一、什么是STL库
STL是“Standard Template Library”的缩写,中文翻译为“标准模板库”。C++STL是一套功能强大的C++模板类,提供了通用的模板类和函数,这些模板类和函数可以实现多种流行和常用的算法和数据结构,如字符串操作、链表、队列、栈。
C++标准模板库的核心包括以下三个组件:
C++标准模板库组件 组件 描述 容器(顺序容器、关联容器) 容器是用来管理某一类对象的集合。C++提供了各种不同类型的容器,比如list, vector, map 算法 算法作用于容器,提供了执行各种操作的方式,包括对容器内容执行初始化、排序、搜索和转换等操作 迭代器 迭代器用于遍历对象集合的元素。类似于指针
二、STL的使用案例
1、可以去看官网的操作文档,C++中文参考手册
2、字符串模板类string
加上头文件#include <string>
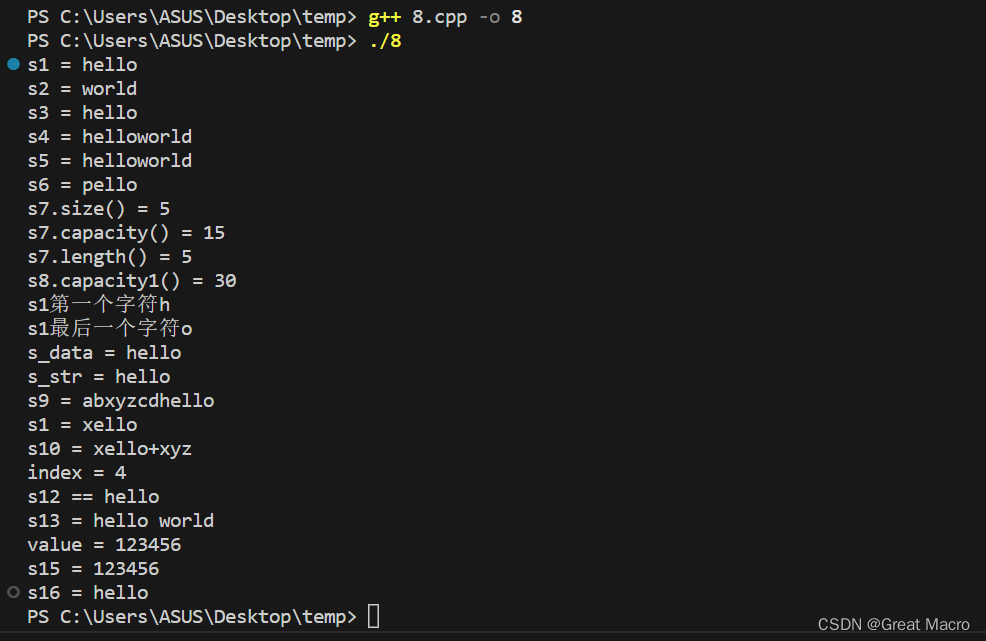
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; int main() { // 1、定义 string s1("hello"); string s2 = "world"; cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl; cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl; // 2、赋值 string s3 = s1; string s4 = s1 + s2; string s5 = s1; s5 += s2; cout << "s3 = " << s3 << endl; cout << "s4 = " << s4 << endl; cout << "s5 = " << s5 << endl; // 3、at, 返回某个位置的引用 string s6 = s1; s6.at(0) = 'p'; cout << "s6 = " << s6 << endl; // 4、容量 string s7 = s1; cout << "s7.size() = " << s7.size() << endl; cout << "s7.capacity() = " << s7.capacity() << endl; cout << "s7.length() = " << s7.length() << endl; string s8 = s1+s1+s1+s1+s1+s1; cout << "s8.capacity1() = " << s8.capacity() << endl; // 5、第一个字符和最后一个字符 cout << "s1第一个字符" << s1.front() << endl; cout << "s1最后一个字符" << s1.back() << endl; // 6、返回字符串类中,字符串的指针地址 const char* s_data = s1.data(); const char* s_str = s1.c_str(); cout << "s_data = " << s_data << endl; cout << "s_str = " << s_str << endl; // 7、插入 string s9 = s1; s9.insert(0, "abcd"); s9.insert(2, "xyz"); cout << "s9 = " << s9 << endl; // 8、[] s1[0] = 'x'; cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl; // 9、追加 string s10 = s1; s10.push_back('+'); s10.append("xyz"); cout << "s10 = " << s10 << endl; // 10、查找 int index = s1.find("o"); cout << "index = " << index << endl; // 11、比较 string s12 = "hello"; if(s12 == "hello") { cout << "s12 == hello" << endl; } // 12、迭代器 string s13 = "hello world"; cout << "s13 = "; for(string::iterator it = s13.begin(); it != s13.end(); it++) { cout << *it; } cout << endl; // 13、数值转换 string s14 = "123456"; int value = stoi(s14); cout << "value = " << value << endl; string s15 = to_string(value); cout << "s15 = " << s15 << endl; // 14、 获取子串 string s16 = s13.substr(0, 5); cout << "s16 = " << s16 << endl; return 0; }
3、顺序容器vector
加上头文件#include <vector>
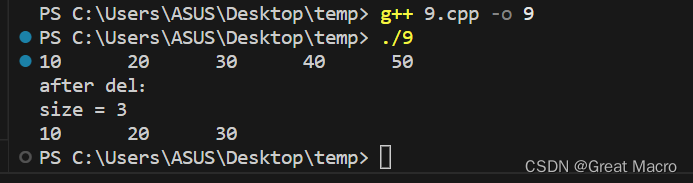
#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; struct node { char *name; void func() { } }; int main() { vector<int> myvector; // 1、插入 myvector.push_back(10); myvector.push_back(20); myvector.push_back(30); myvector.push_back(40); myvector.push_back(50); // 2、迭代器遍历 vector<int>::iterator it; for(it = myvector.begin(); it != myvector.end(); it++) { cout << *it << '\t'; } cout << endl; // 3、删除 cout << "after del:" << endl; myvector.pop_back(); myvector.pop_back(); // 4、容量 cout << "size = " << myvector.size() << endl; // 5、使用数组形式遍历 for(int i = 0; i < myvector.size(); i++) { cout << myvector.at(i) << '\t'; } cout << endl; return 0; }
4、双向链表容器list
加上头文件#include <list>
#include <iostream> #include <list> using namespace std; class Student { private: string name; int age; int score; public: Student(string name = string(), int age = 18, int score = 30) { this->age = age; this->name = name; this->score = score; } void show() { cout << name << '\t' << age << '\t' << score << endl; } friend bool cmp(const Student &s1, const Student &s2); string getName()const { return name; } void setAge(int Age) { this->age = Age; } }; bool cmp(const Student &s1, const Student &s2) { return s1.score > s2.score; } int main() { list<Student> mylist; // 插到后面,尾插 mylist.push_back(*(new Student("zhang3", 20, 90))); mylist.push_back(*(new Student("zhang4", 21, 79))); // 插到前面,头插 mylist.push_front(*(new Student("zhang7", 19, 89))); mylist.push_front(*(new Student("zhang8", 25, 80))); // 遍历,用迭代器 cout << "before sort" << endl; list<Student>::iterator it; for(it = mylist.begin(); it != mylist.end(); it++) { it->show(); } // 排序 mylist.sort(cmp); // cmp函数是自定义的排序内容 cout << "after sort" << endl; for(it = mylist.begin(); it != mylist.end(); it++) { it->show(); } // 删除 it = mylist.begin(); it = mylist.erase(it); cout << "after del first" << endl; for(it = mylist.begin(); it != mylist.end(); it++) { it->show(); } // 查找和修改 for(it = mylist.begin(); it != mylist.end(); it++) { if(it->getName() == "zhang7") { cout << "find zhang7" << endl; it->setAge(50); } } for(it = mylist.begin(); it != mylist.end(); it++) { it->show(); } return 0; }
5、栈容器stack
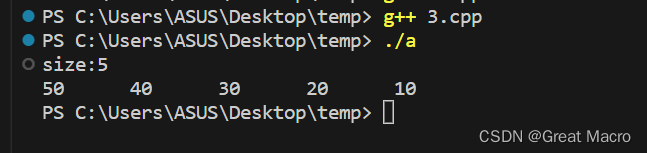
#include <iostream> #include <stack> using namespace std; int main() { stack<int> mystack; // 入栈 mystack.push(10); mystack.push(20); mystack.push(30); mystack.push(40); mystack.push(50); // 栈的元素个数 cout << "size:" << mystack.size() << endl; // 栈没有空,就一直出栈 int data; while(!mystack.empty()) { data = mystack.top(); // 出栈前需要先获取栈顶元素 mystack.pop(); cout << data << "\t"; } cout << endl; return 0; }
6、队列容器queue
#include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std; int main() { queue<int> myqueue; // 入队 myqueue.push(10); myqueue.push(20); myqueue.push(30); myqueue.push(40); myqueue.push(50); // 获取队列的元素个数 cout << "size: " << myqueue.size() << endl; // 队头元素 cout << "front: " << myqueue.front() << endl; // 队尾元素 cout << "back: " << myqueue.back() << endl; // 遍历 int data; while(!myqueue.empty()) { data = myqueue.front(); myqueue.pop(); // 从队头出队的,先要保留队头元素 cout << data << "\t"; } cout << endl; return 0; }
7、关联容器map
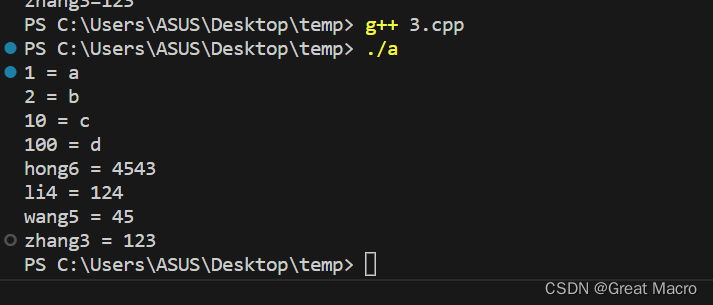
#include <iostream> #include <map> using namespace std; int main() { // map是以键值对的方式存放数据 // 第一个类型是键,第二类型是值,其中键不一定是整形可以是字符串 map<int, string> mymap1; // 插入或者访问,键不一定要连续 mymap1[1] = "a"; mymap1[2] = "b"; mymap1[10] = "c"; mymap1[100] = "d"; for(map<int, string>::iterator it = mymap1.begin(); it != mymap1.end(); it++) { // 键用first来访问,值用second来访问 // 不允许使用cout << it << endl; 来访问 cout << it->first << " = " << it->second << endl; } // 不一定要连续 map<string, string> mymap2; mymap2["zhang3"] = "123"; mymap2["li4"] = "124"; mymap2["wang5"] = "45"; mymap2["hong6"] = "4543"; for(map<string, string>::iterator it = mymap2.begin(); it != mymap2.end(); it++) { // 键用first来访问,值用second来访问 cout << it->first << " = " << it->second << endl; } return 0; }
三、总结
以上就是STL库中常用的容器以及对应的操作,使用时需要添加对应的头文件名,同时不同容器之间的有些相同操作是同名的,具体更多细节可以去看看官网的中文参考手册。

























 371
371











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








