Java类和对象
一、认识面向对象
什么是面向对象
Java是一门纯面向对象的语言(Object Oriented
Program,简称OOP),在面向对象的世界里,一切皆为对象。面向对象是解决问题的一种思想,主要依靠对象之间的交互完成一件事情。用面向对象的思想来涉及程序,更符合人们对事物的认知,对于大型程序的设计、扩展以及维护都非常友好。
面向过程和面向对象
面向过程:强调处理问题的过程。
面向对象:利用对象间的消息传递来驱动程序的执行
二、类和对象的基本概念
类是对象的抽象,而对象是类的具体实例。
类:具有相似内部状态和运动规律的实体的集合。具有相同属性和行为食物的统称。
对象:是现实世界中的一个实体。
三、类定义和使用
类的定义格式
class ClassName{
field; // 字段(属性) 或者 成员变量
method; // 行为 或者 成员方法
}
Java中用class关键字定义类
类名采用大驼峰(每个单词首字母大写)命名
定义一个学生类
public class Student {
//成员变量
public String name;
public String gender;
public short age;
public double score;
//成员方法
public void DoClass(){
System.out.println(name+"在上课");
}
public void DoHomework(){
}
public void Exam(){
}
}
注意事项:
- 一般一个文件当中只定义一个类
- main方法所在的类一般要使用public修饰(注意:Eclipse默认会在public修饰的类中找main方法)
- public修饰的类必须要和文件名相同
类的实例化
定义了一个类,就像与定义了一个新类型,例如上述的Student类。
用类类型创建对象的过程,称为类的实例化,在java中用new关键字来实例化对象
public static void main(String[] args) {
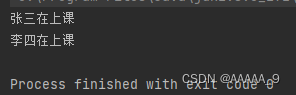
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.name = "张三";
s1.gender = "男";
s1.age = 18;
s1.score = 4.0;
s1.DoClass();
Student s2 = new Student();
s2.name = "李四";
s2.gender = "男";
s2.age = 18;
s2.score = 4.5;
s2.DoClass();
}
输出结果:
说明:
- new关键字用于创建一个对象的实例
- 使用.来访问对象的属性和方法
- 同一个类可以定义多个对象
四、this引用
public class Date {
public int year;
public int month;
public int day;
public void setDay(int year, int month, int day){
year = year;
month = month;
day = day;
}
public void printDate(){
System.out.println(year + "年" + month + "月" + day + "日");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date d1 = new Date();
d1.setDay(2022,11,12);
d1.printDate();
}
}
输出结果:
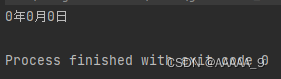
因为在setDay方法中的形参与成员变量名相同,setDay优先使用自己的形参,就相当于形参给形参赋值,所有对象d1的成员变量没有被赋值。
this的作用:
this引用指向当前对象(成员方法运行时调用该成员方法的对象),在成员方法中所有成员变量的操作,都是通过该引用去访问。只不过所有的操作对用户是透明的,即用户不需要来传递,编译器自动完成。
this.成员变量 就相当于 当前对象.成员变量
public class Date {
public int year;
public int month;
public int day;
public void setDay(int year, int month, int day){
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
public void printDate(){
System.out.println(year + "年" + month + "月" + day + "日");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date d1 = new Date();
d1.setDay(2022,11,12);
d1.printDate();
}
}
输出结果
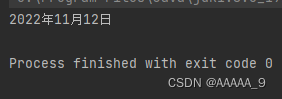
this引用的特性
- this的类型:对应类类型引用,即哪个对象调用就是哪个对象的引用类型
- this只能在"非静态成员方法"中使用
- 在"成员方法"中,this只能引用当前对象,不能再引用其他对象
- this是“成员方法”第一个隐藏的参数,编译器会自动传递,在成员方法执行时,编译器会负责将调用成员方法对象的引用传递给该成员方法,this负责来接收
五、对象的构造及初始化
默认初始化
定义一个局部变量,不初始化就使用会报错
而对象不会报错,创建对象时,对象的属性会被默认初始化
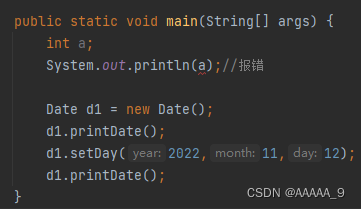
上述中的Date类 创建好对象后调用SetDate方法设置具体日期,比较麻烦,那对象该如何初始化?
构造方法
构造方法(也称为构造器)是一个特殊的成员方法,名字必须与类名相同,在创建对象时,由编译器自动调用,并且在整个对象的生命周期内只调用一次。
public class Date {
public int year;
public int month;
public int day;
public Date(int year, int month, int day){
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
System.out.println("Date(int,int,int)方法被调用了");
}
public void printDate(){
System.out.println(year + "年" + month + "月" + day + "日");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date d1 = new Date(2021,6,9);
d1.printDate();
}
}
输出结果:
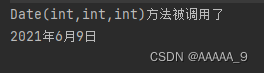
构造方法的特性
- 名字必须与类名相同
- 没有返回值类型,设置为void也不行
- 创建对象时由编译器自动调用,并且在对象的生命周期内只调用一次
- 构造方法可以重载(用户根据自己的需求提供不同参数的构造方法)
public class Date {
public int year;
public int month;
public int day;
public Date(){
System.out.println("Date()方法被调用了");
}
//构造方法重载
public Date(int year, int month, int day){
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
System.out.println("Date(int,int,int)方法被调用了");
}
public void printDate(){
System.out.println(year + "年" + month + "月" + day + "日");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date d1 = new Date(2021,6,9);
d1.printDate();
Date d2 = new Date();
}
}
输出结果:
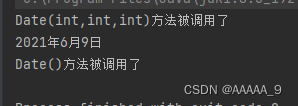
5. 如果用户没有显式定义,编译器会生成一份默认的构造方法,生成的默认构造方法一定是无参的。
但是如果你定义了,编译器就不会生成。
public class Date {
public int year;
public int month;
public int day;
public Date(int year, int month, int day){
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
System.out.println("Date(int,int,int)方法被调用了");
}
public void printDate(){
System.out.println(year + "年" + month + "月" + day + "日");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date d2 = new Date();//报错,没有无参的构造方法
}
}
- 构造方法中,可以通过this调用其他构造方法来简化代码
public class Date {
public int year;
public int month;
public int day;
public Date() {
this(2020,1,1);//必须放在构造方法中的第一行
System.out.println("Date()方法被调用了");
}
//构造方法重载
public Date(int year, int month, int day){
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
System.out.println("Date(int,int,int)方法被调用了");
}
public void printDate(){
System.out.println(year + "年" + month + "月" + day + "日");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date d1 = new Date();
d1.printDate();
}
}
输出结果:
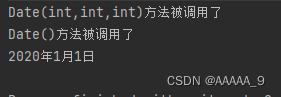
注意:
- this(…)必须是构造方法中第一条语句
- 不能形成环(两个构造方法互相调用对方)
就地初始化
public class Date {
public int year = 2020;
public int month = 1;
public int day = 1;
public Date() {
System.out.println("Date()方法被调用了");
}
public Date(int year, int month, int day){
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
System.out.println("Date(int,int,int)方法被调用了");
}
public void printDate(){
System.out.println(year + "年" + month + "月" + day + "日");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date d1 = new Date();//Date()方法被调用了
d1.printDate();//2020年1月1日
}
}
六、static成员
在Java中,被static修饰的成员,称之为静态成员,也可以称为类成员,其不属于某个具体的对象,是所有对象所共享的。
static修饰成员变量
static修饰的成员变量,称为静态成员变量,静态成员变量最大的特性:不属于某个具体的对象,是所有对象所共享的。
【静态成员变量特性】
- 不属于某个具体的对象,是类的属性,所有对象共享的,不存储在某个对象的空间中
- 既可以通过对象访问,也可以通过类名访问,但一般更推荐使用类名访问
- 类变量存储在方法区当中
- 生命周期伴随类的一生(即:随类的加载而创建,随类的卸载而销毁)
public class Student {
private String name;
private String gender;
private int age;
private double score;
private static String classRoom = "a123";
public Student(String name, String gender, int age, double score) {
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//静态成员变量可以直接通过类名访问
System.out.println(Student.classRoom);//a123
Student s1 = new Student("zhangsan", "男", 18, 3.8);
Student s2 = new Student("lisi", "女", 19, 4.0);
//也可以通过对象访问:但是classRoom是三个对象共享的
System.out.println(s1.classRoom);//a123
System.out.println(s2.classRoom);//a123
}
}
static修饰成员方法
一般类中的数据成员都设置为private,而成员方法设置为public,那设置之后,Student类中classRoom属性如何在类外访问呢
Java中,被static修饰的成员方法称为静态成员方法,是类的方法,不是某个对象所特有的。静态成员一般是通过静态方法来访问的。
【静态方法特性】
- 不属于某个具体的对象,是类方法
- 可以通过对象调用,也可以通过类名.静态方法名(…)方式调用,更推荐使用后者
- 不能在静态方法中访问任何非静态成员变量
public class Student {
private String name;
private String gender;
private int age;
private double score;
private static String classRoom = "a123";
public static String getClassRoom() {
return classRoom;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Student.getClassRoom());//a123
}
}
七、代码块
代码块概念以及分类
使用 {} 定义的一段代码称为代码块。根据代码块定义的位置以及关键字,又可分为以下四种:
- 普通代码块
- 构造块
- 静态块
- 同步代码块
普通代码块
普通代码块:定义在方法中的代码块
用处不大
public static void main(String[] args) {
{ //直接使用{}定义,普通方法块
int x = 10 ;
System.out.println("x1 = " +x);
}
int x = 100 ;
System.out.println("x2 = " +x);
}
// 执行结果
x1 = 10
x2 = 100
构造代码块
构造块:定义在类中的代码块(不加修饰符)。也叫:实例代码块,非静态代码块。
构造代码块一般用于初始化实例成员变量。
public class Student {
private String name;
private String gender;
private int age;
private double score;
private static String classRoom = "a123";
//构造代码块,一般用于初始化实例成员变量。
{
this.name = "张三";
this.gender = "男";
this.age = 18;
this.score = 4.0;
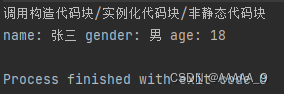
System.out.println("调用构造代码块/实例化代码块/非静态代码块");
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("name: "+name+" gender: "+gender+" age: "+age);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
s.show();
输出结果:
静态代码块
使用static定义的代码块称为静态代码块。一般用于初始化静态成员变量。
public class Student {
//private 修饰类外不能访问
private String name;
private String gender;
private int age;
private double score;
//静态代码块,一般用于初始化静态成员变量。
static {
classRoom = "a101";
System.out.println("调用静态代码块1");
}
//静态成员变量
private static String classRoom = "a123";
//构造方法
public Student() {
System.out.println("调用不带参数的构造方法");
}
public Student(String name, String gender, int age, double score) {
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
System.out.println("调用4个参数的构造方法");
}
//构造代码块,一般用于初始化实例成员变量。
{
this.name = "张三";
this.gender = "男";
this.age = 18;
this.score = 4.0;
System.out.println("调用构造代码块/实例化代码块/非静态代码块");
}
//静态代码块
static {
classRoom = "a101";
System.out.println("调用静态代码块2");
}
//静态成员方法
public static String getClassRoom() {
return classRoom;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student();
System.out.println("====================");
Student s2 = new Student("haha","ha",1,2);
System.out.println("====================");
System.out.println(Student.getClassRoom());
}
}
// 执行结果
// 调用静态代码块1
// 调用静态代码块2
// 调用构造代码块/实例化代码块/非静态代码块
// 调用不带参数的构造方法
// ====================
// 调用构造代码块/实例化代码块/非静态代码块
// 调用4个参数的构造方法
// ====================
// a101
说明:
- 上述代码可以看出,先执行静态代码块,再执行构造代码块,最后执行构造方法。
- 静态代码块不管生成多少个对象,其只会执行一次
- 构造代码块与构造方法类似创建对象时执行
- 如果一个类有多个代码块,在编译代码时,编译器会按照定义的先后次序依次执行(合并)





















 504
504











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








