |
| LDAP | new LdapShaPasswordEncoder() |
| PBKDF2 | new Pbkdf2PasswordEncoder() |
| SCRYPT | new SCryptPasswordEncoder() |
| MD4 | new Md4PasswordEncoder() |
| MD5 | new MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("MD5") |
| SHA_1 | new MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("SHA-1") |
| SHA_256 | new MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("SHA-256") |
2、UserDetailsService
-
在service包下创建一个UserDetailsService类
/** * spring security认证业务类 */ @Service public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService { @Autowired private UserDao userDao; @Autowired private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder; @Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException { //调用dao到数据库中根据username查找用户信息 Users users = userDao.getByUserName(username); String anths = String.join(",", userInfo.getAnths()); try { //将查找到的用户帐号与密码保存到Security的User对象中由Security进行比对 return new User(users.getUsername(), passwordEncoder.encode(users.getPassword()), //配置登录用户有哪些角色和权限,此处模拟直接写死 AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList(anths); }catch (Exception e){ throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户"+username+"不存在"); } } }
-
修改spring security配置类
@EnableWebSecurity public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Autowired private MyUserDetailsService userDetailsService; @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService); } /** * 将PasswordEncoder注入到ioc容器 * @return */ @Bean public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() { return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); } }
3、Spring Security 自带的表单认证
-
准备自定义登录页面
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>登录</title> </head> <body> <form action="dologin" method="post"> <!--注意:帐号和密码的名称必须是username和password否则spring security无法识别--> <p>帐号:<input type="text" name="username"></p> <p>密码:<input type="text" name="password"></p> <p><button type="submit">登录</button></p> </form> </body> </html>
-
SpringSecurityConfig 类中的配置代码
@Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.formLogin() .loginPage("/login.html")//配置需要显示的登录页面 .loginProcessingUrl("/dologin") //配置登录请求路径,很from表单的 action 要对应上 .permitAll()//这句配置很重要,新手容易忘记。放开 login.html和dologin 的访问权 .and().authorizeRequests() .anyRequest().authenticated(); // 除了antMatchers() 配的页面,其他都需要认证 http.csrf().disable(); }
五、鉴权配置
1、鉴权配置
| 权限表达式 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| permitAll() | 永远返回 true |
| hasRole("role") | 当用户拥有指定身份时,返回 true |
| hasAnyRole("role1", "role2", ...) | 当用户返回指定身份中的任意一个时,返回 true |
| hasAuthority("authority1") | 当用于拥有指定权限时,返回 true |
| hasAnyAuthority("authority1", "authority2") | 当用户拥有指定权限中的任意一个时,返回 true |
hasRole():数据库用户角色必须加 ROLE_ 前缀,而用hasRole() security会自动加上ROLE_ 前缀,自己不能加上ROLE_ 前缀,例如
AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("ROLE_admin")
对上
hasRole("admin")hasAuthority() 数据库角色名称和方法内容一致 例如:
AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin")
对上
hasRole("admin")没有权限跳转到自定义页面
http.formLogin()
.loginPage("/hello")//配置需要显示的登录页面
.loginProcessingUrl("/dologin") //配置登录请求路径
.permitAll()//这句配置很重要,新手容易忘记。放开 login.html和dologin 的访问权
.and().authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/","/hello").permitAll()// 设置哪些路劲不需要登录,能直接当问
.antMatchers("/toupdate").hasAuthority("admin") //设置资源具有指定角色才能访问
.anyRequest().authenticated(); // 除了antMatchers() 配的页面,其他都需要认证
http.csrf().disable();2、使用注解实
在实际的使用过程中用户的鉴权并不是通过置来写的而是通过注解来进行,Spring Security 默认是禁用注解的。
要想开启注解功能需要在配置类上加入 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity注解来判断用户对某个控制层的方法是否具有访问权限。
注解就是用来替换springSecurity配置类中的http.authorizeRequests()配置
Spring Security 支持三套注解:
| 注解类型 | 注解 |
|---|---|
| jsr250 注解 | @DenyAll、@PermitAll、@RolesAllowed |
| secured 注解 | @Secured |
| prePost 注解 | @PreAuthorize、@PostAuthorize |
使用什么注解在@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity开启,默认是关闭的,例如
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(jsr250Enabled = true,securedEnabled=true) //开启jsr250和secured注解
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
}-
secured 注解
@Secured 注解是 jsr250 标准出现之前,Spring Security 框架自己定义的注解。
@Secured 标注于方法上,表示只有具有它所指定的角色的用户才可以调用该方法。如果当前用户不具备所要求的角色,那么,将会抛出 AccessDenied 异常,注解和配置类都要加上ROLE_ 前缀
@RestController public class UserController { @Secured({"ROLE_USER","ROLE_ADMIN"}) // 这里加ROLE_前缀 @RequestMapping("/all-can-do") public String show7(){ return "all-can-do"; } @Secured("ROLE_USER") @RequestMapping("/admin-can-do") public String show6(){ return "admin-can-do"; } }配置类
return new User(users.getUsername(), passwordEncoder.encode(users.getPassword()), AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("ROLE_USER")); //配置类也要加上ROLE_前缀 -
JSR-250 注解
@DenyAll: 所有用户都不可以访问
@PermitAll:所有用户都可以访问
@RolesAllowed:用法同@Secured差不多,区别是注解上ROLE_ 可加可不加,但是配置类上必须加ROLE_ 前缀
-
prePost 注解
@PreAuthorize可以用来控制一个方法是否能够被调用。
@PreAuthorize(“hasAuthority(‘admin’)”) publicvoid addUser(User user) { System.out.println(“addUser…” + user); }
3、 登录返回处理
在某些前后端完全分离,仅靠 JSON 完成所有交互的系统中,一般会在登陆成功时返回一段 JSON 数据,告知前端,登陆成功与否。可以通过实现 AuthenticationSuccessHandler 处理登录成功,实现AuthenticationFailureHandler 处理登录失败
-
创建SimpleAuthenticationSuccessHandler和SimpleAuthenticationFailureHandler类来处理登录成功和失败的业务
httpServletResponse.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8"); PrintWriter pw = httpServletResponse.getWriter(); String success = JSON.toJSONString(ResponseResult.LOGIN_FAIL); pw.print(success); pw.flush(); pw.close();
-
修改spring security配置类
//登录相关配置 http.formLogin() .loginPage("/login.html") .loginProcessingUrl("/dologin") .successHandler(new simpleAuthenticationSuccessHandle())//配置登录成功后的处理器 .failureHandler(new SimpleAuthenticationFailureHandler())//配置登录失败后的处理器 .permitAll(); }
4、鉴权的异常处理
Spring Security 的认证工作是由 FilterSecurityInterceptor 处理的。FilterSecurityInterceptor 会抛出 2 种异常:
-
在用户 “该登录而未登录” 时,抛出 AuthenticationException 异常;实现AuthenticationEntryPoint
-
在用户 “权限不够” 时,抛出 AccessDeniedException 异常。实现AccessDeniedHandler
-
修改SpringSecurity配置类
//认证和鉴权异常配置 http.exceptionHandling() .authenticationEntryPoint()//认证异常处理器 .accessDeniedHandler();//鉴权异常处理器
5、退出操作
Spring Security中发送了logout请求成功后会自动跳转到默认的login.html页面。在前后端分离的项目中,所有的页面跳转都是由前端控制的,服务器端只需要返回一个json的状态码即可,实现 LogoutSuccessHandler
-
Spring Security配置类
//前后端项目中要禁用掉session http.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS); //退出成功后的处理器 http.logout().logoutSuccessHandler(new SimpLogoutSuccessHandler());






















 2102
2102











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








